Piaget`s Cognitive Development
advertisement

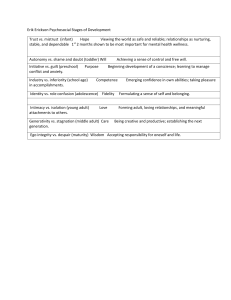
PART 2: FOCUS ON THE LEARNER Educ 221 - Facilitating Learning Melanie Jeane C. Galvez Ateneo de Davao University Piaget’s Stages of Cognitive Development The principal goal of education is to create men (people) who are capable of doing new things, not simply repeating what other generations have done – men (people) who are creative, iInventive and discoverers. Jean Piaget Cognitive Concepts Accommodation Assimilation Schema Cognitive Concepts Assimilation Accommodation Stages of Development 4 3 2 1 Sensorimotor Object permanence Preoperational -symbolic function -egocentrism -centration -reversibility -animism -transductive reasoning Concrete Operational -decentering -reversibility -conservation -seriation Formal Operational -hypothetical -analogical -deductive Principles (Piaget’s Theory) • Children provide different explanations of reality at different stages • Cognitive development is facilitated by providing activities or situations that engage learners and require adaptation • Learning materials and activities should involve the appropriate level of motor and mental operations for a child at a given age • Use teaching methods that actively involve students and present challenges Piagetian-based Learning Activity Plan Instructions: 1. Read the matrices found in the book 2. Make a simple Piagetian-based learning activity plan 3. Formulate learning objectives 4. Pick 2-3 applications from the matrix to help achieve the objectives you make Subject: Lesson Topic: Grade/Year Level: Objectives Application Specific Activity plan Highlight Provide timelines Ask students to significant events for history class make a timeline in Rizal’s life of Rizal’s life Erikson’s Psycho-Social Theory of Development Healthy children will not fear life if their elders have integrity enough not to fear death. Erik Erikson Stage 1 Infancy Too much trust Sensory maladjustment Too little mistrust Trust vs. Mistrust Hope & Drive Withdrawal Stage 2 Toddler hood Too much shame Impulsiveness Too little doubt Autonomy vs. Shame & Doubt Will power & Determination Compulsiveness Stage 3 Preschool Too much initiative Ruthlessness Too little guilt Initiative vs. Guilt Purpose & Direction Sociopathy Stage 4 School Age Too much industry Narrow virtuosity Too little inferiority Industry vs. Inferiority Competency Inertia Stage 5 Adolescence Too little Identity confusion Too much identity Ego Identity Identity vs Identity Confusion Fidelity & Devotion Repudiation Stage 6 Young Adulthood Too much intimacy Promiscuity Too little isolation Intimacy vs. Isolation Love & Affiliation Exclusion Stage 7 Middle Adulthood Too much generativity Overextension Too little stagnation Generativity vs. Stagnation Care Rejectivity Stage 8 Late Adulthood Too much integrity Presumption Too little despair Integrity vs. Despair Wisdom Disdain Synthesis of concepts Life Stage/ Psychosocial Crisis Infancy Toddlerhood Preschool School Age Significant Relationship Virtue Suggestions for the Teacher Hope & Drive Willpower & Self Control Purpose & Direction What teachers should do in order to facilitate learning and development of virtues in each stage Adolescent Period Competence & Method Fidelity & Devotion Young Adult Love & Affiliation