Chapter 6: Psychological Approaches

A Handbook of Critical Approaches to
Literature
I. Aims and Principles
A. Abuses and misunderstandings of the psychological approach
The approach is abused when it is made an exclusive approach
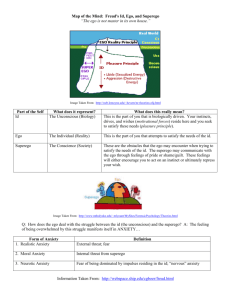
B. Freud’s Theories
Theory of the unconscious (id, ego, superego)
Most of what we do is motivated by the unconscious, especially sexually (libido)
Phallic and yonic symbols
Child development
Oedipus complex, fixation
C. Other Theories
Inspired by Freud, Jacques Lacan developed his own version of the unconscious
Symbolic Order & Realm of the Father
Realm of the Mother
Mirror Stage
II. Psychological Approach in Practice
A. Hamlet: the Oedipus Complex
Theory of Ernest Jones, Norman N. Holland on
Hamlet’s misogyny and ambivalence toward father figures
B. Rebellion against the father in Huckleberry Finn
Huck’s rejection of parental authority parallels his rejection of values of his society, especially racism, slavery, and religion; river as maternal symbol; Jim as androgynous; story of the child as victim (betrayal-of-innocence theme)
C. Prometheus Manqué: The Monster Unbound
Novel’s subtitle points to Oedipal struggle, but revenge turns on Victor’s entire family
D. “Young Goodman Brown”: Id over Superego
Theme of innocence betrayed; allegory, symbolism, ambiguity; town = superego,
Brown = ego, forest = id; obsession, taboos;
Brown is not a mature man
E. Sexual Imagery in “To His Coy Mistress”
From teasing wit to brutal assault
F. Morality Principle Over Pleasure Principle in
“Everyday Use”
Narrator = ego; Dee = id; Maggie = superego