Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
advertisement

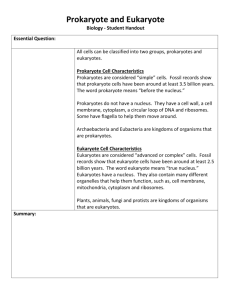
Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes (pg.21/23) MUST WRITE EVERYTHING ON SLIDES! NO COMPLAINING PLEASE. JUST DO IT What is a the basic definition of a prokaryotic cell? Small, single-celled, organism that has no nucleus and no other specialized organelles What is the meaning of “pro-” and “karyo-”? Pro- means before Karyo- means nucleus of a cell So prokaryote=before the nucleus (no nucleus) What specialized structures are present in prokaryotic cells? Cell wall Cell membrane Cytoplasm Ribosomes Genetic material Flagella or cilia What are examples of prokaryotic cells? Eubacteria Archaebacteria How do prokaryotic cells reproduce? Binary fission. The two cells are genetically identical. What are some ways that prokaryotic cells obtain energy? Photosynthesis (light) Chemosynthesis (inorganic compounds) Digesting other organisms. REVIEW of Prokaryotes – What are they? Single-celled organisms with no nucleus Have no specialized organelles Usually have: cell wall, cell membrane, ribosomes, genetic material, cytoplasm, and flagella or cilia Examples: eubacteria and archaebacteria Reproduce through binary fission Get energy through photosynthesis, chemosynthesis, (inorganic chemicals) or digesting other organisms What is the basic definition of a eukaryotic cell? Has a nucleus and other membrane- bound organelles What is the meaning of “eu-” and “karyo”? Eu- means good, well, or true Karyo- means nucleus of a cell So a eukaryote has a true nucleus What specialized structures are present in eukaryotic cells? ALWAYS have a membrane-bound nucleus Other membrane-bound organelles such as: Chloroplasts Golgi apparatus/Golgi body Lysosomes Mitochondrion Plastids Rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER) Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (ER) Vacuoles Vesicles What are examples of eukaryotic cells? Plants Animals Fungi Protists How do eukaryotic cells reproduce? Mitosis (genetically identical) or Meiosis (genetically unique) How do eukaryotic cells obtain energy? Photosynthesis Digesting organic compounds. Review of Eukaryotes – What are they? Cells with a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles that perform special functions Always have a nucleus May also have: chloroplasts, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, mitochondrion, plastids, rough endoplasmic reticulum, smooth endoplasmic reticulum, vacuoles, and vesicles Examples: fungi, protists, plant and animal cells Reproduce by mitosis or meiosis Get energy through photosynthesis or by digesting other organisms. Prokaryote or Eukaryote? Prokaryote or Eukaryote? Prokaryote or Eukaryote? Prokaryote or Eukaryote? Prokaryote or Eukaryote? Prokaryote or Eukaryote? Prokaryote or Eukaryote? Prokaryote or Eukaryote?