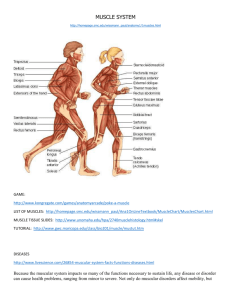
Lifetime Fitness

Lifetime Fitness
Chapter 5
Muscular Strength Assessment and
Prescription
General Principles
• Strength is crucial for optimal performance in activities of daily living
• Strength training over time = decreased HR and
BP
• Most important component in older population
(improves balance, lifting/reaching easier, decreases risk of injuries and falls, stresses bones decreasing osteoporosis)
Strength and Metabolism
• Strength training = muscle hypertrophy
• Muscle tissue uses energy even at rest
• Increased muscle mass = increased resting metabolism
• 1 lb. Muscle gain = resting metabolism increases 35 calories per day
• Higher metabolic rate = more you can eat without gaining fat
Gender Differences
• Men have more muscle fibers – more hypertrophy potential
• Muscle variations determined by differences in M/F hormonal secretions
• Anabolic steroids – detrimental side effects
Changes in Body Composition
• Combined aerobic and strength program =
Decreased adipose tissue around muscle fibers
• Lose girth inches but not body weight
• Women discouraged when do not lose weight with weight training – must also aerobic train for decreased weight
Assessment of Muscular Strength and Endurance
• Muscular Strength = ability to exert max force against resistance
• Muscular Endurance = ability of muscle to exert submaximal force repeatedly over time
• Tests measure: Strength, Endurance, Combination of both
• Strength = 1 RM – one repetition maximum (single lift max)
• Endurance = Total # reps against resistance or time
• Safety, Safety, Safety when testing
Muscular Strength Tests
• Hand Grip Test – 5.2 procedure
• 1 RM Tests – specific large muscle groups
– Bench, leg press, squat, pull down, etc.
Muscular Endurance Tests
• Upper body, Lower body, Mid-body Muscle
Groups (5.3)
– Bench jump
– Modified dip
– Modified push up
– Bent leg curl up
– Abdominal crunch
Muscular Strength and
Endurance Tests
• Submaximal resistance lifts for max reps during six different strength-training exercises (Fig 5.4)
– Lat Pull-Down
– Leg Extension
– Bench Press
– Bent-Leg Curl-Up or Abdominal Crunch
– Leg Curl
– Arm Curl
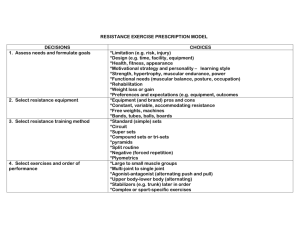
Strength Training Prescription
Factors affecting strength gain:
1. Neural Stimulation -motor neurons, motor unit
2. Types of Muscle Fiber
– genetically determined, can increase efficiency of of each type, can recruit muscle fibers through specificity of training
Slow Twitch = aerobic work
Fast Twitch = anaerobic work and force
3. Overload Principle
– increase demands/resistance over time
4. Specificity of Training
– program designed specific to activity training for
Principles of Strength Training
1. Mode of Training
•
Isometric (Static) Training
– muscle contraction with little/no movement
•
Dynamic Training
– muscle contraction with movement (Isotonic free weights,bands;
Isokinetic machines
)
Concentric Contraction (positives) = shortening of muscle during contraction. (push-up
Eccentric Contraction (negatives)= lengthening of muscle during contraction
Free Weights vs. Machine Weights
• Free Weights
– Require balance
– Low cost
– Variety
– Portability
– One size fits all
• Machine Weights
– Safety
– Selection
– Variable resistance
– Isolation of muscles
– Time
– Flexibility
– Rehabilitation
– Skill acquisition
Principles of Strength Training
2. Resistance
•
80% of max (1 RM) ideal for strength development
Ex. Bench 150 lbs = 150 x .80 = 120 lbs. Work Load
3 to 12 reps = range of work load
– > 12 reps = add weight (progressive resistance training)
Increase strength = 1-6 RM
Increase hypertrophy = 10 RM
Increase endurance = >12 RM
10 RM effective for overall performance gains
Principles of Strength Training
3. Sets
•
Total # repetitions for a given exercise
3 sets of 8-12 reps recommended
Build gradually
General rule = 3 minute rest period between sets
1. 3 min = maximize strength gains
2. 2 min = health fitness purposes
3. 1 min = bodybuilders keeping muscle pumping effect
Circuit Training – alternate two or three exercises that require different muscle groups (bench, ab curl, leg extension…then return to muscle group again)
Principles of Strength Training
4. Frequency of Training
Resistance Sets Strength
Program
Health
Fitness
3
Maximal
Strength
Muscular
Endurance
Body
Building
8-12
Reps max
1-6
Reps max
10-30
Reps
8-20
Reps near max
3-6
3-6
3-8
Rest between sets
2 min
Frequency per week
2-3
3 min
2 min
0-1 min
2-3
3-6
4-12
Principles of Strength Training
General Strength Training Guidelines for Program Design:
Mode 8–10 dynamic strength-training exercises involving the body’s major muscle groups
Resistance Enough resistance to perform 8-12 reps to nearfatigue (10-15 reps for older and more frail individuals)
Sets A minimum of 1 set
Frequency At least two times per week
Plyometrics
• Explosive jump training, incorporating speed and strength training to enhance explosiveness
Strength
Speed
Explosiveness
• Short bouts of jumps or bounds for upper or lower body
• Low reps, low frequency – High risk of injury if done incorrectly or too often
Strength Exercise Guidelines
Work all major muscle groups: chest, shoulders, back, legs, arms, hip, and trunk
Always lift with a partner
Proper warm-up
Exercise larger muscle groups first
Work opposing groups for balance
Do all lifts in a controlled manner
Lift through the entire ROM
Breathe evenly
Inhale during eccentric (bringing wt. down)
Exhale during concentric (lifting/pushing)
Do not hold breath; dizzy, pass out, heart attack
Allow adequate recovery time between lifts
Discontinue or evaluate program if increased pain
Stretch post workout to minimize muscle soreness
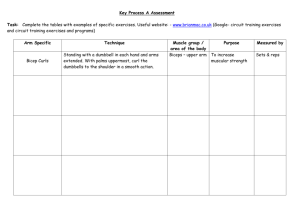
Design Your Own Strength-Training
Program
Assignment:
Design and write a personal strength-training program including the following:
1.
Identify goal to increase Strength Gain, Muscular
Endurance, or both Strength and Endurance Gains
2. List at least 8-10 specific exercises. Briefly explain each.
3. Identify Sets , Repetitions , Frequency , and Approximate
Resistance (Weight/Band)
4. List alternate ways to accomplish some of these same exercises if traditional strength training equipment is not available
Chapter 5
Assignments Due
1. Lab figure 5.5 Strength Test Report
2. Personal Strength Training Program
– Use Lab figure 5.8 or write your design your own
3. Written note Chapter 5 outline
4. Complete Chapter 5 on-line computer quiz http://www.wadsworth.com/cgiwadsworth/course_products_wp.pl?fid=M20b&discipl ine_number=16&product_isbn_issn=0534582575 and e-mail or print results to:
5.
Ke_tslattery@kentschools.net