Geography – Need to know
advertisement

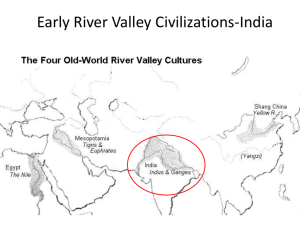
India Study Guide Vocabulary to Study: Word Monsoon Raja caste Plateau Hinduism Stupa Migrate Definition Seasonal winds that bring lots of rain A leader of India; an Indian prince The Indian term for your social class in society A wide flat area of high land A major religion in India that believes in polytheism and reincarnation A Buddhist holy building; it has a dome top To move from one place to another; example: geese fly south for the winter Vocabulary Flashcards Quizlet Games: https://quizlet.com/63920614/ancient-india-flash-cards/ Vocab Visuals PowerPoint : https://docs.google.com/presentation/d/1GcPedWWvdN_0t7FsXKAdzEyiLJE_T7YVXCmYocH8ax4/prese nt?pli=1&ueb=true&slide=id.p Culture: Need to know: 1) Ancient India is made up of many groups of people that moved into the area. a. The first people settled by Mohenjo-Daro and Harappa b. The group then moved, joining the Aryans. The Aryans settled in central India c. After being attacked by Persia and Greece, India became the Mauryan Empire. d. After fighting for over 500 years, the Gupta Empire gained power. 2) India invented many things a. The number system including the zero b. They created the first plumbing system. 3) They had three major religions in Ancient India a. Hinduism – polytheism, reincarnation; started by the Aryans; gods Brahma, Vishnu, and Shiva are important; cows are sacred animals b. Buddhism – started by Siddhartha Gutama; lead a good life following the 8 Fold Path and 4 Noble Truths to earn your way to Nirvana. c. Jainism – no violence; absolute peace 4) Government a. Rajas ruled kingdoms. Raja is the Indian word for ruler (Indian prince) b. There were many kingdoms during most of Ancient times c. Only the Mauryan Empire and Gupta Empire unified the kingdoms to be together. Economy d. The traded on the Silk Road e. Known for their spices f. They had advanced jobs such as mailmen, dentists, doctors, and plumbers. g. Priests, soldiers, merchants, traders, government officials, unskilled workers (using their body instead of their mind to do their job) 5) Caste System – Social Classes a. You were born part of the same social class as your parents and you stayed in that caste for the rest of your life. (Think of a caste as a cast for a broken arm . . . but you are stuck there!) b. See chart on the right. You do NOT need to memorize the names of the groups, but remember who is on top and who is on bottom Geography – Need to know The size of India changed over time Started in the Indus Valley area (Mohenjo-Daro and Harappa) by the Indus River Migrated to the Ganges River and central India Himalayan Mountains and Thar Desert separates India from the rest of the world; this protects them but also isolates them. India use to be a subcontinent (India is on a moving plate that is slowly ramming into Asia. Earthquakes still are common in this area. Read a Chart and answer questions: (The chart looks like the one you completed in class – similar to the one below) Detail Mohenjo-Daro and Harappa Pages to use in textbook Textbook pp 250-252 Years flourished 2600 BC – 1900 BC Location Geography Indus Valley Area now called Pakistan Settled by the Indus River Society: What would be found in cities Houses with flat roofs made of oven-baked bricks 35, 00 people Dozens of streets Wall surrounding the city Buildings to store grain Aryan Textbook pp 252254 1900 BC Migration started 1500 BC – 1000 BC People migrated because of earthquakes, floods or starvation Moved to central India by Ganges River and Deccan Plateau Irrigation systems Sanskrit writing People raiding areas for food at times Mauryan Empire Gupta Empire Textbook pp 265268 Textbook p 268; 270-271 321 BC – 183 BC 320 AD - Indus River Valley and most of India (NOT the southern tip or Sri Lanka) Stupas built in cities (Buddhist shrines Roads Ganges River Valley Northern India Hindu temples Sculptures of deities (gods)