13-NESOY-0135_IdeaBin_Lesson 2 Risk Management & Marketing
advertisement

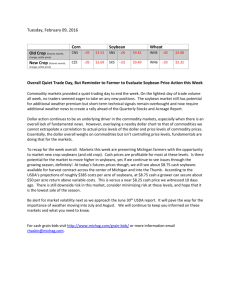
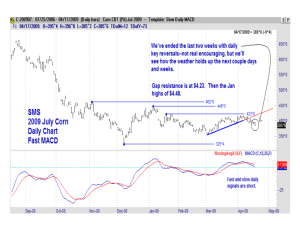
RISK MANAGEMENT AND MARKETING Date: / / OBJECTIVES By the end of the lesson, students will know or be able to: Define: forward contract, cash market, futures contracts, options contracts, hedging, options, commodity swaps, spreads, straddles, risk management, basis, commodity, vertical integration Identify risks of marketing soybeans internationally Explain the role of the Chicago Board of Trade Explain the use of hedging, commodity swaps, vertical integration and math in managing trade risks MATERIALS One guided notes page per student One set of key terms envelope for each small group PREPARATORY WORK Cut apart letters of key terms and place them in envelopes These educational materials provided by the Nebraska Soybean Board. IdeaBin.org ENROLL THE PARTICIPANTS – APPROXIMATELY 10 MINUTES Provide students with the following bell work and time to capture their thoughts: Choose a common object that is located in the classroom and that you know a great deal about. Write down what you would do and say to “sell” that object to someone else. After providing students time to complete the bell work, provide time for students to market the object to their class or a small group within their class. Point out that marketing skills are critical tools for people within the soybean industry to possess, especially as they work to sell soybeans internationally. PROVIDE THE EXPERIENCE – KEY TERMS – APPROXIMATELY 10 MINUTES All Mixed Up Cut apart the letters of each of the words, terms or phrases and place them in separate envelopes so that each word, term or phrase is in an individual envelope. Organize students into small groups and provide them with instructions that might sound like this: In a moment, you’ll receive several envelopes each with a separate word, term or phrase that relates to the marketing of soybeans. As a small group, organize the letters of each term and seek my approval as you figure out each term. Once all terms are correct, use what you know to create a definition of each term. Provide each group with their set of envelopes. LABEL THE INFORMATION – APPROXIMATELY 10 MINUTES Provide each student with a guided notes page and review the terms and definitions with them. Forward contract: an agreement between a buyer and a seller to conclude the sale of an item at a specified time and at a specified price Cash market: an exchange of goods and money between the buyer and seller that takes place in the present. Futures contracts: a contracted agreement to buy or sell a specific commodity at a predetermined price in the future. Options contracts: a contracted agreement that allows the holder to buy or sell an underlying security at a given price. Hedging: making an investment to reduce the adverse price movements of an asset. Options: contracts sold by one party to another that offer the buyer the right to buy or sell a financial asset at an agreed-upon price during a certain period of time. These educational materials provided by the Nebraska Soybean Board. IdeaBin.org Commodity swaps: exchanged cash flows are dependent on the price of an underlying commodity; usually used to hedge against the price of a commodity. Spreads: the difference between the current bid and the current ask. Straddles: an options strategy with which the investor holds a position in both a sale and a purchase with the same cash market. Risk management: the process of identification, analysis and either acceptance or mitigation of uncertainty in investment decision making. Basis: the variation between the spot price of a deliverable commodity and the relative price of the futures contract for the same actual that has the shortest duration until maturity. Commodity: an economic good Vertical integration: when a company expands its business into areas that are at different points on the same production path DEMONSTRATE THE RELEVANCE – APPROXIMATELY 5 MINUTES Instruct students to choose three words and construct a sentence or a short series of sentences that demonstrates how the three words are related. Students write the sentence(s) on their guided notes page. PROVIDE THE EXPERIENCE – RISKS OF MARKETING SOYBEANS – APPROXIMATELY 4 MINUTES Prepare students to watch a management and risk video by saying that the terms the class just defined all apply to the marketing of soybeans. Any farmer takes risks when they choose which crop to produce and those risks affect the marketing of the identified crop. Instruct students to listen for the risks mentioned in the video. Go to http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4sJ8aep9UMg and engage students with the YouTube video called “Nebraska Soybean Board – Marketing and Risk Management.” LABEL THE INFORMATION – APPROXIMATELY 5 MINUTES Discuss with the students the risks identified in the video. If need be, play the video a second time so that students can listen for the risks again. Some of the risks mentioned include insurance, market fluctuation, basis, quality of the plant, farm programs and commodity programs. DEMONSTRATE THE RELEVANCE – TIME VARIES Arrange students in small groups of two or three students. Provide each small group with one of the risks identified in the video. Instruct the small groups to identify one person as the grower of the soybeans and the other(s) as consumers. Within the small groups, the students These educational materials provided by the Nebraska Soybean Board. IdeaBin.org will prepare a discussion that might occur between a producer and a consumer around the specific risk they were assigned. The discussions might include questions that the consumer(s) have about the production process and gratitude to the producer for taking the risk in order to produce the soybeans for the consumer. The producer will answer the questions of the consumers. Provide the groups time to research the answers to questions if need be. Each group may demonstrate their discussion to the larger class. PROVIDE THE EXPERIENCE – CHICAGO BOARD OF TRADE – APPROXIMATELY 15 MINUTES Inform students that knowing some of the basic marketing terminology and knowing some of the basic risks of growing and marketing soybeans prepares a producer to actually market the product. Many producers choose to market their crop on the Chicago Board of Trade. Direct students to this website: http://www.theoptionsguide.com/soybeans-futures.aspx and explain that they’ll explore key points about using the Chicago Board of Trade. LABEL THE INFORMATION – APPROXIMATELY 7 MINUTES Instruct students to use the content of the website to prepare talking points to share with their parents that will inform their parents about the role of the Chicago Board of Trade in marketing soybeans. The presentation will also include a minimum of five marketing terms and a minimum of three risks producers take in choosing to produce and market soybeans. DEMONSTRATE THE RELEVANCE – TIME VARIES Students share their talking points with their parents and write down a minimum of five questions that their parents asked regarding the talking points. PROVIDE THE EXPERIENCE – RISK MANGEMENT TECHNIQUES – APPROXIMATELY 5 MINUTES Read the following scenario to students: You are a soybean producer. You established and use a soybean treatment facility on your operation. Your farm is 1,000 acres in size and you grow multiple row crops, with a heavy emphasis on soybeans. You are to work with your farm consultant to determine how you can use hedging, commodity swaps, vertical integration and mathematical concepts to manage the risks of growing and marketing the soybeans on international markets. LABEL THE INFORMATION – APPROXIMATELY 10 MINUTES Instruct students to review the definitions of hedging, commodity swaps and vertical integration, and to further investigate the use of these terms in marketing soybeans. Students may work in small groups to explain how each term connects to the scenario. These educational materials provided by the Nebraska Soybean Board. IdeaBin.org DEMONSTRATE THE RELEVANCE – APPROXIMATELY 15 MINUTES Arrange students in small groups and instruct them to identify risks and how they can manage them in their own lives. As an alternative, you might consider having the students work within their own career interest(s) to identify 10 risks that might exist and how they could manage those risks. REVIEW THE CONTENT – APPROXIMATELY 5 MINUTES Students create a short tag line or catchy phrase for one concept they learned during this lesson and all students share their phrases with the class. CELEBRATE STUDENT SUCCESS Thank students for their efforts in researching and applying key risk management concepts. Encourage students to assess the risks present in their lives and the choices they make; challenge students to manage their risks appropriately so that they make take wise risks and eliminate unwise ones. These educational materials provided by the Nebraska Soybean Board. IdeaBin.org STUDENT GUIDED NOTES PAGE RISK MANAGEMENT AND MARKETING Forward contract: Cash market: Futures contracts: Options contracts: Hedging: Options: Commodity swaps: Spreads: Straddles: Risk management: Basis: Commodity: Vertical integration: Choose three terms and write a sentence or short series of sentences to demonstrate how the terms are related. Marketing and Risk Management Video Notes: Chicago Board of Trade Talking Points: These educational materials provided by the Nebraska Soybean Board. IdeaBin.org