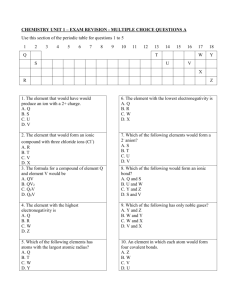
Chapter 5 Review Worksheets Answers
advertisement

Chapter 5 Review Worksheets Answers Section 1: 1. C 2. D 3. B 4. C 5. D 6. C 7. Fluorine isotope with mass number 19 and atomic number 9: a. 9 b. 10 c. 199F 8. Samarium (Sm) is a lanthanide, what is the element below Sm on the periodic table? Difference in atomic #s? a. Plutonium Pu b. 32 9. An isotope contains 53 protons, 78 neutrons, & 54 electrons a. 53 b. 131 c. Iodine d. Fluorine (F), Chlorine (Cl), Bromine (Br), & Astatine (At) 10. Group = Vertical column Period = Horizontal row 11. Atomic mass is the weighted average mass of all the naturally occurring isotopes of the element. Atomic number is number of protons found in the nucleus of each atom of the element. 12. Ar & K; Co & Ni; Th & Pa; U & Np; Pu & Am; Sg & Bh Section 2: 1. Identify the element & write its noble gas notation electron configuration: a. Germanium; Ge [Ar] 4s2 3d10 4p2 b. Bismuth; Bi [Xe] 6s2 4f14 5d10 6p3 c. Scandium; Sc [Ar] 4s2 3d1 d. Radium; Ra [Rn] 7s2 2. Identifying off the periodic table: a. p-block b. B = Alkali Metals C = Alkaline Metals D = Transition Metals E = Main-Group Elements F = Halogens G = Noble Gases H = Actinides 3. Give the symbol, period, group, & block: a. Sulfur; S, 3rd Period, Group 16, p-block b. Nickel; Ni, 4th Period, Group 10, d-block c. ? [Kr] 5s1; Rb, 5th Period, Group 1, s-block d. ? [Ar] 3d5 4s1; Cr, 4th Period, Group 6, d-block * Tricky one with an aufbau exception configuration! 4. Group #s of blocks: a. s-block: Group 1 & Group 2 b. p-block: Groups 13-18 c. d-block: Groups 3-12 Section 3: 1. C 2. D (student worksheet has typo for D (same as #1 above it) D. choice should be ionization energy. 3. Trends across a period: a. Negative b. Increase c. Smaller 4. More Trends: a. Astatine; At b. Lithium; Li c. Argon; Ar d. Carbon; C 5. Electron Configurations: a. Na 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1 b. Na+ 1s2 2s2 2p6 c. O 1s2 2s2 2p4 d. O−2 1s2 2s2 2p6 e. Co+2 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d7 * Tricky one, as it’s a transition metal!!! 6. Atom to Ion sizes: a. The radius of a positive ion is less than the radius of the neutral atom from which it formed. b. The radius of a negative ion is greater than the radius of the neutral atom from which it formed. 7. Metals vs. Nonmetals: a. Metals are on the left side of the staircase on the periodic table, s-block (except H & He), d-block, fblock, and a few elements in the p-block. Nonmetals are to the right of the staircase on the periodic table, Hydrogen in the s-block, and the rest of the p-block. b. Metals tend to form positive ions; nonmetals tend to form negative ions. 8. Successive Ionization Energies: a. 3s2 b. 3s1 c. 2p6 d. As electrons are removed, the shielding effect that the electrons have on the nuclear charge is reduced, and the increased net positive charge holds onto the remaining electrons with more force, requiring more and more energy to remove additional electrons. 9. Valence electrons are the electrons on the outside of the atom and are therefore the electrons available to react with neighboring atoms and ions. Valence electrons are the electrons that are given away, gained, or shared between atoms/ions in reactions. Mixed Review: 1. Neutral atom with 53 protons & 74 neutrons: a. 53 b. 127 c. Atomic number 2. Element with outer electron configuration: 3d10 4s2 4px a. Period 4 b. 5 c. True 3. Blocks: a. p-block b. d-block 4. Most chemically active halogen: a. Fluorine; F b. F 1s2 2s2 2p5 c. F− 1s2 2s2 2p6 5. Periodic Trends: a. In b. Ca c. Ca d. Nonmetals e. Cl f. Negative ion g. Small h. O i. O + 6. Ca & Zn+2 7. Noble gas notations: a. Br [Ar] 4s2 3d10 4p5 b. Br − [Ar] 4s2 3d10 4p6 c. In [Kr] 5s2 4d10 5p1 d. Ce [Xe] 6s2 5d1 4f1 *Tricky f-block elements sometimes have d-sublevel electrons for stability 8. Calcium is in the s-block, group 2, an alkaline metal. Its electron configuration is, Ca [Ar] 4s2; giving it 2 valence electrons and therefore a relatively low ionization energy and low electronegativity. Calcium will form +2 ions and combine with nonmetals to form salt compounds. Oxygen is in the p-block, group 16. Its electron configuration is, O [He] 2s2 2p4; giving it 6 valence electrons and a high ionization energy and high electronegativity. Oxygen will form −2 ions and combine with many other elements to form compounds. 9. Stable electron configurations of copper and the other group 11 elements: a. 3d10 4s1 b. Yes c. True