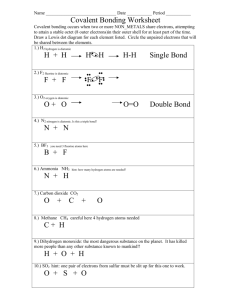
Bond Type To calculate bond type 1. Look up the electronegativity of
advertisement

Bond Type To calculate bond type 1. Look up the electronegativity of the atoms in question. (chart passed out) 2. Find the difference between the electronegativities. (subtract) 3. Use the chart to classify the bond as nonpolar covalent (0.0 - 0.49) polar covalent (0.5 – 1.9) ionic (>2.0) Determine the bond type of each of the following. H2 H2O NaCl MgCl2 Covalent Bonding and Molecular Compounds covalent bonding - bonding between atoms which results from electron sharing The particle which results from covalent bonding is a molecule. molecule - two or more atoms bonded covalently There are eight elements in which two atoms bond forming a diatomic molecule. They do not normally exist as single atoms. They are referred to as diatomic elements. diatomic elements - two identical atoms bonded covalently molecular compound - a chemical compound whose simplest formula units are molecules Formulas Represent Compounds chemical formula - a shorthand method of using atomic symbols and subscripts to represent the composition of a substance molecular formula - a formula indicating the composition of a molecule dot formula - a formula using dot notation to indicate valence electrons formula unit – represents the composition of an ionic compound, empirical formula DIATOMIC ELEMENTS NAME DOT FORMULA MOLECULAR FORMULA hydrogen H2 nitrogen N2 oxygen O2 fluorine F2 chlorine Cl2 bromine Br2 iodine I2 astatine At2 Lewis Structures Lewis structures are formulas in which symbols represent nuclei and inner shell electrons and dots, dashes, etc, represent valence electrons. The Lewis structure of water would be similar to the dot formula. Polyatomic Ions A polyatomic ion consists of two or more atoms bonded covalently which has a net charge. Show the Lewis structure for SO4=. Show the Lewis structure for H2 SO4. Examples Show the Lewis structures for MgBr2 Na2O H3PO4 CH3Cl Al2S3