File
advertisement

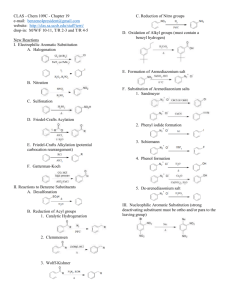
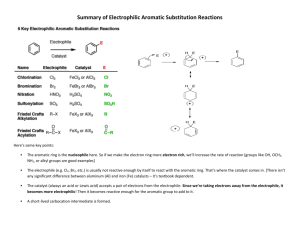
Questions on Electrophilic substitution reactions 1. Describe and explain the structure of benzene by considering the hybridization that occurs on each carbon atom. _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Benzene reacts with a mixture of concentrated nitric and sulfuric acid at a temperature not exceeding 50 oC. (a) State the equation for the reaction that occurs. ____________________________________________________________________________________ (b) Explain the role of the concentrated sulfuric acid. ____________________________________________________________________________________ (c) Identify the electrophile in this reaction. _____________________________________________________________________________________ (d) Explain why substitution rather than addition occurs. _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ (e) Show the mechanism for this reaction using curly arrows. (f) Suggest a reason why the temperature is not raised above 50 oC. _____________________________________________________________________________________ 3. Benzene can also undergo an electrophilic substitution reaction with chlorine in the presence of aluminium chloride, AlCl3, to form chlorobenzene. (a) Deduce the equation for this reaction. (b) Based on your knowledge of electrophiles suggest the identity of the electrophile in this reaction and deduce the role of aluminium chloride in its formation. _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ Download the Electroplilic substitution questions to give to your students Answers 1. Each carbon atom is sp2 hybridized with each sp2 hybrid orbital containing one electron. One of these hybrid orbitals combines with the single electron in the 1s atomic orbital of a hydrogen atom forming a sigma bond. The other two sp2 hybrid orbitals each combine with one of the hybrid sp2 orbitals of two other carbon atoms to form sigma bonds. This results in a planar hexagonal ring with bond angles of 120o. The six remaining outer electrons (one on each carbon atom occupying a p orbital) form a delocalized pi bond spread equally above and below the plane of all six carbon atoms. 2. (a) (b) It is a catalyst. It functions as an acid, protonating the nitric acid to form H2NO3+ which then breaks down to form water and the nitronium ion. H2SO4 + HNO3 → H2NO3+ + HSO4− then H2NO3+ → NO2+ + H2O (c) The nitronium ion, NO2+. (d) Substitution, unlike addition, does not involve the extra energy required to overcome the delocalization energy of the benzene ring. (e) (f) Further nitration of the benzene ring will occur (to form 1,3-dinitrobenzene). 3. (a) (b) Cl+. The AlCl3 acts as a Lewis acid, accepting a pair of electrons from Cl2 to form AlCl4− and Cl+