Chapter 10: Agriculture
advertisement

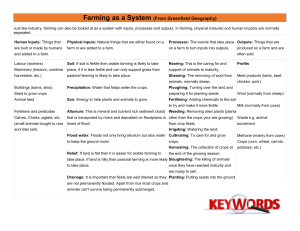
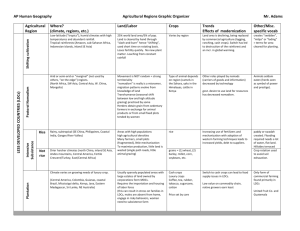
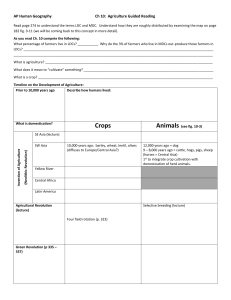
10.2 Purpose of farming Percentage of farmers in the labor force Use of machinery Farm size Relationship of farming to other businesses Shifting Cultivation Pastoral Nomadism Two features: land is cleared by slashing and burning debris Slash and burn Axes Cut down most of the trees Swidden= the cleared area Farm crops on a cleared field for a couple of years and then leave it for many years so the soil can recover Why move locations? Types of crops: vary by region Rice= SE Asia Corn (maize)=Americas Millet= Africa Brazilian shift farming order: Concentric rings Inner rings: sweet potatoes and yams Next: corn and rice, manioc, more yams Outter: Papaya, banana, pineapple, mango, cotton, beans LDCs: “farm field” is much more chaotic than in MDCs Land owned by the village Whole > individual ¼ of the world’s land 5% of the worlds population Not surprising…why not? Declining in tropics Can only support a small population in an area without causing environmental damage Deforestation of rain forests , esp. in Latin America • Large number of trees cut, burning and decay can release large volumes of… • Carbon dioxide • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zDOq7QZXTdI Pastoral nomadism = herding domesticated animals found primarily in arid and semiarid B-type climates animals are seldom eaten the size of the herd indicates power and prestige type of animal depends on the region Camels= N. Africa & SW Asia, Horse=Central Asia transhumance, or seasonal migration, practiced use of pastures, or areas on which animals feed often use similar patterns of migration, not random no longer seen as stage of agriculture, but type of agric. adaptation to environment declining in numbers worldwide Identify two features of shifting cultivation Pastoral nomads depend on animals rather than crops i.e. animals provide milk, skin/hair. Mostly consume grains rather than meats Animals usually not slaughtered, but once dead may be eaten Animals: Camels= long periods without water, carry heavy bags, move quickly Goats= tough and agile and can survive on almost any vegetation Today it is declining partly because of modern technology. Why?? ¾ of the world’s people live in LDCs and the form of agriculture that feeds them= Intensive Subsistence Agriculture East, South, Southeast Asia Most of the work done by hand or with animals b/c of the lack of funds Virtually no land wasted I.e.: Wet-rice farming (Review textbook for the specifics) Dry lands farming various grains using crop rotation Rotating use of different fields from crop to crop each year to avoid exhausting the soil Commercial agriculture in tropics and subtropics esp. Latin America, Africa, Asia Found in LDCs, owned by MDCs and sold to MDCs Plantation= large farm that specializes in one or more crops Sugarcane, cotton, coffee, rubber, tobacco, cocoa, bananas, tea, coconuts. Must import workers and provide housing, food because plantations are isolated USA history with plantations= in the south with cotton, declined after the…