Classifying Living Organisms
advertisement

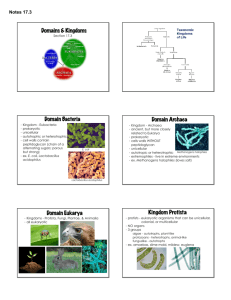
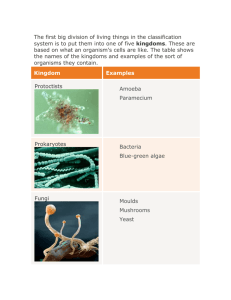
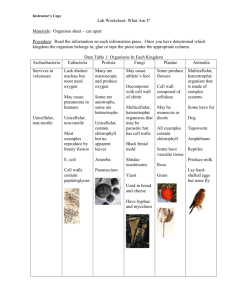
Classifying Living Organisms Domains and Kingdoms Carolus Linnaeus’ Classification System Swedish botanist (1707-1778) Binomial Nomenclature – two-part scientific name Genus species Why Latin? Latin was the language known universally by the educated Also used as a descriptor Carolus Linneaus Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus species Helpful to avoid common names. 3 MAIN Domains Kingdoms Scientists look at the evolutionary history of organisms to divide them into kingdoms. For awhile, there has been 5 kingdoms, but many scientist are now using 6 kingdoms. Scientists place organisms in different kingdoms depending on its characteristics such as: What type of cell? Prokaryote or Eukaryote Unicellular or Multicellular Autotrophic or Heterotrophic Reproduction? Asexually or Sexually 6 Kingdoms of Living Things Eubacteria Archaebacteria Protista Fungi Plantae Animalia DOMAINS BACTERIA ARCHAE EUKARYA KINGDOMS KINGDOMS KINGDOMS Eubacteria Archaebacteria Protista Fungi Plantae Animalia Prefix meanings Pro = Eu = Uni = Multi = Auto = Hetero = Troph = A = Without Kingdom: Eubacteria Found in Domain Bacteria Prokaryote unicellular Often do need oxygen Live and feed by decomposing other cells. Some can do photosynthesis. Reproduce asexually. Domain Archaea or Kingdom Archaebacteria Prokaryote Unicellular Can be autotrophic and heterotrophic Reproduce asexually Live in harsh environments; classified base on where they live (such as thermal vents deep in ocean, salt-lakes, acidic environments, some even in ice!) Heterotrophic Bacteria 1. Free-living consumers: E. coli Azobacter converts initrogen into ammonium, making it available for plant use; E. coli lives in your colon, feeds on your waste and makes vitamin K for you. 2. Parasitic: Always needs an organism to get food or shelter (host): Impetigo is caused by strains Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes. 3. Decomposers: Pseudomonas bacteria in the soil recycles dead plants and animals by turning them into minerals and nutrients that plants and microbes can use. Autotrophic Bacteria Producers -> Use sunlight to make food and are often green. Example: Cyanobacteria: Bluegreen algae Lives in water Has chlorophyll (green pigment for photosynthesis) Some others have blue or red pigment. Domain Eukarya Eukaryote Unicellular or multicellular Includes Kingdom Animalia, Kingdom Plantae, Kingdom Fungi and Kingdom Protista. Kingdom Protista Eukaryote Unicellular Heterotrophic or Autotrophic Reproduce primarily asexually Protista includes Protozoa of 4 main groups: classified based on movement Protista includes several types of Algae and Seaweed classified based on chemical criteria (PS pigments) Kingdom Fungi Eukaryote Usually multicellular Heterotroph: absorb nutrients from decomposing organisms Reproduce both sexually and asexually Fungi are classified by how they make SPORES Kingdom Plantae Eukaryote Multicellular Autotrophic: PHOTOSYNTHESIS Reproduce both sexually and asexually Kingdom Animalia Eukaryote Multicellular Heterotrophic: eat other organisms Sexual reproduction 9 Major Animal Phyla Porifera (sponges) Cnidaria (jellyfish) Platyhelminthes (flatworms) Nematoda (roundworms) Annelida (segmentedworms) Mollusca (snails, clams, squid) Arthropoda (insects, crabs) Echinodermata (starfish) Chordata (vertebrates) VIRUS: NOT A KINGDOM!! What is a virus? • Non-living particle, smaller than a cell that can infect living organisms (hosts). Structure of Virus: •Capsid (Protein coat) •Genetic Material (DNA or RNA) Are virus alive? Don’t eat, grow, or break down food. They are not made of cells. They need a host cell to reproduce. There is no cure, only a treatment. Antibiotics DO NOT kill viruses Antiviral medications only stop viruses from reproducing.