PowerPoint Presentation - Ch.14 Mendel and the Gene Idea
advertisement

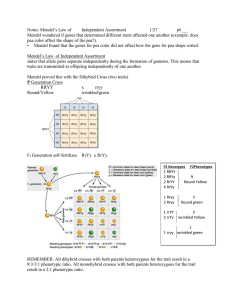
Ch.14 Mendel and the Gene Idea These notes are going to be relatively short because I believe practicing with problems is the best way to cover genetics. Obviously, this is Gregor Mendel. Mendel’s discoveries A Blending- Hereditary material- Both parents contribute genetic material. B Inheritable factors, genes are passed from generation to generation Pea experiments 1. Worked with 7 traits 2. Used purebreeding plants first then crossed them. Mendels Pea Crosses Law of independent assortment. a homologous chromosomes move independently. b Ex. Chromosome with A or a will go separate from chromosome with B or b. Law of Segregation • Homologous pairs segregate during gamete formation(meiosis ) and pair again after fertilization • Ex. If a pea is Pp then half the gametes will receive a P and half a p. Know the vocabulary Homozygous Heterozygous Phenotype Genotype Testcross- Mating an unkown to a homozygous recessive Monohybrid Cross- a cross between parents that are heterozygous for one trait. Dihybrid Cross Incomplete dominance • Incomplete dominance leads to a blending of traits, red + white yields pink Codominance - is not a blending but a mixing of the traits Codominance • Codominance - A and B are both dominant to O but not to each other, giving the AB blood type Epistasis • One gene has an effect on another. C leads to deposition of color while B or b leads to color BBcc would be white even though the genes code for black color. Polygenic inheritance • Combinations of genes can yield cumulative effects. The more dominant alleles the more color. Environmental Effects • Sometimes the environment can change the way a gene is expressed, like these hydrangia, and the color based on pH of the soil. Pleiotropy • One gene can have an effect on other parts of the body. The sickle cell gene which causes problems with blood cells has far reaching affects on the body. Pedigree analysis- square is male,circle is female. Achondroplasia Amniocentesis Cystic Fibrosis Sickle Cell Anemia Tay- sachs Huntington’s Corea Sample problems Mendel crossed short and tall pea plants(purebred cross) TT x tt = P gen. t t T Tt Tt All offspring are heterozygous T Tt Tt All are tall (Tt) Mendel crossed round, yellow pea plants to wrinkled, green pea plants (RRYY x rryy) The only possible gametes are RY from parent 1 and ry from parent 2 so ry ry RY RrYy RrYy All offspring are round RY RrYy RrYy and yellow (RrYy) Monohybrid Cross -two heterozygotes mated Tt xTt T t T TT Tt 1TT:2Tt:1tt t Tt 3 tall: 1 short tt Dihybrid cross Heterozygotes for 2 traits are crossed RrYy x RrYy You can make the folowing gametes for each parent RY,Ry,rY,ry, this means a four by four box as in the next slide Dihybrid Cross Dihybrid crosses can also be done like this; R r Y y R RR Rr Y YY Yy r Rr y Yy rr yy Now calculate the chances of RRYY (1/4 x 1/4) RRYy (1/4 x2/4) RrYY (2/4 x 1/4) RRyy (1/4 x 1/4) RrYy ( 2/4 x 2/4) Rryy (2/4 x 1/4) rrYY (1/4 x/1/4) rrYy (1/4 x 2/4) rryy (1/4 x 1/4)