Naming Compounds
advertisement

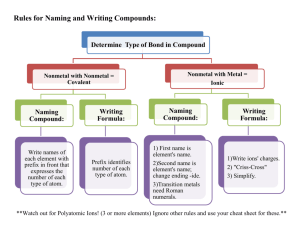
Naming Compounds and Writing Formulas Naming Compounds The chemical formula represents the composition of each molecule. In writing the chemical formula, in almost all cases the element farthest to the left of the periodic table is written first. So for example the chemical formula of a compound that contains one sulfur atom and six fluorine atoms is SF6. If the two elements are in the same period, the symbol of the element of that is lower in the group (i.e. heavier) is written first e.g. IF3. Naming Ionic Compounds Ionic compounds are combinations of positive and negative ions. In writing the chemical formula the positive ion is written first, It is then followed by the name of the negative ion. Monatomic anions end in ide. Special endings apply for polyatomic ions Examples NaCl Sodium chloride BaF2 Barium Fluoride ZnO Zinc Oxide Writing Formulas for Ionic Compounds Write the positive ion (cation) first, then the negative ion. The positive charges must balance the negative charges. Use subscripts to show how many times each ion must appear in order for the charges to balance. A subscript is not used if the ion appears only once Use parenthesis around polyatomic ions that appear more than once in the formula Examples 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Na+ Zn2+ K+ Ca2+ Fe2+ Fe3+ Ca2 + NH4+ NH4+ and Cland Brand OHand OHand SO42and SO42and PO43and Cland CO32- = NaCl = ZnBr2 = KOH = Ca(OH)2 = FeSO4 = Fe2(SO4) 3 = Ca3(PO4)2 = NH4Cl = (NH4)2CO3 Names of Polyatomic Ions with Oxygen Polyatomic ions usually contain oxygen in addition to another element. Normally they have a negative charge. They end in either "ate" or "ite" depending on the number of oxygen atoms present. ClO- hypochlorite ClO2ClO3- chlorite chlorate ClO4- perchlorate NO2- Nitrite NO3- Nitrate PO33- phosphite PO43- phosphate SO32SO42- sulfite sulfate Polyatomic Ion -- Exceptions Most polyatomic ions contain oxygen Their names end in “ite” or “ate”. There are several exceptions OHCNSCN- hydroxide cyanide thiocyanate Transition Metal Cations 1. 2. 3. 4. When an element can form more than one cation a Roman numeral is used to distinguish the oxidation state of the compound. Metals not in group I, II, and III are common elements with more than one cation. (Exceptions: silver, zinc, and cadmium) Examples PbSO4 = lead (II) sulfate This compound is formed from Pb2+ and SO42Pb(SO4)2 = lead (IV) sulfate This compound is formed from Pb4+ and SO42Fe(OH)2 = iron (II) hydroxide This compound is formed from Fe2+ and OHFe(OH)3 = iron (III) hydroxide This compound is formed from Fe3+ and OH- Molecular compounds • Two nonmetals or nonmetal + metalloid • element further left in periodic table is 1st • element closest to bottom of group is 1st • use prefixes to indicate number of each kind of atom • Add prefix to first element name to show how many of that element are present. (omit ‘mono’) • Add prefix to stem of last element name plus “-ide” 2.7 Naming Covalent Compounds Examples: SF6 – sulfur hexafluoride P4O10 – tetraphosphorous decoxide CO – carbon monoxide CO2 – carbon dioxide Binary compounds of Hydrogen The binary compounds of hydrogen are special cases. They were discovered before a convention was adopted and hence their original names have stayed. Water (H2O ) is not called dihydrogen monoxide Hydrogen forms binary compounds with almost all nonmetals except the noble gases. Examples HF - hydrogen fluoride HCl - hydrogen chloride H2S - hydrogen sulfide Molecular Compounds HI hydrogen iodide NF3 nitrogen trifluoride SO2 sulfur dioxide N2Cl4 dinitrogen tetrachloride NO2 nitrogen dioxide N2O dinitrogen monoxide TOXIC! Laughing Gas 2.7 An acid can be defined as a substance that yields hydrogen ions (H+) when dissolved in water. HCl •Pure substance, hydrogen chloride •Dissolved in water (H+ Cl-), hydrochloric acid An oxoacid is an acid that contains hydrogen, oxygen, and another element. HNO3 (aq) nitric acid H2CO3 (aq) carbonic acid H2SO4 (aq) sulfuric acid HNO3 2.7 Naming Acids Anion ending Acid Name -ide hydro______ic acid -ate ___________ic acid -ous ___________ous acid 2.7 Acids When many hydrogen compounds are dissolve in water they take on the form of an acid. Special rules apply to acids. The “ite” suffix becomes “ous” and the “ate” suffix becomes “ic” HCl Hydrochloric Acid Cl- Chloride HNO2 Nitrous Acid NO2- Nitrite HNO3 Nitric Acid NO3- Nitrate H2SO3 Sulfurous Acid SO32- Sulfite H2SO4 Sulfuric Acid SO42- Sulfate H3PO3 Phosphorous Acid PO33- Phosphite H3PO4 Phosphoric Acid PO43- Phosphate H2CO3 Carbonic Acid CO32- Carbonate Diatomic Molecules Certain elements exist as diatomic molecules in nature H2 Hydrogen N2 Nitrogen F2 Fluorine O2 Oxygen I2 Iodine Cl2 Chlorine Br2 Bromine