PowerPoint
advertisement

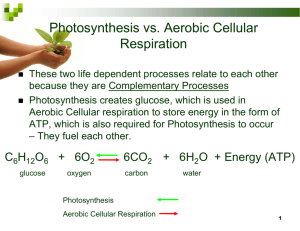
Marking Period 2 Quarterly Exam Review Mrs. Jackson 2015-2016 Cell Transport, Homeostasis, Photosynthesis, Cellular Respiration, Mitosis Cell Membrane O 1. Label the following parts of the cell membrane pictured below: hydrophilic (attracted to water) heads, hydrophobic (repelled by water) tails, membrane transport protein. O Hydrophilic head (polar) Hydrophobic tails (nonpolar) Membrane Transport Protein Cell Membrane O 2. How does this arrangement help the cell? O THIS ALLOWS THE CELL MEMBRANE TO BE SEMI-PERMEABLE, CONTROLLING THE MOVEMENT OF SUBSTANCES INTO AND OUT OF THE CELL. Cell Membrane O 3. Why do we call the cell membrane a fluid mosaic model? O The cell membrane is fluid like because the parts that are in it move like a fluid. O It is a mosaic because it has many molecules in it, like a mosaic tile piece of art. Cell Membrane O What is the purpose of the cell membrane? O Controls what moves in and out of the cell. Cell Transport Passive Transport Active Transport Conc. Gradient High to Low Low to HIgh Requires ATP No Yes Diffusion Yes No Osmosis Yes No Facilitated Diffusion Yes No Endocytosis No Yes Exocytosis No Yes Sodium Potassium Pump *Pump=think active! No Yes Cell Transport O 1. What is the main difference between passive & active transport? O Use of energy (active uses ATP energy, passive does not) Cell Transport O 2. Give an example of a molecule or gas that could easily diffuse into or out of a cell. Show a simple picture of diffusion of food coloring in a beaker of water. O Oxygen or Carbon Dioxide Cell Transport O Below is a picture of plant cells in either an isotonic, hypertonic, or hypotonic state. Circle the name of the state of osmosis for each cell, and circle the description as to why the water is moving in the direction it is moving in. Circle One: Isotonic, Hypertonic, Hypotonic Circle One: A. Water moves equally in and out because the solute concentration is equal inside the cell and outside the cell. B. Water moves out of the cell and the contents inside the cell shrink because there was more water in the cell than its surrounding environment. C. Water moves into the cell and the cell expands because there was more water in the surrounding environment than there was inside the cell. Circle One: Isotonic, Hypertonic, Hypotonic Circle One: A. Water moves equally in and out because the solute concentration is equal inside the cell and outside the cell. B. Water moves out of the cell and the contents inside the cell shrink because there was more water in the cell than its surrounding environment. C. Water moves into the cell and the cell expands because there was more water in the surrounding environment than there was inside the cell. Circle One: Isotonic, Hypertonic, Hypotonic Circle One: A. Water moves equally in and out because the solute concentration is equal inside the cell and outside the cell. B. Water moves out of the cell and the contents inside the cell shrink because there was more water in the cell than its surrounding environment. C. Water moves into the cell and the cell expands because there was more water in the surrounding environment than there was inside the cell. Cell Transport O 4. What is the same about facilitated diffusion and the sodium potassium pump? What is different? O Same: Both forms of transport use a special transport protein to move substances across the cell membrane. O Different: Facilitated Diffusion is passive transport, the Sodium Potassium Pump is active transport. Cell Transport Endocytosis Exocytosis Form of active transport Yes Yes Uses a vesicle Yes Yes Removes large waste No molecules to maintain homeostasis Yes Takes in large Yes nutrients to maintain homeostasis No Helps a cell to maintain homeostasis Yes Yes Cell Transport O 6. Where are cellular protein receptors found and how do they help with cell transport? O They are found in the cell membrane. O A receptor is a protein that detects a signal molecule and performs an action in response. O Signal molecules include hormones, etc. Homeostasis O 7. What is homeostasis? O