2presentationActivities
advertisement

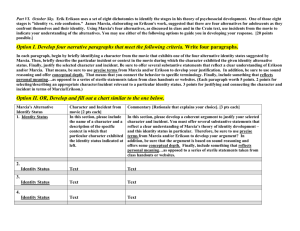
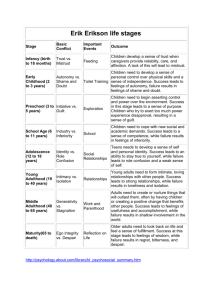
Week 2 Chapter 4 Life Span Development • What are traditional birthing procedures in your culture of origin? What are alternative birthing procedures? Share what you think about them with your group. • What are the ‘typical’ problems in childhood? When do they become out of control? When should you do an intervention if a child is developing ‘differently’? • Have you interacted with people diagnosed with (or do you have) learning disabilities, or developmental disabilities, such as Autism? What kinds of challenges did they face? You are getting older by the minute • Looking at the clock right now, figure out your age to the minute. Start with the exact time you were born if you know it. • None of us will get these minutes back, have you invested them well? Personality Traits in Happy Adults • Are their certain personality traits that protect people from difficulty adjusting after negative life events? • Discuss the advantages or disadvantages of: • Optimism vs Pessimism • Flexibility vs Rigidity • Self-efficacy vs External locus of control End of Life • What are the advantages and disadvantages of euthanasia? • Why is it accepted in some countries and not others? • Are there moral differences between active and passive euthanasia? Erik Erikson • Born out of an affair, he was adopted by his step father at the age of 7 and wasn’t told who his real father was until he was an adult. He felt alienated by both his Norse and Jewish peers. He spent a lot of time studying “identity crisis”. Stage 1 Trust vs Mistrust • Trust is established when infants are given warmth, touching, love and physical care. • Mistrust is caused by inadequate or unpredictable care. Stage 2 Autonomy vs Doubt • Parents can foster a sense of autonomy by encouraging their kids to try something new • Parents who overprotect or ridicule their kids may cause them to doubt their abilities or feel shame about their actions Stage 3 Initiative vs Guilt • Initiative is reinforced by giving children freedom • Guilt develops by criticizing, preventing play or discouraging questions Stage 4 Industry vs Inferiority • Industry is when children are successful at producing activities (building, painting, reading, etc) • Inferiority is when they feel unsuccessful at these new activities Stage 5 Adolescence: Identity vs Role Confusion • Identity is formed by a consistent combination of values, skills, roles, culture • Role Confusion occurs when people can’t develop coherent fusion Stage 6 Intimacy vs Isolation • Intimacy is the ability to care about others, and share life with them • Isolation is when this hasn’t occurred Stage 7 Generativity vs Stagnation • Generativity is being interested in the next generation • Stagnation is only being interested in yourself Stage 8 Integrity vs Despair • Integrity is when someone has lived their life to the fullest • Despair is when someone is full of regrets about their life James Marcia’s Adolescence • Two important criteria determine the status of the adolescent: • Crisis: extent person is examining and choosing their alternatives • Commitment: degree of personal investment adolescent puts into attitude, belief, occupational choice, etc Marcia: Identity Diffusion • Impulsive, no self-direction • Avoids getting involved in school work or personal relations • Doesn’t consider major issues • Has not thought about future roles: occupation, sex roles, values, etc Marcia: Moratorium • Is aware of being in a crisis • Thought about identity problems but has no answers • Dissatisfied with school or college and whatever else they are involved in • Short lived relationships • Changes majors • Rejects parental values Marcia: Identity Achievement • Begun to make commitments regarding roles • Working on getting other aspects of life together • New trauma will bring back identity crisis, but hope of recovery is good Marcia: Identity Foreclosure • • • • No doubts about choices May accept values and choices of parents Does not have to be result of Identity Crisis Appears self-assured Marcia: Role Confusion • Defiant and destructive behavior • Disdain for traditionally valued roles, rebellion • May be easier to identify with what should not be done • Punishment by parents and society may confirm these roles • Cults or Gangs provide role for these people • Gangs require certain behaviors and attitudes that relieve the stress from the person Atypical Development • Autism • Genetically caused, 1 out of 250 children in Oregon • Inability to understand others minds and thinking • 25% chance of improvement Conduct Disorders • • • • When rebellion gets out of control Oppositional Defiance Causes Consequences Child Abuse • Combination of stress and lack or resources of parents • Something pathological with parents • Cyclical in nature Aging • • • • Only 25% of declining abilities is medical People age better with planning Biological aging: maximum life span Choices: Life expectancy Activities • Erikson’s Ages and Stages (more info on page 123) • Changes in Aging Video