The 8 Cranial Bones
advertisement

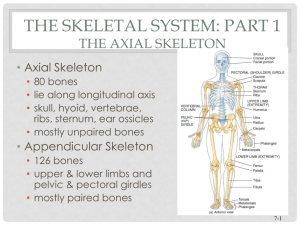
Chapter 7 The Skeletal System:The Axial Skeleton • Axial Skeleton – 80 bones – lie along longitudinal axis – skull, hyoid, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, ear ossicles Bone Surface Markings • Surface features-- rough areas, grooves, openings, process, knobs • Specific functions 206 • Appendicular Skeleton – 126 bones – upper & lower limbs and pelvic & pectoral girdles 7-1 The Skull (8 Cranial & 14 Facial bones) Important Bony Words Table 6.1 J o i n t s 7-2 • Foramen = opening Depressions/openings • Fossa = shallow depression • Sulcus = groove • Meatus = tubelike passageway or canal • Fissure = slit through a bone • Sinus = air filled space in bone • Condyle = large, round protuberance • Facet = smooth flat articular surface • Head = Rounded articular projection Extentions & Projections (Attachment points for CT) • Trochanter = very large projection • Tuberosity (tubercle) = large, rounded projection • Epicondyle = projection above a condyle • Spine = slender narrow process • Crest = narrow ridge 7-3 Frontal Bone (1) The 8 Cranial Bones Frontal Parietal (2) Sphenoid Temporal (2) Ethmoid Occipital 7-4 • Forehead, roof of orbits, & anterior cranial floor • Supraorbital margin and frontal sinus 7-5 7-6 1 Temporal Bones (4 & 5) Parietal (2 & 3) • Temporal bone: – zygomatic process forms part of arch – external auditory meatus – mastoid process – mandibular fossa – Styloid process • Parietal – sides & roof of cranial cavity 7-7 Occipital bone (6) 7-8 Sphenoid bone (7) • Occipital bone • foramen magnum • occipital condyles • External occipital protuberance • superior & inferior nuchal lines • At base of skull • Pterygoid processes 7-9 7-10 Sphenoid from Superior View • Lesser wing & greater wing 7-11 7-12 2 Ethmoid Bone (8) Ethmoid bone • Contain sinuses • Superior & middle nasal concha or turbinates Perpendicular plate is upper part of nasal septum • Anterior cranial floor, medial wall of orbits, lateral nasal walls & superior nasal septum 7-13 7-14 Sutures = immovable joints • • • • Coronal suture: unites frontal and both parietal bones Squamous suture: unites parietal and temporal bones Lamboid suture: unites parietal and occipital bones Sagittal suture: unites parietal bones 7-15 7-16 14 Facial Bones Zygomatic Process of Temporal bone Nasal (2) Maxillae (2) Mandible (1) Lacrimal (2) Inferior nasal conchae (2) Zygomatic (2) Palatine (2) Vomer (1) 7-17 Temporal Process of Zygomatic bone 7-18 3 Nasal Mandible (1) • • • • Condylar process (mandibular condyle) Coronoid processes Alveolar processes for lower teeth Mandibular & mental foramen 7-19 7-20 Details of the orbit (eye socket) Paranasal Sinuses • Paired cavities in ethmoid, sphenoid, frontal and maxillary • Lined with mucous membranes and open into nasal cavity 7-21 7-22 Paranasal Sinuses Cranial fossa On floor of cranial cavity • Resonating chambers, lighten skull • Sinusitis Bless you 7-23 7-24 4 Hyoid Bone Vertebral Column • Backbone or spine built of 26 vertebrae • Five vertebral regions – cervical vertebrae (7) in the neck – thoracic vertebrae ( 12 ) in the thorax – lumbar vertebrae ( 5 ) in the low back region – sacrum (5-fused) – coccyx (4-fused) 7-25 7-26 Typical Vertebrae: 3 Bony Parts Intervertebral Discs (process) • absorbs vertical shock • Permit movement of V. column • Fibrocartilagenous ring with a pulpy center 1. Body – weight bearing 2. Vertebral arch – pedicles – laminae • Vertebral foramen 3. Processes (7) – 2 transverse – 1 spinous – 4 articular 7-27 Intervertebral Foramen & Spinal Canal 7-28 Cervical Vertebrae (C1-C7) • 1st and 2nd cervical vertebrae are unique – atlas & axis • Spinal canal = all vertebral foramen together • Intervertebral foramen are 2 vertebral notches together 7-29 7-30 5 Atlas & Axis (C1-C2) Cervical Vertebrae (C1-C7) • • • • C3 – C7 Smaller Larger canal Transverse processes shorter - transverse foramen for vertebral artery • Bifid spinous process • Atlas -- ring of bone, superior facets for occipital condyles – nodding movement “yes” • Axis -- pivotal movement “no” 7-31 7-32 Lumbar Vertebrae L1 - L5 Thoracic Vertebrae (T1-T12) • Strongest & largest • Short thick spinous & transverse processes – back musculature • Longer transverse & spinous processes • Facets or demifacets on body for head of rib • Facets on transverse processes (T1-T10) for tubercle of rib 7-33 7-34 Coccyx Sacrum • Union of 4 vertebrae (Co1 - Co4) by age 30 • Union of 5 vertebrae (S1 - S5) by age 30 7-35 7-36 6 Normal Curves of the Vertebral Column Abnormal curves of the vertebral column 7-37 7-38 Thorax – The Chest Thoracic Cage: Thorax – The Chest – Bony cage flattened from front to back 1. Sternum (breastbone) 2. Ribs 3. Costal cartilages 4. Thoracic vertebrae. Ribs – 1-7 are true ribs (vertebrosternal) – 8-12 are false ribs 8-10 vertebrochondral – 11-12 are floating 7-39 Sternum 7-40 Ribs • Manubrium 1st & 2nd ribs clavicular notch • Body Costal cartilages of 2-10 ribs • Xiphoid process 7-41 • Increase in length from ribs 1-7, thereafter decreasing • Head and tubercle articulate with facets Intercostal spaces contain intercostal muscles 7-42 7 Rib Articulation • Tubercle articulates with transverse process • Head articulates with vertebral bodies 7-43 8