The Knee Joint
advertisement
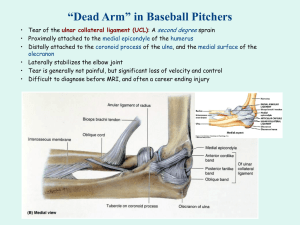
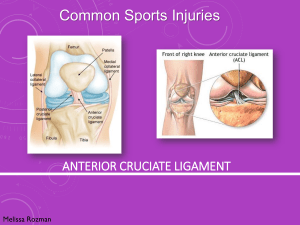
**Longest and heaviest bone in the body** **Large, weight bearing (shin bone)** **The patella provides leverage for the quadriceps muscles by placing the tendon anterior to the joint’s axis. This creates a mechanical advantage** *ACL- anterior cruciate ligament *PCL- posterior cruciate ligament prepatellar suprapatellar A flattened sac containing a lubricating fluid that reduces friction between two moving structures in the body, as a tendon and a bone. deep infrapatellar subcutaneous infrapatellar Thick fibrous band from apex of patella to tibial tuberosity Also called the patellar tendon Patellar ligament **Allows the menisci to move together during knee movements** Clinical Concern: ACL Women are 4 to 6 times more likely to suffer an ACL injury than men (playing the same sport) Numerous theories include social factors, hormonal factors, differences in quadriceps/hamstring strength, anatomical differences in LE, and biomechanical differences while running and jumping. Clinical Concern: ACL ACL repairs are made with grafts: 1. Autograft- using a tendon from your own body (patellar, hamstring) 2. Allograft- tendon from a cadaver Recovery ranges from 4 to 12 months, depends on a lot of factors (age, health status) Arthroscopic surgery is most common, although some surgeons perform open surgery with a larger incision. Origin Medial and lateral condyles of femur Insertion Posterior Calcaneus Action flex knee Innervation Tibial nerve Vascular supply Popliteal artery *See pg. 361 and 365 Essential of clinical anatomy for additional pictures