NervousSystemGuidedNotes
advertisement

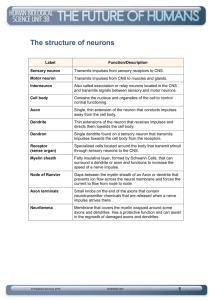
Name: ______________________________________ Date: ______________ Teacher: ____________________________________ Section: ____________ The Nervous System LG: ____________________________________________________________________________________________ Regulation-any activity that helps the body maintain ______________________________. –Controls and ____________________________ life ____________________________. Includes ___________________________& _______________________________ systems. Nervous System- system of specialized cells to _____________________ ______________________ throughout the body. Impulses are sent by ____________________to and from the CNS (_____________________________________________). Main Organs 1-Brain 2-Spinal Cord. Stimuli Receptors Responses: Stimuli= anything (internal/external) that causes _____________________. Ex: ________________________ Receptors= Structures on the ___________________________ that detect __________________________. Ex: _____________________________________. Shapes matters! Enzymes are very specific and only work with _________________________________________________________. Neurons: Specialized cells that carry _____________________________________ impulses. You are born with most of the neurons ________________________________. They are not replaced when they die!! Neuron Structure: 3 Main Parts-1)Cell Body (_________________) Contains nucleus and _____________________. Metabolism such as ________________________________________. 2)Dendrites: Short branch extensions receives _______________________ from other _________________ or _______________________. Send them ____________________ the cell body. 3) Axon: Long fiber sends impulses __________________ from the cell body to __________________________________. Myelin Sheaths- insulating layers form ______________________________ Function: Allow impulses to ______________________________. Schwann Cells-________________________________ Node of Ranvier (__________)Gaps between adjacent Schwann cells. Function: Allow nerve impulses to move along the _____________________ efficiently. Types of Neurons 1)Sensory or Afferent Neuron (Organs _____________) Moving away from a central organ or point. __________________________________ from receptors to the brain or _______________________________. 2) Motor or Efferent Neuron(Brain muscle) Moving toward a _____________________________or point. Relays messages from the ________________________________ to the ______________________________________. 3)Interneuron: Relay message from ______________________________ to motor neuron. Make up ____________________________________________. Neuron Communication- Synapse: the space between __________________________. One end of a neuron secretes ________________________________________________that travel across this space thus carrying ________________ from cell to cell. Neurotransmitters (NTs)- Chemical ___________________________________ The process represented in the diagram best illustrates (1) cellular communication (2) muscle contraction (3) extraction of energy from nutrients (4) waste disposal Drugs & Poisons Stimulants-Speed up __________________________and __________________ of ___________________________ Caffeine-increases ____________________________________________________. Causes _____________________ and _________________________________. Depressants-Block formation of _____________________________. Barbiturates produce ____________________________________. Ex: _______________________________________ Brain has 2 Hemispheres-Each side of the brain is _______________________________. Each hemisphere contains 4 different ___________________. Frontal Lobe Functions & Actions-Memory formation, ____________________, decision making/reasoning, _________________________. Critical Regions of the F.L.-Primary Motor Cortex (_______________________________)-involved with controlling ___________________________ of the body. Broca’s Area- Controls facial neurons, ________________ and ___________________ comprehension. Located on ________ ______________________________. Olfactory Bulb (___________________)-Cranial Nerve 1, responsible for __________________________________. Parietal Lobe FunctionsSenses, spatial awareness and perception. Primary Gustatory Cortex=the sensation of _____________. Occipital Lobe- The processing, ________________________, interpretation of vision and ________________________________. Temporal Lobehearing, language comprehension, memory ___________________/_____________________. Cortical Regions: Primary Auditory Cortex-responsible for ____________________________. Primary Olfactory Cortex-interprets the __________________________________ once it reaches the ________________ via the ___________________________________________. Wernicke’s Area-Language comprehension. Located __________________________________. Meningitis-Viral or bacterial disease that infects fluid surrounding brain and spinal cord. Symptoms__________________________________________________________________________________________________ Cerebral Palsy Causes Treatment