Philosophy Theorists
advertisement

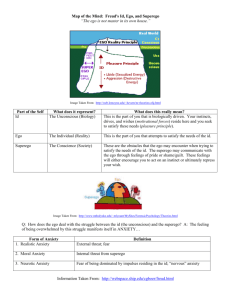
Philosophy Theorists Freud, Adler, Maslow, Erikson What is Personality? the quality or state of being a person. : the complex of characteristics that distinguishes an individual. the totality of an individual's behavioral and emotional characteristics. Nature vs. Nurture Sigmund Freud Known as Father of Psychology Oldest of 8 children Father - Discipline Mother - Nurturer Born Czechoslovakia Father blue collar worker Moved to Vienna when father lost job Freud Cont… Studied a patients thoughts (Feelings, not illness) Studied Neurology Strong psychological interest Volumes of writings Psychoanalytic approach Freud Famous Work Iceberg theory 1st 6 years of childhood are the most important Nature - 100% instincts Oedipus complex ID, EGO, Superego Iceberg Theory Iceberg Cont.. According to Freud there are three levels of consciousness to the mind Conscious (small) 10% - part of the mind that holds what you are aware of. Preconscious (small-medium) 10-15% Regarded as ordinary memory. Not in conscious but can be readily brought to conscious Unconscious (enormous) 75-80% - Not directly accessible to awareness. “Dump box” for urges, feelings and ideas tied to anxiety. Iceberg Cont… Much of Freud’s work on the ID, Ego, Superego comes from this theory. Believes Information passes easily between conscious and preconscious. To access truly unconscious information from the mind you need a psychoanalyst. ID, EGO, SuperEgo ID, EGO, SuperEgo ID - Pleasure seeking 100%. You are here to serve me. Ex: An infant or young child mentality. EGO - Reality somewhere between the Id and Superego. May be one sided more than others. SuperEgo - The giving altruistic person. Always moral, law abiding. Altruistic - unselfish regard for or devotion to the welfare of others. Oedipus Complex Believes we all end up married to someone exactly like mother or father. At some point in an infant/toddlers life they will desire to possess parent of opposite sex and dispose of parent of same sex. Between ages 3-5 Becomes a repressed feeling in the unconscious. Freud’s Stages of Development Believes we are all pleasure seeking individuals. Focus’ on that for each stage Oral stage - (0-2yrs) centered around the sensitive area of mouth. Communication develops Anal stage - (2-3yrs) potty training Phallic stage - (3-5yrs) start to realize gender differences ex: oedious complex Latency - (6-12yrs) play with same sex ignore opposite. Genital - (12yrs - ) puberty Defense Mechanisms Freud believes they come about when the EGO can not deal with the demands put on it. Three types of anxiety Neurotic Anxiety Reality Anxiety Moral Anxiety Types of Defense Mechanisms - Denial, Repression, Regression, Suppression, Sublimation, Displacement. Dream Interpretation Freud begins to analyze dreams in order to understand aspects of personality as they relate to pathology. He believes that nothing you do occurs by chance every action and thought is motivated by your unconscious