AP Biology Discussion Notes wed 325
advertisement

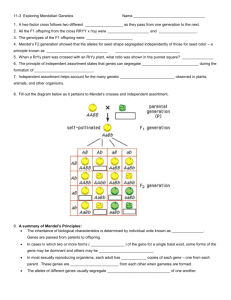
AP Biology Discussion Notes Wednesday 3/25/2015 Goals for the day • Be able to predict the outcomes of crosses with intermediate inheritance, co-dominance, or multiple alleles • Be able to define and perform dihybrid crosses and use multiple strategies to predict the outcomes • Be able to use probabilities to simplify & complete complex problems. Question of the day 3/25 • Fill out the 3 questions at the top of your note sheet - Intermediate Inheritance & CoDominance Answer the 3 questions at the top of your page. Intermediate Inheritance & CoDominance 1. Based on the problems you have done previously, predict the PHENOTYPE(s) of the offspring from a cross between a Red flower and a white flower where red is dominant to white. Intermediate Inheritance & CoDominance 2. How many phenotypes were possible in the problems we have done so far (look at the legend or the phenotypic ratio)? Intermediate Inheritance or Incomplete Dominance 3. What does intermediate mean? What does incomplete mean? Intermediate Inheritance Intermediate Inheritance/Incomplete Dominance - is when two alleles BLEND together. Example: When you cross a Red (FRFR) flower with a White flower (FWFW) you get all pink flowers (FRFW) in the offspring. (Red x White = 100% Pink) Legend Parents Cross it Genotypic Phenotypic Ratio Ratio Intermediate Inheritance or Incomplete Dominance Note in the cross that the Genotype & Phenotype ratios are now the same! Co-Dominance What does Dominance mean? What does “CO” mean? (As in cooperate or Coauthors) Co-Dominance = Dominant together Co-Dominance means: BOTH alleles are represented that is they both SHOW UP! (They are dominant together) Intermediate inheritance & CoDominance * The difference between Intermediate Inheritance & Codominance is in the PHENOTYPE. In Intermediate Inheritance (aka Incomplete Dominance) the alleles _________ together. In Codominance both alleles _____ _______, are EXPERESSED (Both traits are seen in the phenotype) Cross a homozygous black dog with a homozygous white dog Legend Parents Cross it Genotypic Phenotypic Ratio Ratio Intermediate inheritance & CoDominance Questions? Multiple alleles Some traits may be expressed by more than two possible alleles. This is multiple allele expression. One very important trait expressed through multiple alleles is human blood type. Multiple alleles There are four possible types of human blood: – A, B, AB, and O •These are expressed by immunoglobulin proteins, so the three possible alleles are written in this way: IA & IB are both CO-DOMINANT (they both _______ ___) and i is recessive to them. Multiple alleles Multiple alleles – Traits are controlled by more than 2 possible alleles. Multiple alleles Even with multiple alleles each individual still only gets _______ alleles for each trait! One allele from _______ and one allele from ______ Multiple alleles Blood types in Blood Type Alleles humans are a good (________type) (_______type) example of a multiple allele trait. AIA or IAi I - They are also an example of IBIB or IBi CO-Dominance – dominant together – I A IB Both alleles/traits ii _________ _____. Multiple alleles Very Important in Blood Transfusions! Multiple alleles Very Important in Blood Transfusions! Multiple alleles 1. One parent is homozygous type A and the other is heterozygous type A Leg Parents end Cross it Genotypic Ratio Phenotypic Ratio Mendel’s Law of Segregation • Each individual has a pair of factors (alleles) for each trait • The alleles segregate (separate) during gamete (sperm & egg) formation • Each gamete contains only one factor (allele) for each trait • Fertilization gives the offspring two factors (alleles) for each trait Dihybrid Crosses Up until now we have been looking at Monohybrid crosses. Mono means _______. This is to say that we have been looking at one ________, or characteristic, at a time. Often times we want to look at two traits at once. If we are looking at the outcomes of two traits in one cross we will call it a __________ ___________. •Di = _______ Mono = _________ Dihybrid Crosses Often times we want to look at two traits at once. If we are looking at the outcomes of two traits in one cross we will call it a Dihybrid Cross Di = _______ Mono = ______ Dihybrid Crosses Dihybrid cross – two trait cross In monohybrid crosses each parent was represented with ___ alleles and there were ____ possible allele combinations. (Ex. A parent could be AA, Aa, or aa) Dihybrid Crosses Dihybrid cross – two trait cross In Dihybrid crosses there are ___ alleles/parent