Turgor Pressure - Ms. Gordon's online classroom
advertisement

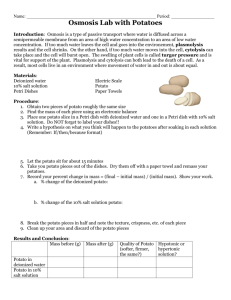
TURGOR PRESSURE Lab What is Turgor Pressure? Plant cells are very much like your own cells, except they are surrounded by a cell wall. This cell wall is part of what gives plants such a rigid and sturdy structure. Plant cells need a certain amount of pressure to make sure that the cell wall stays rigid, and this pressure is called turgor pressure. How It Works The way a cell maintains pressure is through a process called osmosis. When a plant cell is in a hypertonic solution. The solute is greater where? The water from the inside of the cell rushes out to the surrounding solution, and the cell becomes plasmolyzed. This is very unhealthy for the cell because it loses not only its water but also its rigidity and structure, often causing the plant to wilt. How It Works If a plant cell is placed in an isotonic solution. Water neither rushes in or out of the cell because the ratio of solute to solution is the same on both sides of the cell wall. However, this is still not enough rigidity for the plant cell, and the cell is flaccid. When a plant cell is in a hypotonic solution. The water from the inside of the cell rushes out to the surrounding solution, and the cell becomes cytolyzed. This is healthy for the cell because it gains not only its water but also its rigidity and structure, often causing the plant to stay strong. Lab: Turn to the next two blank pages in your notebook and label the left page Turgor Pressure Lab. Add the date and page number, and put it into your table of contents Write the first three sections of your laboratory report OBJECTIVE: To explore how force affects turgor pressure in plants. BACKGROUND INFORMATION: Turgor pressure is the pressure, or force of the water inside a plant cell against the outside, or cell wall. Think about what happens when a plant is in need of water and what the plant looks like before and after you water it. These changes happen because Turgor pressure changes. There is less force before you water the plant. Protocols: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Get 2 pieces of potatoes of the same length and size. Get two petri dishes. Label one A for salt water and the other B for distilled water. Obtain the mass of petri dishes A and B. Place two pieces of potatoes in each petri dish. Obtain the mass of the petri dishes with the potatoes in them. Add salt water to petri dish A Add distilled water to petri dish B Let potatoes soak for 20 minutes. When the potatoes are done soaking, dry them with paper towel and measure their mass and record it in the data table. Test the firmness of each potato by trying to bend them. Record your observation in the data table. Lab Work: Mass of Petri Mass of Petri Dish Dish and Potato Salt Water A Distilled Water B Mass of potato before soaking Mass of potato after soaking Firmness of potato Results: 1. 2. 1. What does the amount of bend tell you about the Turgor pressure inside the potato cells? What effect did the salt solution have on the potato? Which caused greater Turgor pressure inside the cell - water or salt solution? Conclusion: Write a conclusion in paragraph form. The following should be in your conclusion: state the purpose/objective and your original hypothesis Very briefly summarize the experiment. State the results, quote data. What was the direction of water movement in the potatoes? Does the data support the hypothesis? Use actual data to