Endocrine System
advertisement

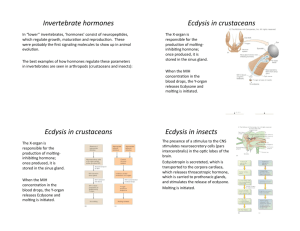
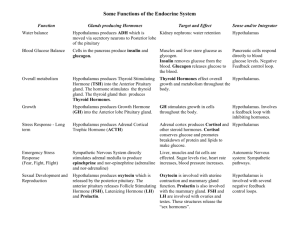
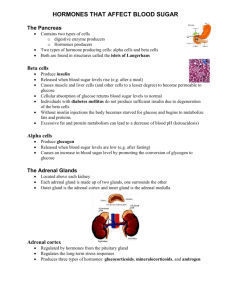
Endocrine System for copying Endocrine vs nervous system • act together to coordinate body’s activities • both: – use chemical messengers to communicate cell to cell – major function: homeostasis • endocrine: slower response time – hormones transported thru circulatory system – target cells (any cell with hormone receptor) anywhere in body • nervous: quicker conduction of signals – neurotransmitters – act on cells close by Glands • no ducts • secretions released and diffuse into blood capillaries • have ducts • secretions released onto surface • example: sweat glands, salivary glands Endocrine Exocrine 2 types of hormones • bind to protein receptors in cell membranes (do not enter cell) • receptor-hormone activate enzyme in cytoplasm series of reactions result in cell response • enter cell & bind to receptor in cytoplasm or nucleus • Activates transcription of gene protein produced • generally action slower than peptide hormone Peptide Steroid Endocrine system hypothalamus • part of brain • secretes “releasing” hormones that act on pituitary gland • axons that store the 2 posterior pituitary hormones end there Pituitary gland • 2 lobes: posterior & anterior Negative Feedback Inhibition Thyroid Gland • stimulated by TSH • secretes thyroxin (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) – (-) feedback inhibition • both have similar effects on target cells hypothyroidism • Thyroid produces too little hormone • several causes: Hashimoto’s autoimmune/ lack of Iodine in diet goiter (enlargement of thyroid due to increased TSH stimulation • Symptoms: – Adults: lethargy, weight gain, anovulatory cycles – Infants:cretinism: dwarfism, low IQ, failure to reach sexual maturity hyperthyroidism • excessive secretion of thyroid hormones Parathyroid Glands • 4 small glands embedded in posterior surface of thyroid gland • secrete: parathyroid hormone (PTH) – regulated by serum Ca++ levels • actions: 1. stimulates removal of Ca++ from bone 2. increases kidney tubules reabsorption of Ca++ 3. activates vit D which enhances Ca++ absorption from food thymus • upper thorax, posterior to sternum • largest in infants, decreases as we age • produces: thymosin – programs T cells Adrenal Cortex • outer layer • produces 2 kinds of steroid hormones 1. Glucocorticoids – – major 1 – cortisol: reduces swelling by inhibiting immune system/ raises serum glucose (stimulates liver to make glucose from proteins or lipids 2. Mineralocorticoids – – major 1- aldosterone acts on kidney to promote absorption of Na+ & excretion of K+ pancreas 1. Insulin – – – protein reduces blood glucose by increasing entry of glucose into cells/making glycogen in hepatocytes regulated by blood glucose levels 2. Glucagon – – – protein raises blood glucose by acting on glycogen stores in liver regulated by blood glucose levels testes • paired oval organs suspended in scrotum • site of: spermatogenesis production of androgens: Testosterone major one made by interstitial cells/stimulated by FSH & LH – produces male 2◦ sex characteristics in puberty – promotes growth & maturation of reproductive system organs – increases libido – – 1. – ovaries • paired, almond-shaped organs in pelvic cavity • produce ova • release: estrogens & progesterone • begin functioning in puberty in response to anterior pituitary gonadotrophins estrogens • Estrone &Estradiol made by follicle where ova is maturing • stimulate: – development of 2◦ sex characteristics • work with progesterone to prepare uterine lining for implantation • help maintain pregnancy & prepare breasts to lactate(those