Atomic Structure II

Atomic Structure II
Electron Configurations
Barbara A. Gage PGCC CHM 1010
Atomic Orbitals
• Each electron is assigned to:
Primary energy level (shell), n
Orbital type in the shell (s,p,d,f)
Specific orbital of the type
Because of repulsion considerations only 2 electrons can occupy any orbital
(spinning in opposite directions)
Barbara A. Gage PGCC CHM 1010
Atomic Shells and Orbitals
Shell
(n)
# s orbitals
# p orbitals
# d orbitals
# f orbitals
Total e -
1
2
3
4
5
1
1
1
1
1
3
3
3
3
5
5
5
7
7
2
8
18
32
50
Barbara A. Gage PGCC CHM 1010
Barbara A. Gage PGCC CHM 1010
This diagram shows the energy levels of the atomic orbitals.
Electrons fill orbitals from bottom to top of the diagram.
A vertical orbital diagram for the Li ground state.
no color-empty light - half-filled
The electron configuration is written as:
1s 2 2s 1 # electrons in orbital dark - filled, spin-paired shell orbital
Barbara A. Gage PGCC CHM 1010
Barbara A. Gage PGCC CHM 1010
Barbara A. Gage PGCC CHM 1010
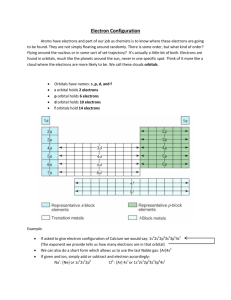
You can use a chart like this to determine the electron configuration.
(But there is an easier way.)
Barbara A. Gage PGCC CHM 1010
A periodic table of partial ground-state electron configurations.
Barbara A. Gage PGCC CHM 1010
Determining Electron Configuration
PROBLEM: Using the periodic table on the inside cover of the text (not
Figure 8.12 or Table 8.4), give the full and condensed electrons configurations, partial orbital diagrams showing valence electrons, and number of inner electrons for the following elements:
(a) potassium (K: Z = 19) (b) molybdenum (Mo: Z = 42) (c) lead (Pb: Z = 82)
SOLUTION:
Use the atomic number for the number of electrons and the periodic table for the order of filling for electron orbitals.
Condensed configurations consist of the preceding noble gas and outer electrons.
(a) for K (Z = 19) full configuration partial orbital diagram
1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 1 condensed configuration [Ar] 4s 1
There are 18 inner electrons.
4s 1 3d
Barbara A. Gage PGCC CHM 1010
4p
(b) for Mo (Z = 42) full configuration 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 10 4p 6 5s 1 4d 5 condensed configuration partial orbital diagram
[Kr] 5s 1 4d 5
There are 36 inner electrons and 6 valence electrons.
5s 1 4d 5 5p
(c) for Pb (Z = 82) full configuration 1s
2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 10 4p 6 5s 2 4d 10 5p 6 6s 2 4f 14 5d 10 6p 2 condensed configuration partial orbital diagram
[Xe] 6s 2 4f 14 5d 10 6p 2
There are 78 inner electrons and 4 valence electrons.
6s 2 6p 2
Barbara A. Gage PGCC CHM 1010
Configuration for Ions
• What is the electron configuration for
Na + ?
Na = 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 1
Na + = 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 1
• What is the electron configuration for
Se 2?
Se = 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 10 4p 4
Se 2= 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 10 4p 6
Barbara A. Gage PGCC CHM 1010
Configuration for Ions
• Transitions metals have a twist…
Fe = 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 6
Fe 2+ = 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 6
Fe 3+ = 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 5
Barbara A. Gage PGCC CHM 1010