Osmosis - WordPress.com

What can you remember about
Osmosis from GCSE?
• Definition?
• Passive/active?
• Direction of movement
• The difference between a solute, solvent & solution
• The difference between concentrated & dilute solutions in terms of FREE water molecules
Osmosis
Explain what is meant by Osmosis, in terms of water potential
Recognise & explain the effects of solutions of different water potentials on plant & animal cells
At AS, you must call it water potential (not concentration!)
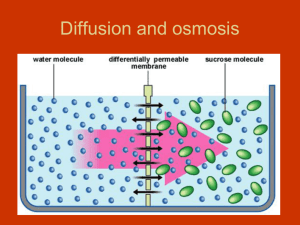
Osmosis
• Diffusion of water molecules that are free to move from an area of high water potential to a low water potential through a partially permeable membrane
Water Potential
• Measured in Kilopascals
(kPa) .
• Pure-0 kPa.
• Cell cytoplasm contains dissolved sugars, salts etc so water potential is more negative
• A solution with a high water potential has a large number of water molecules that are free to move.
What happens?
Hypotonic vs. Hypertonic solutions
Hypotonic
• One of two solutions with
MORE water and less solute
(e.g. very watery)
• Which solution will have the most negative water potential?
• Write a definition for
Isotonic
Hypertonic
• One of two solutions with less water and MORE solute (e.g. very salty or very sugary)
• What will happen to animal and plants cells placed in a) Hypertonic solutions?
b) Hypotonic solutions?
What happens in pure water?
• Animal cell will eventually burst-HAEMOLYSED
• Plant cells-swelling cytoplasm
& vacuole will push against the cell wall which will stop the cell getting any larger-
TURGID
What happens in conc. Sugar?
• Animal cell: cell contents shrink & membrane wrinkles-
FLACCID
• Plant cell-cytoplasm & vacuole shrink and PM pulls away from cell wall-
PLASMOLYSIS
Draw the table below & fill with annotated diagrams to explain what is happening…
Hypotonic solution
Hypertonic solution
Animal cells
Plant cells
Keywords to include:
Turgid
Flaccid
Plasmolysis
Water potential
kPa
Solute
Free water
Haemolysed
Animal cells
Hypotonic solution Hypertonic solution
Water potential lower outside cell than inside cell, water diffuses out of cell via osmosis down water potential gradient.
Plant cells
Draw the table above & fill with annotated diagrams to explain what is happening…
Animal cells
Hypotonic solution Hypertonic solution
Water potential higher outside cell than inside cell, water diffuses into cell via osmosis down water potential gradient
Water potential lower outside animal cell than inside cell, water diffuses out of cell via osmosis down water potential gradient.
Plant cells Water potential higher outside cell than inside cell, water diffuses into cell via osmosis down water potential gradient
Water potential lower outside cell than inside cell, water diffuses out of cell via osmosis down water potential gradient
Plant cell wall prevents cell wall from bursting. The cell is turgid.
Plant cell membrane pulls away from cell wall. Cell is flaccid.
Osmosis Investigation
• Laptops
• G:\Science\Science
Investigations 2
• Osmosis
• Complete Worksheet