What are the layers and characteristics of Earth's Interior?
advertisement

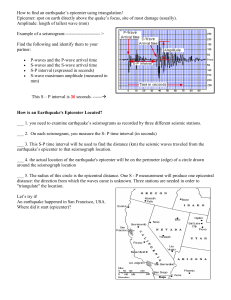
Key Terms: seismograph, seismometer, seismogram, S-P interval, amplitude Detecting Seismic Waves Please turn to page 119 in your textbook. Seismograph An instrument used to record and measure seismic waves. Records the ground movements caused by seismic waves as they move through the earth. Records the P waves, S waves, and Surface waves. 2 How a Seismograph Works As the animation is being shown, read the captions. You may also want to make a quick sketch in your notes. Animation The paper record produced by the seismograph is called the seismogram. 3 Reading the Seismogram A highly simplified simulated recording of earthquake waves (a seismogram) will be shown on the next slide. Label the handout of the sample seismogram and be sure you can identify these parts: P-waves and the P-wave arrival time S-waves and the S-wave arrival time S-P interval or S-P lag time (expressed in seconds) S-wave maximum amplitude (measured in mm) 4 P Wave Arrival Time S Wave Arrival Time Amplitude S-P Interval Time in Seconds 5 Seismogram Animation As the animation is being shown, watch and identify these parts: P-waves and the P-wave arrival time S-waves and the S-wave arrival time S-P interval (also known as the S-P lag time) Animation On the next slides, we will be trying to determine the S-P interval for 2 different seismograms. 6 Calculate the S-P Interval (lag time) 56 Seconds 7 Calculate the S-P Interval 44 Seconds 8 Stop Complete Using the S-P interval on a seismogram to determine the distance to the epicenter of an earthquake activity before continuing. 9