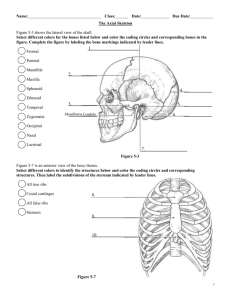
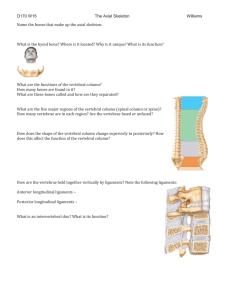
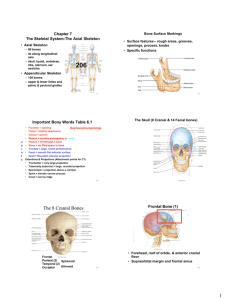
Transverse processes
advertisement

Human anatomy SHANDONG UNIVERSITY Liu Zhiyu Special techniques X-rays radiograph MRI scan of head in sagittal plane. MR scan showing an enhancing mass which is a meningioma growing from the meninges at the edge of the foramen magnum. The tumour is benign but is causing compression of the brain stem and secondary hydrocephalus. Examination Identify 20 structures (30 marks) Written examination 35 single-choice questions (35 marks) 15 multi-choice questions (15 marks) 4 short answer questions (20marks) Descriptive anatomical terms The anatomical position: The body is upright, legs together, and directed forwards. The palms are turned forward, with the thumbs laterally. The terms of the direction superior (cranial ) inferior (caudal ) Anterior (ventral ) Posterior (dorsal ) medial lateral internal external superficial profound proximal distal The terms of the direction ulnar radial tibial fibular left right vertical horizontal central unilateral bilateral contralateral homolateral Anatomical axes and planes Axis : Vertical axis Sagittal axis Coronal axis Anatomical axes and planes Plane: Sagittal plane Coronal plane Horizontal plane or transverse plane Planes of the Body Fig 2.8 Sagittal Frontal Transverse Abbreviations of terms a., aa. artery, arteries ant. anterior f. fibre or fiber inf. inferior lig. ligament ln. lymph node m., mm. muscle, muscles n., nn. nerve, nerves post. posterior sup. superior v. vein The Locomotor System Composed Bones Joints Muscles Major function Support Protection Locomotion Introduction of the osteology Classification of bone Bones in adult are 206 in number. Bones are classified according to their position and shape. The position can be: skull bones of trunk appendicular skeleton Types of shape include: 1. long bone 2. short bone 3. flat bone 4. irregular bone Introduction of the osteology 1. Long bones (found in limbs): Diaphysis or shaft , which is hollow (medullary cavity ,filled with bone marrow Two ends-epiphysis Articular surface Metaphysis Epiphysial cartilage Epiphysial line 2. Short bones: cuboidal in shape, e.g. carpal bones Introduction of the osteology 3. Flat bones: thin, 4. Irregular bones: have any irregular or mixed shape, e.g. vertebrae, pneumatic bones * Sesamoid bones develop within tendon General structures of bone Bony substance Periosteum Bone marrow General structures of bone 1. Bony substance compact bone spongy bone Trabeculae General structures of bone ※In the flat bones of the skull, the layers of compact bone are called the outer plate ,and inner plate , while the layer of spongy bone is called the diploë General structures of bone 2. Periosteum : Outer or fibrous layer Inner layer is vascular and provides the underlying bone with nutrition. It also contains osteoblasts Endosteum is a single-cellular osteogenic layer lining the inner surface of bone. 3. Bone marrow Red marrow :haematopoietic 造血 Yellow marrow: fatty Chemical composition and physical properties Organic material :the main one is collagen gives the bones resilience and toughness Inorganic salts : the main one is calcium phosphate give the bones hardness and rigidity Organic material Inorganic salts Children 1 1 Adult 3 7 Old 1 4 Ⅰ. Bones of trunk Composition: Vertebrae Sacrum Coccyx Sternum Ribs 1. Vertebrae There are 33 vertebrae in children, arranged as follows: Cervical vertebrae C. 7 Thoracic vertebrae T. 12 Lumbar vertebrae L. 5 Sacral vertebrae S. 5 →sacrum Coccygeal vertebrae Co.3-4 →coccyx 1)General features of vertebra Vertebral body Vertebral arch pedicle of vertebral arch : sup. and inf. vertebral notch lamina of vertebral arch process (7): spinous process transverse process sup. and inf. articular processes Vertebral foramen Vertebral canal Intervertebral foramen 2)Regional variations of vertebrae (1)Thoracic vertebrae Vertebrae Body : heart-shape, superior and inferior costal fovea Vertebral foramen: smaller, rounder Spinous processes: long, point obliquely downward Transverse processes: transverse costal fovea Articular processes: coronal (2)Cervical vertebrae Vertebrae Body: small uncus of vertebral body Vertebral foramen: large and triangular in shape Spinous processes: short and bifid in C3 to C5, long in C6, and longer in C7 Transverse processes: short and bifid, transverse foramen Articular processes: horizontal Atypical vertebeae Atlas (C1) Body and spinous process absent consists of anterior and posterior arches, and two lateral masses Groove for vertebral artery Atypical vertebeae Axis (C2): Distinguished by dens Which articulates with dental fovea of anterior arch of atlas Atypical vertebeae Carotid tubercle: anterior tubercle of transverse process of C6 Vertebra prominens (C7):contains long and non-bifid spinous process, it is visible with neck flexed, used as clinical landmark in counting cervical and thoracic spinous processes (3)Lumbar vertebrae Vertebrae Body: larger, kidney-shape Vertebral foramen: larger and triangular Spinous processes: projects horizontally Transverse processes: long Articular processes: sagittal Regional variations of vertebrae Cervical vertebrae Thoracic vertebrae Lumber vertebrae Body Small Heart-shape, have superior and inferior costal fovea for rib heads Larger, kidney-shape Vertebral foramen Larger and triangular Smaller, rounder Larger and triangular Spinous processes Short and bifid in C3 to C5, long in C6,and longer in C7 Long, point obliquely downward Projects horizontally Transverse processes Short and bifid, transverse foramen Have transverse costal fovea for rib tubercles Long Articular processes Horizontal Coronal Sagittal (4)Sacrum Anterior surface: Posterior surface: Promontory anterior sacral foramina (four pairs) median sacral crest posterior sacral foramina (four pairs) sacral canal sacral hiatus sacral cornu Lateral part: auricular surface sacral tuberosity Cornua Sacral hiatus palpation caudal anaesthesia 2. Sternum Manubrium sterni Body of sternum jugular notch clavicular notch Costal notches Xiphoid process 2. Sternum ★ Sternal angle : the junction of manubrium and body which connects 2nd costal cartilage laterally lies opposite lower border of T4 posteriorly 3. Ribs General features 12 pair Ribs 1~7 called true ribs Ribs 8~10 called false ribs Ribs 11~12 called floating ribs 1)Characteristics of “typical” rib Posterior end Shaft costal head costal neck costal tubercle costal angle costal groove Anterior end Atypical rib First rib: tubercle for scalenus anterior sulcus for subclavian vein and artery 11th and 12th ribs lack costal necks, tubercles and angles You must identify follow structures! Vertebral body Vertebral arch pedicle of vertebral arch sup. and inf. vertebral notch lamina of vertebral arch spinous process transverse process sup. and inf. articular processes Vertebral foramen Intervertebral foramen superior and inferior costal fovea transverse costal fovea transverse foramen Atlas Groove for vertebral artery Promontory anterior sacral foramina median sacral crest posterior sacral foramina You must identify follow structures! sacral canal sacral hiatus sacral cornu auricular surface sacral tuberosity Manubrium sterni jugular notch clavicular notch Body of sternum Xiphoid process Sternal angle costal head costal neck costal tubercle costal angle costal groove