Freud-Id, Ego, Superego Handout
advertisement
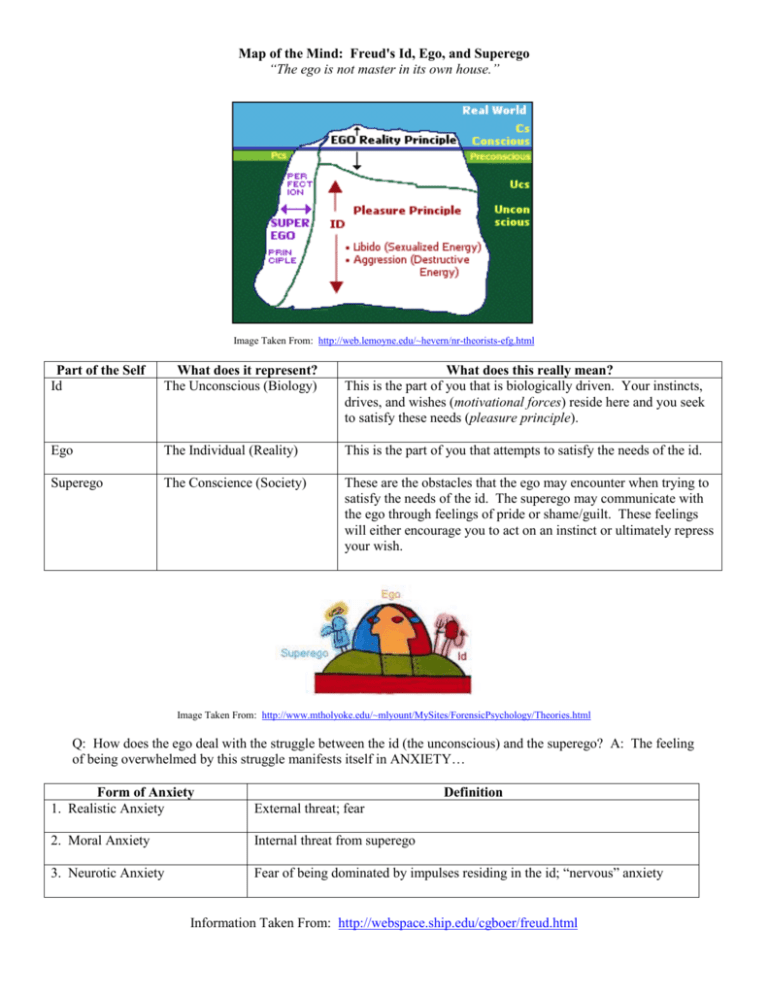
Map of the Mind: Freud's Id, Ego, and Superego “The ego is not master in its own house.” Image Taken From: http://web.lemoyne.edu/~hevern/nr-theorists-efg.html Part of the Self Id What does it represent? The Unconscious (Biology) What does this really mean? This is the part of you that is biologically driven. Your instincts, drives, and wishes (motivational forces) reside here and you seek to satisfy these needs (pleasure principle). Ego The Individual (Reality) This is the part of you that attempts to satisfy the needs of the id. Superego The Conscience (Society) These are the obstacles that the ego may encounter when trying to satisfy the needs of the id. The superego may communicate with the ego through feelings of pride or shame/guilt. These feelings will either encourage you to act on an instinct or ultimately repress your wish. Image Taken From: http://www.mtholyoke.edu/~mlyount/MySites/ForensicPsychology/Theories.html Q: How does the ego deal with the struggle between the id (the unconscious) and the superego? A: The feeling of being overwhelmed by this struggle manifests itself in ANXIETY… Form of Anxiety 1. Realistic Anxiety Definition External threat; fear 2. Moral Anxiety Internal threat from superego 3. Neurotic Anxiety Fear of being dominated by impulses residing in the id; “nervous” anxiety Information Taken From: http://webspace.ship.edu/cgboer/freud.html Map of the Mind: Freud's Id, Ego, and Superego “The ego is not master in its own house.” Q: How does the ego handle this anxiety? A: The individual may engage in the following DEFENSE MECHANISMS… Defense Mechanism Definition 1. Denial Refuse to experience a certain situation 2. Repression “Motivated forgetting”; failure to remember a traumatic event 3. Compensation Striving to make up for unconscious impulses or fears 4. Isolation (Intellectualization) Removing emotion involved with difficult/painful experience 5. Displacement Redirecting impulse on a symbolic substitute 6. Reaction Formation Changing desire into its opposite 7. Undoing Use of rituals you believe will remove unpleasant thoughts or feelings 8. Introjection (Identification) Incorporating personality characteristics of someone else into your own personality in order to deal with a specific situation 9. Projection Unconscious attributing one’s own unacceptable thoughts to another person 10. Regression Revisiting/returning to a mental/psychological time when you were faced with stress or conflict 11. Rationalization Distorting facts to make an event or desire less threatening 12. Sublimation Transforming an unacceptable impulse into a socially acceptable one Example Information Taken From: http://webspace.ship.edu/cgboer/freud.html