Homeostasis is when an organism is able to maintain a stable internal environment even when external conditions change. Homeostasis O 8. How does our body maintain homeostasis through thermoregulation when our body temperature is too hot? O Sweating. Thermoregulation is maintaining your proper temperature. This is a negative feedback loop. If we are too hot, our cells will not function properly. Homeostasis O 9. How does our body maintain homeostasis through thermoregulation when our body temperature is too cold? O We shiver. Hypothermia is when your body loses heat faster than it can produce it. Our muscle cells shiver to try and create more heat to warm us up. Cell Energy O What is the purpose of photosynthesis? What organelle is responsible for photosynthesis? O Purpose: transform light energy into chemical energy (glucose). O Organelle: chloroplast. Cell Energy O What are the energy changes/transformations that happen in photosynthesis? O Light to Chemical Energy Cell Energy O The light dependent reactions occur in the thylakoids of the chloroplast. What molecule that is located in the thylakoid’s absorbs the sun’s energy? O Chlorophyll Cell Energy O What is the purpose of cellular respiration? What organelle is responsible for producing the energy in cellular respiration? O The purpose of cellular respiration is to change/release chemical energy (food/glucose) into useable energy (ATP) for cellular work/activities. O Organelle: mitochondria Cell Energy O What are the energy changes/transformations that happen in cellular respiration? O Chemical Energy (glucose) to Chemical Energy (ATP). Cell Energy O What is ATP used for in living things? O Carries usable energy for the cell O It is used by cells so that cells do their “work” Cell Energy O Draw a diagram showing how energy is released from an ATP molecule when we “use” energy O Energy is “used” or released from ATP when a phosphate group is removed (becomes ADP) phosphate removed Cell Energy O Draw a diagram showing how energy is stored when ADP is converted into ATP. O Energy is stored when a phosphate group is added to ADP to make ATP. phosphate removed Cell Energy O What types of cells go through photosynthesis O Some prokaryotes (bacteria) & Some Eukaryotes (Plants, algae) Cell Energy O What types of cells go through cellular respiration? O All living things go through at least parts of cellular respiration (Both Prokaryotes & Eukaryotes). Cell Energy O What are the reactants of photosynthesis? The products? Cell Energy O What are the reactants of cellular respiration? The products? O Reactants: glucose, oxygen O Products: ATP, carbon dioxide, water Cell Energy O Refer to your previous two answers: How do photosynthesis and cellular respiration form a cycle? Cell Energy O What is similar about the energy transfers in photosynthesis and cellular respiration? O Both processes store energy in chemical bonds. Mitosis O What does G1 stand for, what happens to a cell in G1? O Gap One O The cell grows, replicates its organelles, performs normal functions. Mitosis O What does S stand for, what happens to a cell in S? O Synthesis O DNA is replicated (copied) Mitosis O What does G2 stand for, what happens to a cell in G2? O Gap Two O The cell grows more and goes through a final checkpoint. Mitosis O What three parts make up Interphase? O Gap One O Synthesis O Gap Two Mitosis O What does M in M Phase stand for, what happens to a cell in M? O M stands for Mitosis O Cell division occurs – O Mitosis & Cytokinesis Mitosis O What is the second part of the M phase before a cell goes back into Interphase? O Cytokinesis (cytoplasm splits) Mitosis O Why are there 2 genetically identical cells drawn after cytokinesis? O Mitosis produces 2 genetically identical cells after one round of PMAT. Mitosis O Why does cytokinesis need to happen? O Because the cell would be too large if it didn’t split and there would be one cell with 2 identical nuclei and too many chromosomes. Mitosis O An organism has 36 chromosomes in each somatic cell .If the organism’s cell goes through mitosis, how many chromosomes will be in each somatic cell? O 36 36 36 36