Agricultural Systems & Agricultural Regions
advertisement

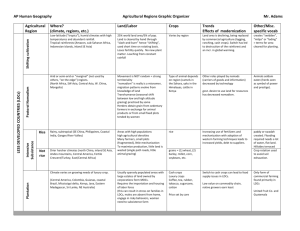
Modern Trends in Global Agriculture Write this somewhere on your sheet • Socioeconomic—Social or economic factors that affect the lives of average, working people in a country • (I think this gave a lot of you trouble on your FRQ’s) The Three Agricultural Revolutions • First (Neolithic) Agricultural Revolution (8,000 B.C. in SE Asia and four hearths) – switch from hunting and gathering to sedentary plant and animal domestication • Second Agricultural Revolution (1700s in Europe) – new farming and storage abilities increased food supplies to meet a growing and urbanizing population • Third Agricultural Revolution (late 1800s – 1950s in N. America) – distributed mechanized farming technology and agricultural chemicals on a global level Third Agricultural Revolution— 1950-present • New machinery • tractors for plowing soil • reapers for cutting crops • threshers for separating grain from stalks • Refrigerated containers! • Chemically-produced fertilizers and pesticides • Genetically Modified Foods • Green Revolution - • Refrigerated containers now used to transport agricultural goods globally Dunedin, New Zealand Industrial Agriculture • As a result of the Third Agricultural Revolution, food production became “industrialized” • Changed – Who produces food – How food is produced – Where food is produced Who produces food • 1st--Family farm – Family farms control most steps in the food production process • Now--Corporate farm under industrial agriculture – Large companies called agribusinesses control most steps in food production (seed design, raising animals/growing plants, processing, packaging, advertising, and distribution) How food is produced • 1st--Family farm – Labor-intensive • Now--Corporate farm under industrial agriculture – Food manufactured in large factories – Capital-intensive in all steps (cultivation, processing, distribution) Where food is produced • 1st--Family farm – Local farms in MDCs • Now--Corporate farm under industrial agriculture – Often produced in LDCs and exported to MDCs (globalization of agriculture) – Small farmers in LDCs now work for foreign agribusiness corporations – Ex. During winter in North America, Chile is the primary source of fruits and vegetables in grocery stores Neocolonialism • European powers used colonies in Africa, Asia, and the Americas to supply Europe with raw materials • Now, most LDCs still survive by producing cash crops for export to MDCs that were once their masters. – Colombia – coffee, Guatemala -- bananas, Egypt – cotton, Caribbean and Brazil – sugar, flowers Subsistence vs. Commercial Agriculture • Five characteristics that distinguish subsistence agriculture from commercial agriculture – Purpose of farming – Use of machinery – Percentage of farmers in the labor force – Farm size – Where predominant Purpose of farming • Subsistence Agriculture • Commercial Agriculture – provide food for the farmer’s own family Uganda – Produce products for sale off the farm to other places Use of machinery • Subsistence Agriculture • Commercial Agriculture – Labor-intensive – Capital-intensive / mechanized Farm Size and Scale of production • Subsistence Agriculture • Commercial Agriculture – Small size – Small-scale Terraced Fields in Malaysia – Large size – Large-scale % of Labor Force in Agriculture, 2005 In LDCs, is the percentage of workers involved in agriculture high or low? In MDCs, is the percentage of workers involved in agriculture high or low? Predominant in which regions • Is subsistence agriculture predominant in LDCs or MDCs? • So where is commercial agriculture predominant? Land Use • Extensive activity – using a large amount of land to produce crops and livestock. (inefficient) • Intensive activity – using small amounts of land very efficiently to produce crops and livestock (rice, wheat, corn) intensive subsistence agriculture • 45% of people of world’s population do this! • Farmers cultivate small plots of land very efficiently, but labor-intensive. • Predominately grow one crop, then exchange small amounts for other foods • Wet rice (India, Bangladesh, S & E. China, SE Asia) • Double cropping—Planting twice in a growing season • Done in LDCs • Found in regions with – high population density – abundant summer rainfall • Rice , maize & manioc (S. Am.), millet & sorghum (Africa) Indonesia World Rice Production, 2005 In which two states is most of the world’s rice grown? shifting cultivation / swidden farming • Subsistence Agriculture, multiple crops grown at one time • Growing crops in an area for a short period of time, then leaving it “fallow” (unfarmed) • In tropical areas, soil is poor (rain washes away nutrients, so farmers adapt by moving from field to field to allow soil to replenish its nutrients. • Environmentally sustainable, but inefficient--Largest percentage of world’s total land area (¼), but supports less than 5% of world’s population Guatemala shifting cultivation / swidden farming • Usually involves slash and burn agriculture – land cleared by cutting existing plants, then burn rest, cultivates for a few years, then moves on once soil becomes poor. • Found in LDCs • Found in hot, humid, low-latitude climates (tropical and tropical wet) • Found in areas with low population density • W. Africa, central Africa, Amazon River basin of northern South America, SE Asia, especially Indonesia pastoralism / nomadic herding • subsistence pattern of agriculture in which people make their living by tending herds of animals • Livestock provide food, clothing, shelter. • Different cultures prefer different animals • May be sedentary or nomadic • Done in arid/semi-arid climates because no arable land • Done in Northern Africa, SW Asia, W. China Iran Intertillage • Intertillage is the planting of different crops together in the same field. • This is good for subsistence farmers, but is not part of the global food production process. (not commercial agriculture) • Benefits: – Spreading out food production over the growing season – Erosion control • Problems • Inefficient plantation agriculture • Specialize in one or two highdemand cash crops that will usually be exported to MDCs, (sugar cane, coffee, palms, coconuts, rubber, cotton) • Large-scale commercial agriculture in LDCs. • Started during imperialism • Core-periphery model? Coffee, a cash crop of Ethiopia grain farming • Includes corn and wheat, some for humans, others for animals • Wheat is world’s leading export crop. – U.S. & Canadian farms grow ½ of world’s wheat supply. • Done in MDCs (capital intensive) • Midwestern U.S., North Europe, Canada • Requires mild climate Mediterranean agriculture • Near Mediterranean sea and climates with hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters • Wheat, barley, and specialty crops (grapes, olives, figs) • Mediterranean, California, Chile, South Australia, S. Africa Vineyard in Portugal mixed crop and livestock farming • Most common type of farm found in MDCs. • Most crops grown are fed to animals, especially maize, because most income comes from animal product sales • MDCs • Eastern U.S., N. Europe Cattle feedlot dairy farming / dairying • Near urban areas in northeastern US, southeast Canada, & northwest Europe (MDC’s, capital intensive) • Transport/storage technology, (refrigerated trucks) let dairy farmers locate further from urban market livestock ranching/cattle grazing • Mainly cattle and sheep • Evolution: from seminomadic to small ranches to part of meat-processing industry, often in feedlots to increase efficiency • Semiarid or arid lands. • western U.S., pampas region of S. America –Argentina, southern Brazil, Uruguay(primarily for export)., west coast of Latin America & n. Mexico One Hint, Two Hints Guess the word with one hint, get two points! Guess the word with two hints, get one point. BUT, get it wrong, lose a point… • • • • • • • • • Subsistence Agriculture Commercial Agriculture Extensive Agriculture Intensive Agriculture Shifting Cultivation/Swidden Farming Terracing Intertillage Double Cropping Intensive Subsistence Agriculture • • • • Plantation Agriculture Grain Farming Mediterranean Agriculture Pastoralism/Nomadic Herding • Mixed Crop and Livestock Farming • Dairy Farming • Livestock Farming