estrogens made in placenta) progesterone • made &secreted by corpus luteum • acts with estrogen to prepare uterine lining for implantation • quiets uterine muscle during early pregnancy • helps prepare breasts for lactation placenta • produces hCG (human Chorionic Gonadotropin) – stimulates corpus luteum of ovary to continue producing estrogens and progesterone so lining of uterus does not slough off (like in menstruation) – turns pregnancy tests + – by 3rd mo pregnancy placenta produces estrogen & progesterone (ovaries become inactive rest of pregnancy) – also produces hPL (human placental lactogen) works w/E & P in preparing breasts for lactation Pituitary disorders • Giantism: • hypersecretion hCG during chidhood • abnl increse in length of long bones • hypersecretion hCG in adulthood acromegaly (epiphyseal plates sealed) see thickening of bones of hands, face & thickening of skin on brow • Diabetes Insipidus: • defects in ADH • excrete large volumes of urine dehydration & thirst (bed-wetting in children) • can die w/in 2 days from the dehydration Anterior Pituitary Posterior Pituitary Thyroid gland disorders • Hypothyroidism: • Cretinism: congenital hypothyroidism – severe mental retardation if not tx’d – most states require testing new borns • Myxedema:adults – hallmark:edema of facial tissues, slow HR, low body temp, sensitivity to cold, dry skin & hair, muscle weakness Thyroid gland disorders Graves Disease most common form of hypothyroidism 7 – 10 x more common in females autoimmune disorder: autoantibodies that mimic TSH causes thyroid to grow & make thyroid hormones • signs: enlarged thyroid, exophthalmos • tx: surgical excision of all or part of thyroid or use of antithyroid drugs to block synthesis of hormones • • • • goiter • enlarged thyroid • could be associated with hypo- or hyperthyroidism, or euthyroidism (normal level of hormones) seen when intake of iodine too low Adrenal Gland disorders • Cushing’s Syndrome: • hypersecretion of cortisol • caused by tumors that secrete – cortisol (in adrenal cortex) – ACTH stimulates more cortisol production in adrenal cortex • muscle wasting spindly arms & legs, “moon” face, “buffalo hump” red face • ~80% have hypertension Adrenal gland disorders • Addison’s Disease: • hyposecretion of glucocorticoids & aldosterone • most are autoimmune: antibodies cause adrenal cortex destruction or block binding of ACTH to its receptors • TB can destroy adrenal cortex • symptoms: (after 90% of cortex destroyed) mental lethargy, anorexia, N/V, wt loss, hypotension, hypoglycemia, muscular weakness Pancreatic islet disorders Diabetes mellitus: (honey-sweetened) inabillity to use or produce insulin 4th leading cause death in USA blood glucose levels high glucosuria • 3 polys: polyuria, polydipsia, polyphagia • • • • Diabetes Mellitus • Type 1: autoimmune abys destroy beta cells – mostly develops <20 yrs old – most common in northern European heritage – cells starved for glucose so switch to breaking down fatty acids ketone production ketoacidosis untx’d death – transport of lipids from adipocytes plaque formation in walls of arteries = atherosclerosis – excess glucose attaches to proteins in lens catarracts – small vessel disease: blindness, kidney failure, amputation of toes legs, impotence Diabetes Mellitus Treatment • self-monitoring of blood glucose levels injections of insulin • Diet: – 45 – 50% carbohydrates – <30% fats Exercise Type 2 Diabetes • non-insulin-dependent diabetes (NIDDM) • more common (90% of all cases) • typically occurs in obese people > 35 yrs old – #s children diagnosed increasing • many control it with diet, exercise, wt loss • oral hypoglycemic drugs – stimulates secretion of insulin from beta cells