Power Point - Science Olympiad

BIO-PROCESS LAB (B)
2016
KAREN LANCOUR
National Committee Chair-Life Science
Bio-Process Lab National Supervisor karenlancour@charter.net
Event Rules – 2016
DISCLAIMER
This presentation was prepared using draft rules. There may be some changes in the final copy of the rules .
The rules which will be in your Coaches Manual and
Student Manuals will be the official rules.
Event Rules – 2015
BE SURE TO CHECK THE 2016
EVENT RULES FOR EVENT
PARAMETERS AND TOPICS
FOR EACH COMPETITION
LEVEL
TRAINING MATERIALS
Training Power Point – content overview
Training Handout - content information and needed skille
Practice Activities - sample stations with key
Sample Tournaments – sample problems with key
Event Supervisor Guide – prep tips, event needs, and scoring tips
Internet Resource & Training CD’s – on the Science Olympiad website at www.soinc.org
under Event Information
Biology-Earth Science CD , Bio-Process Lab CD (updated 2015) in Science Olympiad Store at www.soinc.org
Biology lab manuals – identify variables and evaluate the labs
– become familiar with typical bio labs
Bio-Process Lab (B)
Event Description lab-oriented competition involving the fundamental science processes of a middle school biology lab program
Event – lab practical in stations
Event Parameters – be sure to check the rules for resources allowed, type of goggles needed.
Basic Science Process Skills
Observing
Measuring
Inferring
Classifying
Predicting
Communicating
Integrated Science Process Skills
Formulating Hypothesis
Identifying Variables
Defining Variables Operationally
Describing Relationships Between Variables
Designing Investigations
Experimenting
Acquiring Data
Analyzing Investigations and Their Data
Understanding Cause and Effect
Relationships
Formulating Models
GAME PLAN
USE THE POWERPOINT FOR OVERVIEW
USE THE HANDOUT FOR DETAIL OF INFORMATION NEEDED
AND TYPE OF QUESTIONS
GO TO THE INTERNET RESOURCES AND CD’S FOR MORE HELP
DO THE PRACTICE ACTIVITIES TO MASTER SKILLS
DO THE SAMPLE TOURNAMENTS UNDER TIMED CONDITIONS
TO EXPERIENCE COMPETITION SITUATION
DO OLD TOURAMENTS– PRACTICE, PRACTICE, PRACTICE
THE KEY TO SUCCESS – THE BEST WAY TO LEARN THE SKILLS
IS BY DOING
Student Preparation
Team work skills – work as a team
Many mistakes are made when work is split to save time – results in many errors
Time limits – invest in a timer and practice using it
Check station setups – to see what is available to help you
Answering questions – see student preparation guide
Be sure to read questions and do all parts requested
Measurement and Calculations – check graduations and remember units
Reference materials – make them functional for competition under timed conditions
Practice, Practice, Practice using the skills you have learned
Compound Microscope
Parts
Making wet mount
Appearance of objects
Movement of objects
Magnification
Changing objects
Estimating size of objects
Field diameter & area
Principles of Microscopy
Measuring Objects under
Microscope
Sample Station –
Microscopy
Determine the diameter of the field and the length of one cell in mm and convert to mcm.
Stereomicroscope
Parts
Appearance of objects
Magnification
Advantages
Uses
Observing objects
Examining Instrument
Graduations Before Measuring
• Capacity - highest it will read – starts at zero
• Range if does not start at zero as thermometer
• Numbered Increments (graduations)
• Unnumbered Increment (graduations)
MANY ERRORS ARE MADE BECAUSE STUDENTS DO NOT
EXAMINE THE GRADUATIONS BEFORE MEASURING !!!!!
Measuring Liquids
Meniscus – read bottom
Capacity and Range
Graduations – numbered and unnumbered increments
Readability
Making measurements
Estimating
Metric ruler and calipers
Capacity and Range
Numbered and unnumbered increments cm vs mm
Uses of each
Making measurements
Estimating
Vernier Scale
Thermometers
Capacity and Range
Do not start at zero
Numbered and unnumbered increments
Uses of each
Making measurements
Estimating
Sample Station -
Measurement
Identify range, capacity, incrementation
Do measurement – estimate last digit
Triple Beam Balance with
Weights
• Expands capacity of the balance from 610g to 2610 grams
• 2 weight equivalent to 1000 g and 1 weight equivalent to 500 g
• Actual mass of weight is listed on the top of the weight.
Triple Beam Balance
Capacity – auxillary weights
Units – numbered and unnumbered increments
Tare
Using the Balance
Advantages &
Disadvantages
Electronic Balance
Capacity
Units
Tare or Zero
Err
Using the Balance
Advantages &
Disadvantages
Probes
Graphing calculator
Easy link or CBL
Probe
Collect data onto calculator
Transfer data to computer
Graph analysis
Quick data collection
Sample Station – pH
Determine the pH of various solutions using either pH probe or pH test papers.
Data Presentation and
Analysis- Data Tables
Format
Title
Units of measurement
Numbering
Tables
Source
Leg (thigh)
Length (cm)
24
31
37
38
39
42
55
62
Time of 40 yard dash (sec)
9
9.2
11
10
8.2
8.4
9.3
9
Data Presentation and Analysis-
Graphs
Graph – types
X vs Y axis
Scaling axis
Plotting points
Human Error
Curve or best fit line
Labeling
Sample Stations –
Population Density
Measure sample area
Determine population density for symbols
Assign an organism to symbols
Form a food chain
Evaluate sample – predict techniques, etc.
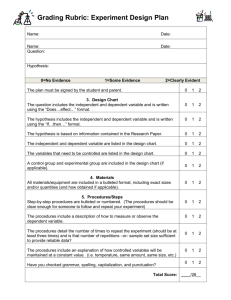
Experimental Analysis
Identify variables
Examine procedure – will it evaluate allow the hypothesis to be tested?
Evaluate observations to understand what happened and why
Analyze data and identify errors
Determine if the hypothesis is true – if false what was not considered?
Propose further testing or new hypothesis
Sample Station –
Experiment Analysis
Analyze the design of the experiment
Identify variables
Explain results – form conclusions
Data Analysis
Use observations to understand what happened during the experiment
Look for possible types errors
Look for patterns in the data
Do data analysis as mean, median, mode
Examine group vs. class results data
Use data to evaluate hypothesis
Sample Station –
Data Analysis
Making hypotheses
Food web analysis
Eating habit analysis
Predictions and conclusions
Inferences
Human Mistakes vs.
Experimental Errors
Human Mistakes – carelessness
Experimental Error – instrument variation or technique
Random Error – chance variation
Systematic Error – system used for designing or conducting experiment
A Sample Dichotomous Key
1. wings covered by an exoskeleton . . . . . . go to step 2
1. wings not covered by an exoskeleton. . . . go to step 3
2 body has a round shape. . . . . . . . ladybug
2 body has an elongated shape. . . . . .grasshopper
3.wings point out from the side of the body . . dragonfly
3 wings point to the posterior of the body.. . . . Housefly
Note: There should be one less step than the total number of organisms to be identified in your dichotomous key.
Sample Station –
Dichotomous Key
Have specimens of leaves
Formulate a key or use a key to identify specimens
Key to Success in
Bio-Process Lab
Learn the Skills – using Practice Activities
Practice under Timed Conditions
Work as a Team – saves time and catches errors
Pay attention to details – avoid silly mistakes
Relax and let the competition show you how much you have learned
Have fun !!!