Patterns of the Periodic Table & Electron Configuration
advertisement

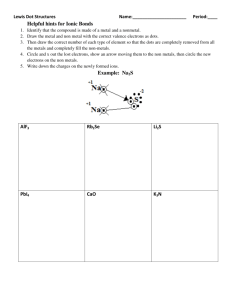
Valence electrons are the electrons in the outer orbit of an atom These electrons determine the chemical bonding properties of elements. The number of valence electrons an atom has corresponds to its group number with the exception of groups 3-12. This is why elements within a group usually have similar properties. Be (Beryllium) Atom Mg (Magnesium) Atom The number of energy levels an atom has corresponds to the period number (row number). These are the total number of rings you have in your Bohr Diagrams 4th Shell K (Potassium) Atom Kr (Krypton) Atom Fe (Iron) Atom A way of representing atoms by showing the number of valence electrons as dots surrounding the element symbol Example: Oxygen gets 6 dots. Chlorine gets 7 dots. There So is an order we fill the dots it would look like this, depending on how many valence electrons we have. Please construct Lewis Structures for the following atoms: 1 Calcium (20) 2 Antimony (51) 3 Bromine (35) 4 Indium (49) 5 Cesium (55) 6 Lead (82) 7 Tellurium (52) 8 Radon (86) 9 Strontium (38) 10 Helium (2) 1 2 3 4 5 6 Which element has 5 valence electrons and 3 energy levels? Which element has 4 energy levels and 6 valence electrons? How many energy levels and valence electrons does Astatine have? How many valence electrons and energy levels does Tin have? How does the mass of Argon compare to Mercury? Why? How does the mass of Potassium compare to Copper? Why?