Reconstruction and the Changing South
advertisement

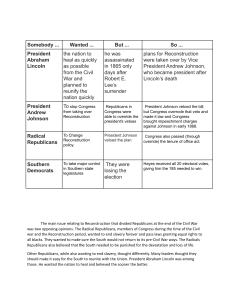
1863-1896 RECONSTRUCTION AND THE CHANGING SOUTH With malice toward none; with charity for all; with firmness in the right, as God gives us to see the right, let us strive on to finish the work we are in; to bind up the nation’s wounds; to care for him who shall have borne the battle, and for his widow, and his orphan—to do all which may achieve and cherish a just, and a lasting peace, among ourselves, and with all nations. -- Lincoln’s 2nd inaugural address March 4, 1865 http://www.eyewitnesstohistory.com/richmond.h tm THE VICTORIOUS NORTH Some 800,000 returning Union soldiers needed jobs The North lost more soldiers than the South had Since only a few battles had taken place on Northern soil, farms and cities were hardly touched. THE DEFEATED SOUTH Cities and farms lay in ruins 2/3 of railroad tracks had been torn up Columbia, Richmond, and Atlanta had been leveled Confederate money was worthless 4 million freedmen had “joined” the population FINANCIAL COST TO SOUTH (P. 404) Livestock killed – 40% Farm machinery destroyed – 50% Drop in total property wealth – 66% Total national wealth held by South,1860 – 30% Total national wealth held by South,1870 – 12% What questions might there be post Civil War? WHAT TO DO? Richmond, Virginia Atlanta Virginia farm Confederate money - The reverse side of the $1 bill was blank. Notice the lack of color ink on the second bill. This was because as the Civil War continued, the South had less money to make money FREEDMEN’S BUREAU Congress & Lincoln agreed on one proposal, creating an agency to help former slaves. Food, clothing, jobs, schools, and medical care for former slaves and poor whites. Provided care for more than 1 million people. Black schoolhouse during reconstruction. Sharecropper’s cabin in South Carolina, 1866 How do you get states functioning again after war? WHAT’S A REASONABLE SOLUTION? RECONSTRUCTION PLANS Lincoln’s 10% Plan A southern state could return if 10% voters swore loyalty, Had to abolish slavery, Amnesty for those who swore loyalty to the Union (except Conf. leaders) “When the doctrine that quality and not the number of voters is to decide the right to govern, then we no longer have a republic.” -Thaddeus Stevens Wade-Davis Bill Majority of southern white men had to swear loyalty Anyone who had volunteered in the Confed. army couldn’t vote or hold office Lincoln wouldn’t sign it because he felt it was too harsh Pocket-veto LINCOLN IS ASSASSINATED Lincoln never got the chance to persuade Congress to accept his Reconstruction plan. He was shot by John Wilkes Booth April 14, 1865, five days after Lee’s surrender. Booth was later caught and killed in a barn outside the city. Determined to keep the Union intact whatever the cost, Lincoln had presided over the nation through her darkest hour, serving in a way that few in history have ever been called upon to do. His leadership made him one of the most revered of all American heroes, and poll after poll has named him the favorite president of most American citizens. There is never a close runner-up. “Now he belongs to the ages.” Edwin Stanton, U.S. Secretary of War V-P ANDREW JOHNSON BECOMES PRESIDENT His plan was much milder than expected Majority of voters had to pledge loyalty to the United States. State had to ratify the 13th Amendment (banning slavery nationwide) The southern states quickly met Johnson’s conditions and were admitted back into the Union Southern states didn’t allow blacks to vote Congress was upset that former Confederate leaders were allowed to be reps so they refused to let reps take their seats SHOWDOWN! BLACK CODES convict labor, vagrancy, must have home and means of support in Mississippi, blacks forbidden to rent or own land outside towns in South Carolina, black children could be apprenticed to whites if parents did not educate the point? to keep blacks in slavery - insure labor supply enforced by southern "county militia" RADICAL RECONSTRUCTION Black codes angered Congress Congress thought President Johnson’s mild approach encouraged the black codes Radical Republicans vowed to take control of Reconstruction They joined with the moderate Republicans to reduce the power of the southern Democrats Civil Rights Act – gave citizenship to African Americans. Johnson vetoed, Congress overrode veto 14th Amendment – defined citizens and guaranteed protection against discrimination for all citizens Reconstruction Act – threw out state governments that refused to ratify 14th Am.,established martial law in South, forced any returning states to ratify 14th Amendment IMPEACHMENT OF PRES. JOHNSON Didn’t succeed, one vote shy Moderate Republicans said you can’t impeach the President just because you disagree with him. ULYSSES GRANT ELECTED With 500,000 blacks voting, Grant easily won the election. The next year, the 15th Amendment was passed, forbade any state to deny the right to vote based on race. NEW FORCES IN THE SOUTH White Southern Republicans (scalawags) Northerners: some hope to get rich off the South, Some just fell in love with the South (carpetbaggers) African Americans KKK Secret society formed to help southern Democrats gain power Threatened Southern republicans and African Americans Used destruction, torture, and murder. Testimony of a former slave to Congress about the KKK GRANT’S ADMINISTRATION Marked by widespread corruption ($1,000 for a horse bet, coffins, perfume, and hams) Grant had appointed many friends to government, stole large sums of money Amnesty Act in 1872 – nearly all white southerners could vote again END OF RECONSTRUCTION Democrat Tilden v. Republican Hayes Election too close to call House decided to elect Rutherford B. Hayes For the next 100 years, the South would be Democrat JIM CROW LAWS Laws specifically discriminating against blacks States could impose legal punishments on people for consorting with members of another race. The most common types of laws forbade intermarriage and ordered business owners to keep their black and white clientele separated. (segregation) examples ATTEMPTS TO PREVENT BLACK SUFFRAGE Literacy tests Poll tax Grandfather clause Example of literacy tests and voter application http://www.crmvet.org/info/lithome.htm PLESSY V. FERGUSON Supreme court case Ruled segregation was ok “Separate but equal”