and ____ possible Allele Combinations. Mendel tested Two-Trait Inheritance • Dihybrid cross Mendel used truebreeding (__________/____________) plants differing in two traits – Observed phenotypes among F2 plants – Formulated Law of Independent Assortment Mendel’s Law of Independent Assortment The Alleles for one trait segregate (separate) independently of the alleles for other traits All possible combinations of alleles can occur in the gametes(________/_______) *These are ____________ cells ( __ n) and made through the process of ____________ Meiosis Review Let’s refresh our Memory! Organism Cell type & chromosome # Mountain Goat Horn cell = 50 Leopard Seal Tongue cell = 10 Amaryllis Bulb Egg cell = 15 Emperor Penguin Sperm cell = 20 Bald Eagle Heart cell = 100 Haploid # Diploid # Meiosis Review Let’s refresh our Memory! Organism Cell type & chromosome # Mountain Goat Horn cell = 50 Leopard Seal Tongue cell = 10 Amaryllis Bulb Egg cell = 15 Emperor Penguin Sperm cell = 20 Bald Eagle Heart cell = 100 Haploid # Diploid # 25 50 Meiosis Review Let’s refresh our Memory! Organism Cell type & chromosome # Mountain Goat Horn cell = 50 Leopard Seal Tongue cell = 10 Amaryllis Bulb Egg cell = 15 Emperor Penguin Sperm cell = 20 Bald Eagle Heart cell = 100 Haploid # Diploid # 25 5 50 10 Meiosis Review Let’s refresh our Memory! Organism Cell type & chromosome # Mountain Goat Horn cell = 50 Leopard Seal Tongue cell = 10 Amaryllis Bulb Egg cell = 15 Emperor Penguin Sperm cell = 20 Bald Eagle Heart cell = 100 Haploid # Diploid # 25 5 15 50 10 30 Meiosis Review Let’s refresh our Memory! Organism Cell type & chromosome # Mountain Goat Horn cell = 50 Leopard Seal Tongue cell = 10 Amaryllis Bulb Egg cell = 15 Emperor Penguin Sperm cell = 20 Bald Eagle Heart cell = 100 Haploid # Diploid # 25 5 15 50 10 30 20 40 Meiosis Review Let’s refresh our Memory! Organism Cell type & chromosome # Mountain Goat Horn cell = 50 Leopard Seal Tongue cell = 10 Amaryllis Bulb Egg cell = 15 Emperor Penguin Sperm cell = 20 Bald Eagle Heart cell = 100 Haploid # Diploid # 25 5 15 50 10 30 20 40 50 100 Mendel’s Law of Independent Assortment In honor of Mendel we will do an example of a dihybrid cross with pea plants. R – Round Round is _______________ to wrinkled. r – wrinkled Y – Yellow y - green Yellow is ________________ to green. Dihybrid Cross Parental Generation (P1): RRYY x rryy Possible Gamete(s) from RRYY: Possible Gamete(s) from rryy: F1 gen. all (100%) RrYy Dihybrid Cross – F.O.I.L F1 generation: RrYy F – first O – Outside I – Inside L - Last RrYy Possible Gametes from RrYy: ______ , ______ , ______ , _______ R=Round r =wrinkled Y= Yellow g= green RY RY Ry rY ry Ry RrYy rY ry R=Round r =wrinkled Y= Yellow g= green RY rY ry RY RRYY RRYy RrYY RrYy Ry RRYy RRyy RrYy Rryy rY RrYY RrYy rrYY rrYy RrYy Rryy rrYy rryy ry Ry RrYy Phenotype (Phenotypic Ratio) Round & Yellow: ___/16 Round & ________: ___/16 _________ & Yellow: ___/16 __________ & __________ : ___/16 Phenotype (Phenotypic Ratio) Round & Yellow: ___/16 Round & ________: ___/16 _________ & Yellow: ___/16 __________ & __________ : ___/16 R=Round r =wrinkled Y= Yellow g= green RY rY ry RY RRYY RRYy RrYY RrYy Ry RRYy RRyy RrYy Rryy rY RrYY RrYy rrYY rrYy RrYy Rryy rrYy rryy ry Ry RrYy Dihybrid Crosses Phenotypic Ratio: ___: ___: ___: ___ - This will always be the phenotypic ratio for a Heterozygote cross in normal patterns of inheritance. *This will also be a test question! Typically for Dihybrid Crosses we will only ask you to find the Phenotypic Ratio, and not the Genotypic Ratios Dihybrid Crosses REVIEW There are now __ possible allele combinations that could be passed on in the gametes of these parents. Remember that Crossing over, which happens during Prophase 1 of Meiosis, is a source of _______________. *This Variation is in part why we might be able to have __ different allele combinations. Dihybrid Crosses REVIEW *This Variation is in part why we might be able to have 4 different allele combinations. If I had a heterozygote AaBb I might have AB on one chromosome and ab on another. The possible gametes then would only be AB and ab. The ONLY WAY to get the other possible gametes ___ ___ & ___ ___ are through crossing over which allows the gametes to inherit the alleles in a different way to have (VARIATION)!!! Wednesday PM • I will be unavailable – talk to me if you plan to work on corrections after school. Species of the Day 3/25 Common Grackle - Quiscalus quiscula Species of the Day 3/25 Common Grackle - Quiscalus quiscula Species of the Day 3/25 Common Grackle - Quiscalus quiscula European Starling - Sternus vulgaris