File
advertisement

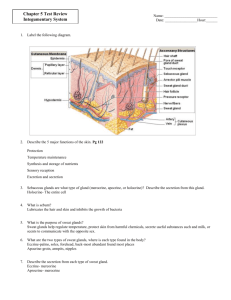
Ch 5: Integumentary System (SKIN) • • Consists of two distinct regions – Epidermis—superficial region – Dermis—underlies epidermis Hypodermis (superficial fascia) • • Epidermis – • • Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium Four or five distinct layers – Stratum basale – Stratum spinosum – Stratum granulosum – Stratum lucidum (only in thick skin) – Stratum corneum Four cell types – Keratinocytes – – Melanocytes – – Dendritic (langerhans) cells – – Tactile (merkel) cells – • • • • Layers of the Epidermis: Stratum Basale (Basal Layer) • Layers of the Epidermis: Stratum Spinosum (Prickly Layer) • • • • • Layers of the Epidermis: Stratum Granulosum (Granular Layer) • • • • Layers of the Epidermis: Stratum Lucidum (Clear Layer) • • • Layers of the Epidermis: Stratum Corneum (Horny Layer) • 20–30 rows of dead, flat, anucleate keratinized membranous sacs • • Cell Differentiation in Epidermis – • Accomplished by specialized form of apoptosis – – – • Cells change from stratum basale to stratum corneum Dermis – – • Two layers – Papillary • Dermal papillae • – Reticular • • • • – • Cleavage lines because most collagen fibers parallel to skin surface Skin Markings – Flexure lines – • Striae • Blister • Skin Color • Three pigments contribute to skin color – Melanin Carotene – • Hemoglobin Skin Color in Diagnosis – Cyanosis – Erythema (redness) – Pallor (blanching) – Jaundice (yellow cast) – Bronzing – Bruises • • Derivatives of the epidermis – Hairs and hair follicles – Nails – Sweat glands – Sebaceous (oil) glands Hair – • Functions include : – – • Hair pigments – • Hair Follicles – • Hair bulb – Hair follicle receptor (root hair plexus) – Hair matrix • Arrector pili • Hair papilla • Types and Growth of Hair • – Vellus hair – Terminal hair Nutrition and hormones affect hair growth – • • • • • • Nails – • Nail matrix • Sweat Glands – • • Also called sudoriferous glands Two main types – Eccrine (merocrine) sweat glands – Apocrine sweat glands Function in thermoregulation • • Apocrine Sweat Glands – • • • Confined to axillary and anogenital areas Sweat + fatty substances + proteins – Viscous; milky or yellowish – Odorless until bacterial interaction body odor Modified apocrine glands – Ceruminous glands—lining of external ear canal; secrete cerumen (earwax) – Mammary glands – secrete milk Sebaceous (Oil) Glands – – – Secrete sebum • Functions of the Integumentary System • Three types of barriers • – Chemical barriers – Physical barriers – Biological barriers • Functions of the Integumentary System • Body temperature regulation – – • • Functions of the Integumentary System – Cutaneous sensations – Metabolic functions – Blood reservoir – Excretion—nitrogenous wastes and salt in sweat Skin Cancer Three major types of skin cancer – Basal cell carcinoma – Squamous cell carcinoma – Melanoma – ABCD rules • Burns • Partial-thickness burns • – First degree – Second degree Full-thickness burns – • Third degree Aging skin