Dihybrid Crosses: Inheritance Patterns Explained
advertisement

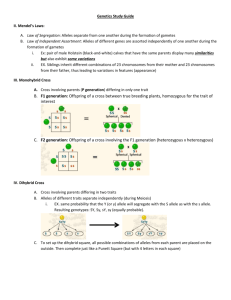
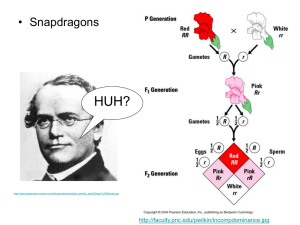
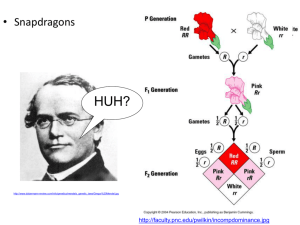
Dihybrid crosses a study of inheritance patterns for organisms differing in two traits… more realistic Dihybrid cross Monohybrid: heterozygous (having 2 different alleles for one gene pair). Ex: Aa So what is a dihybrid???? Di: meaning two Hybrid: means heterozyous instead of one trait we are looking at two traits at the same time AaBb represents the genotype of a dihybrid Remember Mendels laws: Law of segregation. Only one allele for each trait can be passed at a time. Only pass on one ‘A’ AND one ‘B’ and one… Law of independent assortment. How each type of letter (allele) sorts or is passed on to the next generation is independent i.e. Which “A” is passed on doesn’t affect which “B” is passed on What combinations of alleles are possible? If an organism has a genotype of AaBb What are all the different combinations of A’s and B’s? AB Ab aB ab These combinations represent the possible gametes (sperm or egg) that could form during meiosis. An example of a dihybrid cross Key: E = Two Eyes, T = Triangular e = one eye Head, t = pentagonal head So, lets have two dihybrid parents; therefore their genotypes are: EeTt x EeTt: What do they look like? Phenotype= Phenotype: two eyes and triangular heads. physical characteristics of an organism: what you “see”. What ET, types of combinations are possible? Et, eT, et. Is this all? Punnett squares Incomplete Dominance Incomplete Dominance = neither allele is dominant. Heterozygous individuals show an intermediate (in between) phenotype. Example: petal color in carnations RR = red RW = pink WW = white Codominance Codominance = both alleles contribute to the phenotype. Heterozygous individuals show both traits separately (not blended like in incomplete dominance). Example: coat color in cattle RR = red WW = white RW = roan Multiple Alleles Multiple Alleles = genes that have more than two alleles. Example: blood type in humans