Ch 5: The Integumentary System
advertisement

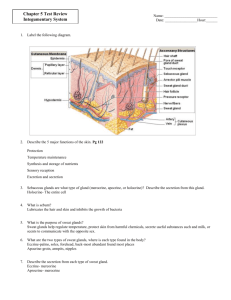
Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology Study Guide: CH 5: THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM E. S. Gustafson INTRODUCTION: Name the 2 major components of the Integumentary System. Name the 2 components of the cutaneous membrane. List 3 accessory structures of the integument. What structure lies beneath the dermis? What other 2 terms refer to this structure? List & describe 6 functions of the integument. THE EPIDERMIS: What type of epithelium comprises the epidermis? What is the most abundant type of epithelial cell found in the epidermis? How many layers of epidermis are found on the palms of the hands & soles of the feet? How many layers are found covering the rest of the body? 1 Give a brief description of the following layers of the epidermis noting the relative position of each above the basement membrane, the number of cell layers, & the presence of any specialized cells or materials: stratum germinativum (a.k.a., basale) – stratum spinosum – stratum granulosum – stratum lucidum – stratum corneum – Be able to label a diagram of the skin showing the layers of the epidermis. What 2 factors contribute to skin color? Describe the color & source of the epidermal pigments: carotene – melanin – 2 What specialized cell produces melanosomes? How does the distribution of melanosomes differ in lightskinned & dark-skinned people? What is the function of carotene? What is the function of melanin? How does dermal circulation contribute to skin color? What causes temporary “paleness” or blushing? How are sunlight, vitamin D3 (the “sunshine vitamin”), & calcitrol related? How does epidermal growth factor (EGF) affect the epidermis? THE DERMIS: Briefly describe the location & characteristics (including connective tissue types) of the following dermal layers: papillary layer – reticular layer – Be able to label a diagram of the skin showing the layers of the dermis. Describe the origin of wrinkles & stretch marks. What are lines of cleavage & how do they relate to cuts in the skin? 3 Distinguish between the location & function of the papillary plexus & the cutaneous plexus. List 3 functions of nerve fibers in the dermis. THE SUBCUTANEOUS LAYER: How is the hypodermis attached to the overlying reticular layer dermis? What type of tissue comprises the subcutaneous layer? What is the most abundant cell type in this tissue? Describe 3 functions of the subcutaneous layer? Be able to label a diagram of the skin showing the subcutaneous layer. ACCESSORY STRUCTURES: Describe the structure of hair & explain how hair is produced. Identify the structures associated with a typical hair follicle. What is the function of arrector pili muscles? Discuss the functions of hair associated with the following: the scalp – the nostrils – 4 the eyelashes – the eyebrows – axillary hair – genital hair – general body hair – root hair plexuses – the contraction of arrector pili muscles – Name 2 other functions of hair not covered in the list above. Name the two types of hair found on the human body & describe their characteristics. How does hair obtain its color? Briefly describe how hair grows in cycles. What 2 common types of exocrine glands are found in the skin? 5 Give a brief physical description of the following types of glands; &, discuss the secretory product(s), the secretory mechanisms, & the general locations of each type: sebaceous gland – apocrine sweat gland – merocrine (eccrine) sweat gland – What is the function of sebum? Describe 3 functions of sweat glands. What is the function of mammary glands? What is the function of ceruminous glands? Where are they located in the human body? Contrast the regulation of sebaceous glands & apocrine & merocrine sweat glands? Describe the structure of a nail. What is the function of nails? Be able to label a diagram of the various skin glands & the nails showing the important structures. 6 LOCAL CONTROL OF INTEGUMENTARY FUNCTION: Describe how injuries to the skin undergo repair. Distinguish between a scab & a keloid. AGING AND THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM: List 10 changes to the integument as a result of aging. Be able to draw a diagram to illustrate the layers and structures of the integument (or complete a color plate showing these layers & structures). 7