File - Dr. Afxendiou's Classes
advertisement

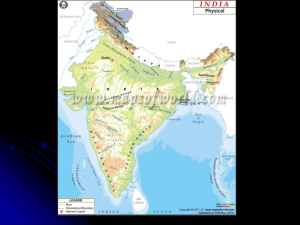
CLASSICAL INDIA SACHEM NORTH HIGH SCHOOL AP WORLD HISTORY 9 DR. AFXENDIOU India - Geography • India is a peninsula, located on the south Asian subcontinent. • Features: • Mountains – Himalayas – Hindu Kush » Khyber Pass • Deccan Plateau • Indo-Gangatic Plains • Rivers – The Indus and Ganges Rivers make up a large area that stretches 1,500 miles across Northern India called the IndusGanges Plain or Indo-Gangetic Plain. • Monsoons – seasonal winds – Winter (October to May) – Summer (June to September) – Problems – hard to predict, heavy rains cause flooding Physical Map 1 Physical Map 2 Effect of Geography India open to influences from the early civilizations of the Middle East and the Mediterranean Allowed for interaction with Persian Empire, which affected art and political ideas invasion by Alexander the Great brought Hellenistic culture Despite connections with other civilizations, India had relative isolation because of surrounding mountains that set it apart from the rest of Asia - subcontinent geological divisions within the subcontinent made full unity difficult led to greater diversity than found in China Regions: Agricultural regions of Indus and Ganges Herding economy of mountainous northern regions Trading and seafaring economy in the southern coastal rim separated from the rest of the country by mountains and the Deccan plateau racial, cultural and language differences Aryan Influences Origin: The Aryans were lightArrival: skinned, Indo-European nomadic hunters and herders • Around 1500 BC, these tribes migrated from central and northern Asia south through Khyber Pass who adopted agriculture in the Contributions: plains of the Indus and • Literary epics developed by Aryans – Ganges Rives Vedas the sacred books of Hinduism • entrenched Aryan ideas about society and family and began to give shape to the Caste system • Caste system (Varna) – has been suggested that the caste system was a way of allowing the newcomers (Aryans) to coexist with the native populations (seen as inferior) • Sanskrit – written language Aryan Routes To India Social Classes: Varnas • In order to separate Aryans from non-Aryans, a Rigid Class System emerged. – Varna or skin color was a distinguishing feature of this system • As time when on, people were born into their caste for life. Caste determines: – – – – The job you hold The person you marry The people with whom you eat The clothes you wear HINDUISM Brahma Shiva • Origin – Classical Theory or Emerging Theorgy Hindu • Texts – the Vedas and the Upanishads, the Trinity sacred scriptures of Hinduism • Beliefs &Goals – release from repeated reincarnation (rebirth of the soul) – Karma – good or bad deeds – follows you through reincarnation – Dharma – the duties and obligation of your caste • Deities – worshipped at shrines – the divine trinity, representing the cyclical nature of the universe, are Vishnu • Brahma the creator • Vishnu the preserver • Shiva the destroyer 2 of 4 Brahma Vishnu The Preserver Shiva millions of local deities world of humans: dharma fulfillment of life roles karma reincarnation death The Destroyer BUDDHISM • Founded: – in southern Nepal in the 5th and 6th centuries B.C. – Siddharta Gautama, known as the Buddha (Enlightened One). • Key Beliefs – meditation and the practice of good religious and moral behavior – leads to Nirvana, the state of enlightenment, – Reincarnation – the soul is reborn over and over based on Karma • Four Noble Truths – Life is full of pain and suffering. – Human desire causes this suffering. – By putting an end to desire, humans can end suffering. – Humans can end desire by following the Eightfold Path. • Eightfold Path – Wheel of Life represents the endless cycle of life through reincarnation. – Each of its eight spokes represents one of the teachings of the Eightfold Path. Political Institutions • Most persistent political feature of India is regionalism – However, some centralization did occur • Example: Gupta promotion of Sanskrit and law code • Caste system provided local control and regulation often fulfilled by government Why regionalism? PEOPLE IDENTIFY WITH THEIR REGIONAL LEADERS RATHER THAN EMPIRE. ALLEGIANCE IS CLOSE TO HOME NOT TO A FAR OFF CAPITAL Political Structure • India was divided into regional city states • Invasion ( by Alexander the Great) helped lead to some unity • Two major empires emerged in Classical India Maurya and Gupta Two major empires of Classical India – The Mauryan and Gupta Empires The Mauryan Empire 321 B.C. – 232 B.C. • • • • • Founder: Chandragupta Maurya – Defeats Alexander the Great (Greece) – United India under one ruler – Maintained HUGE army: over 600,000 – Set up bureaucracy that included a postal service – Autocratic form of government Asoka – 301B.C. – Chandragupta’s grandson Greatest ruler of Mauryan Extended Mauryan conquest – bloody campaigns – Following a bitter battle with heavy casualties, he converts to Buddhism. • Religious Toleration – still honors Hinduism • Sends missionaries out to spread Buddhism – Built extensive road network • Planted trees along routes for shade • Every 9 miles dug a well and built rest houses – Changed his rule to be more humanistic Decline – Imperial kingdoms regain independence following Asoka’s death The Gupta Empire 320 – 500 CE • • Founder: – Chandragupta Maurya I (no relation) Under the next 3 Emperors – society was ordered in accordance with Hindu beliefs. – peace and prosperity enabled the pursuit of scientific and artistic endeavors. • Chandragupta II (375 - 415 CE) – The Golden Age of India (next slide) • Expands Empire • Achievements • Decline – Death of CG II – series of invasions – Weak leaders – many of their cultural and intellectual achievements were saved and transmitted to other cultures and live on today. The Gupta Empire: India’s Golden Age • • • • http://www.cs.dartmout h.edu/whites/nepal/stup a.jpg Math – concept of zero – decimal system based on the number 10 – Calculated the value of pi (3.14) – Arabic Numerals (0-9) Medicine – – plastic surgery – vaccine against smallpox Architecture – Stone temples to gods – Stupas (shrines) Arts & Literature Gupta literature consists of fables and folktales written in Sanskrit. – stories spread west to Persia, Egypt, and Greece – became the basis for many Islamic literary works such as, Ali Baba and the Forty Thieves and Aladdin and his Magic Lamp.