Nuclear Half-life Notes & Practice
advertisement

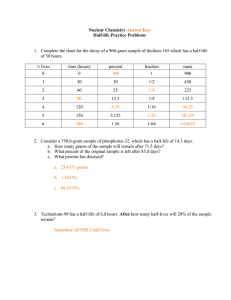
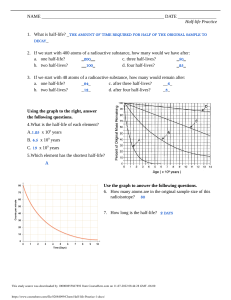
Name: ________________________________ Date: ______________ Period: _________ Ch. 21 Nuclear Chemistry: Half Notes & Practice Half-life: The _____________________ of the isotope is what determines the ______________________. __________________________ = __________________________ Example: After each half life 50% of the sample decays. Start = 100% _________ blue particles are present 1 half-life = 50% _________ blue remain 2 half-lives = 25% _________ blue remain 3 half-lives = 12.5% _________ blue remain 4 half-lives = 6.25% _________blue remain After ____________half-lives sample considered nonradioactive because it approaches the level of background radiation. Because the amount never reaches zero, radioactive waste disposal and storage causes problems. Would you want radioactive waste stored in your community? How can we get rid of nuclear radioactive waste? CALCULATING HALF LIFE Example: The half-life of mercury-195 is 31 hours. If you start with a sample of 5.00 g, how much of it will still be left after 93 hours? How many half lives have passed if there is only 1.875 g left of a 30 g sample? If the half life for this sample is 1 hour, how many total hours have gone by? Practice: 1. The half-life of sulfur-38 is 2.5 hours. After 12.5 hours, how much of a 200 g sample remains? 2. Germanium-66 has a half-life of 45 minutes. If the original sample contains 400 g, how much of the sample is left after 180 minutes? 3. How many half lives have passed if there is only 31.25 g left of a 500 g sample? If the half life for this sample is 2 days, how many total days have gone by? 4. There are 5.0 grams of Iodine – 131 left after 40.35 days. How many grams were in the original sample if its half-life is 8.07 days?