Earthquake Study Guide - Jessamine County Schools
advertisement
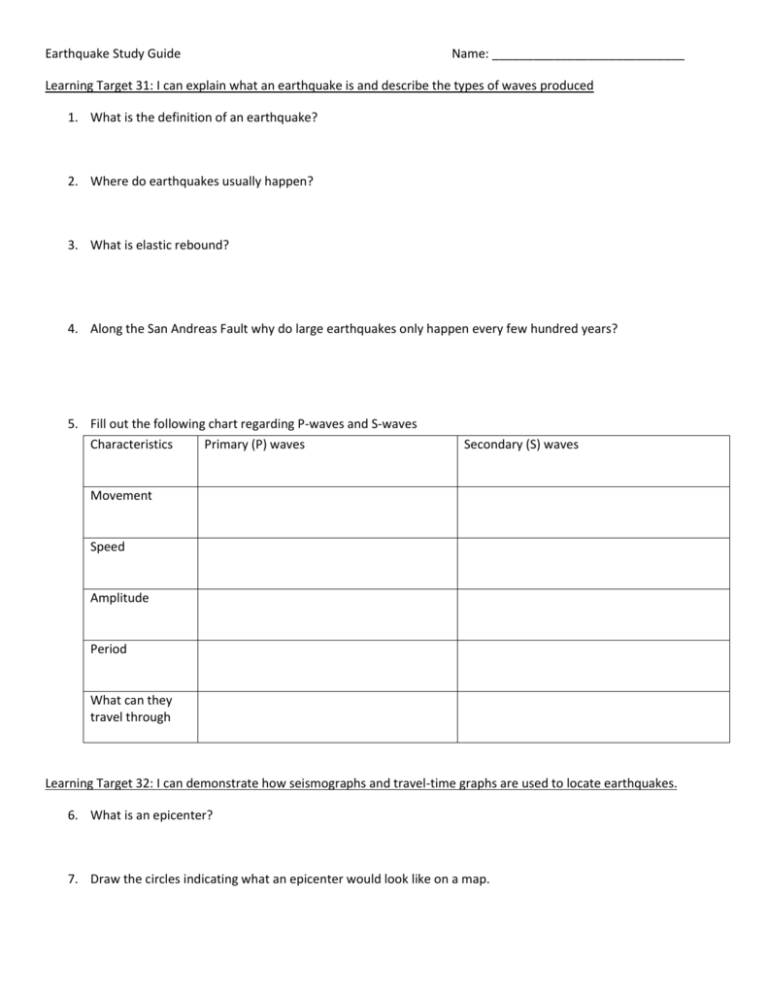
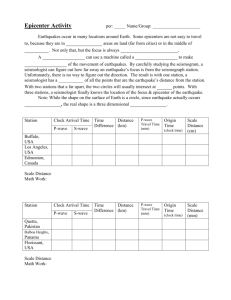
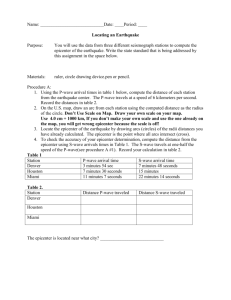
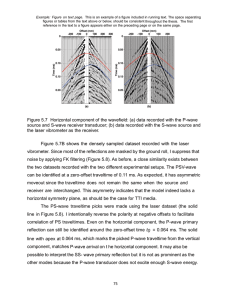
Earthquake Study Guide Name: ____________________________ Learning Target 31: I can explain what an earthquake is and describe the types of waves produced 1. What is the definition of an earthquake? 2. Where do earthquakes usually happen? 3. What is elastic rebound? 4. Along the San Andreas Fault why do large earthquakes only happen every few hundred years? 5. Fill out the following chart regarding P-waves and S-waves Characteristics Primary (P) waves Secondary (S) waves Movement Speed Amplitude Period What can they travel through Learning Target 32: I can demonstrate how seismographs and travel-time graphs are used to locate earthquakes. 6. What is an epicenter? 7. Draw the circles indicating what an epicenter would look like on a map. 8. What are the arrival times of P –wave and S-wave for city A? What is the time difference? P-wave ___________ S-wave_____________ Time Difference_____________ 9. What are the arrival times of P –wave and S-wave for city B? What is the time difference? P-wave ___________ S-wave_____________ Time Difference_____________ 10. What are the arrival times of P –wave and S-wave for city C? What is the time difference? P-wave ___________ S-wave_____________ Time Difference_____________ 11. Use the travel time graph on the attached page to find the distance of each city away from the epicenter. City A= _____________________________ KM City B= _____________________________ KM City C= _____________________________ KM Use the travel – time graph to answer the following questions. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. How long does it take a p-wave to travel 3000 KM____________________________ How long does it take an s-wave to travel 1800 KM___________________________ How far does a p-wave travel in 3 minutes___________________________________ How far does an s-wave travel in 13 minutes_________________________________ What happens to the times of the p-wave and s-wave as you get farther from the epicenter