Feudalism & Manorialism
advertisement

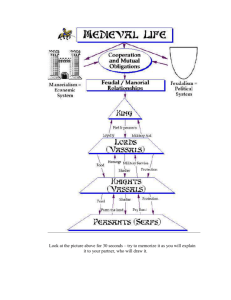
Ch. 10.2 Feudalism & Manorial System Bell Work: What would todays society be like today if there was a collapse of Central government? Components: Cornell Notes Daily Quiz Article Questions feudalism/Manorialism Class Notes Objective Review Feudalism System Kings Land (fief) Land, Armed Forces, Roads,Bridges, dams & Justices in disputes among vassals (Trial by combat) Fees, loyalty, Military support Lords Three feudal dues (ransom, Dowry, Knighthood )Fees, loyalty,Military support Vassals/ Knights Protection & Economic Security Fees, loyalty, labor, Help in defending the castle Serfs Feudal Relationships Overlord provided Vassals with: •Landed estates [FIEF] •Armed forces. ♦ Roads, bridges, dams. ♦ Justice in disputes among vassals [TRIAL BY COMBAT] Vassals Provide Overlord with: ♦ Allegiance [HOMAGE, FEALTY] ♦ Tributary money or goods. ♦ Military service and fighting men when summoned. ♦ Ceremonial duty. ♦ Three feudal dues; ransom, dowry, knighthood. ♦ Hospitality and entertainment on visits. Feudal Relationships Overlord / Vassals Provide Serfs with: ♦ Land to support peasant’s and/or serf’s livelihood. ♦ Military protection against invasion. ♦ Economic security against invasion. Serfs Provide Overlord / Vassal with: ♦ Payments in kind for use of arable land. ♦ Labor to the lord for tasks such as building roads, bridges and dams. ♦ Help in defending the castle in case of attack. ♦ Labor on the land farmed for the lord’s household [LORD’S DEMESNE, property] manage by Stewards Manorial System A Manor was an agricultural estate run by a Lord & worked by peasants. Free peasants existed. Serfs: peasants that were legally bound to the land. Serfs had to provide labor services, pay rents, & subject to the Lord’s control. (60%). Worked on a Cycle of Labor. • Paid the lord for the use of the manor’s common pastures, ponds, streams, woodlands. • Worked 3 days a week on the Lord’s land than on growing his own. • his land could not be taken away. • Could not leave the manor without the Lord’s permission. • Lived in cottages made of wood frames, sticks and rubble, plastered with clay. • Daily diet was adequate; mainly breads(Millet & oats), vegetables, cheese, nuts & berries, and eggs. Only ate meat on festival days. Wine & Ale. Peasant’s Wheel of Life The Knights Code of Chivalry A knight was expected to have not only the strength and skills to face combat in the Middle Ages but was also expected to temper this aggressive side of a warrior with a chivalrous side to his nature. There was one single Code of Chivalry - it was a moral system which went beyond rules of combat and introduced the concept of “Chivalrous conduct” or the qualities idealized by knighthood, such as bravery, courtesy, honor, and gallantry toward women. The Song of Roland was the most famous 'chanson de geste' (songs of heroic deeds) of the Middle Ages and was composed between 1098-1100 A.D. It describes the betrayal of Count Roland at the hand of Ganelon (his step-father), and his resulting death in the Pyranee Mountains at the hands of the Saracens (people who lived in the deserts of the Middle East). Roland was a loyal defender of the king and his code of conduct is a description of the meaning of chivalry: The Knights Code of Chivalry To fear God and maintain His Church To serve the liege* lord in valour and faith To protect the weak and defenceless To give succor (aid) to widows and orphans To refrain from the wanton giving of offence To live by honour and for glory To despise pecuniary (monetary) reward To fight for the welfare of all To obey those placed in authority To guard the honour of fellow knights To eschew (avoid) unfairness, meanness and deceit To keep faith At all times to speak the truth To persevere to the end in any enterprise begun To respect the honour of women Never to refuse a challenge from an equal Never to turn the back upon a foe *A lord or sovereign to whom allegiance and service are due according to feudal law 1. Of the seventeen entries in the Knights Codes of Chivalry, according to the Song of Roland, at least 12 relate to acts of chivalry as opposed to combat. Highlight those above with a magic marker Target/objective Review Target 10.2-Fuedalism & Manorialism SWBAT: Analyze the Political, Economic, and Codes of Europe during the Middle Ages. /5 Objective 1: Describe & Explain Feudalism as a political system and its loyalties. Objective 2: Describe the Manorial System as an Economic system & how it complements Fuedalism. Objective 3: Describe what life was like for serfs and for the nobility on the manor. Objective 4: Summarize the characteristics of the code of Chivalry. Ch 10.2 EXTENSION In table your table group, create a poster depicting Middle Ages Feudalism, Manorialism & Chivalry. Show how they compliment each other. Show as many vocabulary terms from section 2. Be sure to show loyalties, life of a serf/noble, economic system, & political system. Possible terms to show: Vassal fief manor serfs 3 field system chivalry