Plasmolysis and Osmosis Lab with Potatoes
advertisement

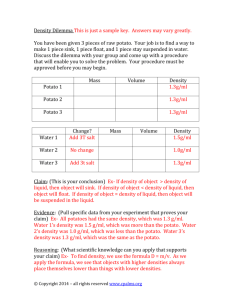
Name: _________________________________________________________ Period: ___________________ Osmosis Lab with Potatoes Introduction: Osmosis is a type of passive transport where water is diffused across a semipermeable membrane from an area of high water concentration to an area of low water concentration. If too much water leaves the cell and goes into the environement, plasmolysis results and the cell shrinks. On the other hand, if too much water moves into the cell, cytolysis can take place and the cell will burst open. The swelling of plant cells is called turgor pressure and is vital for support of the plant. Plasmolysis and cytolysis can both lead to the death of a cell. As a result, most cells live in an environment where movement of water in and out is about equal. Materials: Deionized water 10% salt solution Petri Dishes Electric Scale Potato Paper Towels Procedure: 1. Obtain two pieces of potato roughly the same size 2. Find the mass of each piece using an electronic balance 3. Place one potato slice in a Petri dish with deionized water and one in a Petri dish with 10% salt solution. Do NOT forget to label your dishes!! 4. Write a hypothesis on what you think will happen to the potatoes after soaking in each solution (Remember: If/then/because format) 5. Let the potato sit for about 15 minutes 6. Take you potato pieces out of the dishes. Dry them off with a paper towel and remass your potatoes. 7. Record your percent change in mass = (final – initial mass) / (initial mass). Show your work. a. % change of the deionized potato: b. % change of the 10% salt solution potato: 8. Break the potato pieces in half and note the texture, crispness, etc. of each piece 9. Clean up your area and discard of the potato pieces Results and Conclusion: Mass before (g) Potato in deionized water Potato in 10% salt solution Mass after (g) Quality of Potato Hypotonic or (softer, firmer, hypertonic the same?) solution?