File
advertisement

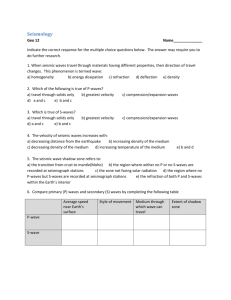
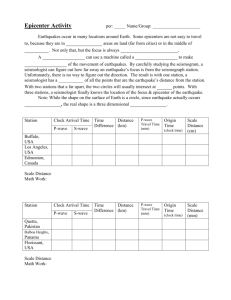
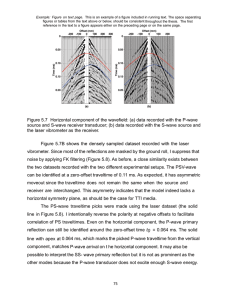
Name: _________________________________ Pd. ______ Date: ______________ Examining Seismograms The three basic types of seismic wave generated by an earthquake at its focus are P-waves, Swaves, and Surface waves. P and S-waves are body waves and travel through the interior of the earth. P=waves have the greatest velocity and reach the seismic station first. S-waves arrive at the seismic station after the P-waves. The amount of time that passes between the Pwave arrival and the S-wave arrival is important in helping seismologists determine the epicenter of the earthquake. Today we will be using a travel-time chart, where the vertical separation between the P and S curves is equal to the difference in the arrival times between the P-wave and S-wave. To accurately locate an earthquake epicenter, records from three seismograms are necessary Figure 1: A typical Seismogram. (Earlier) Time (Later) 1. Which of the two waves arrives at the seismic station first? ______________________ 2. From the seismogram in Figure 1. What is the difference in arrival times between the first P-wave and the first S-wave? _________________ Figure 2: Seismograms from three different stations. (Earlier) Time (Later) 3. Using the Seismograms in Figure 2, Fill in Table 1. Table 1. Seismogram Data Table. Station P-Wave Start Time S-Wave Start Time Lag Time (S-P wave) Station A: St. Louis, Missouri Station B: Houston, Texas Station C: Los Angeles, California 4. Use Figure 3 to determine the time in minutes or distance in km of the various P-waves and S-waves. a. How long does it take the P-wave to reach 4000 km: ____________ minutes b. How long does it take the S- wave to reach 4000 km: ____________ minutes c. What is the lag-time of these two waves at 4000 km: ____________ minutes (S-wave – P-wave) = Lag-time d. How long does it take the P-wave to reach 9000 km: _____________ minutes e. How long does it take the S-wave to reach 9000 km: _____________ minutes f. What is the lag-time of these two waves at 9000 km: _____________ minutes (S-wave – P-wave) = Lag-time g. How far has the P-wave traveled at 4 minutes: ________________ km h. How far has the S-wave traveled at 4 minutes: ________________ km i. How far has the P-wave traveled at 13 minutes: ________________ km j. How are has the S-wave travels at 13 minutes: _________________ km Figure 3: Travel Time Graph 7 minutes 4000 km