Metals - chemistry
advertisement

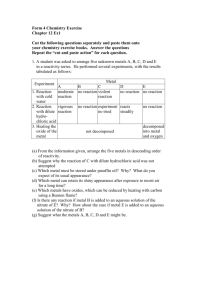
Reactivity Series of Metals Reactions of Metals Effect of Heat on Metal Carbonates Chemical Properties of Metals ◦ Metal reaction with cold water & steam ◦ Metal reaction with hydrochloric acid Reaction of Metals: Displacement Reactions ◦ With aqueous ions of another metal ◦ With the oxide of another metal Reaction of Metal Oxides ◦ With carbon ◦ With hydrogen Effect of Heat on Metal Carbonates ◦ Thermal stability & reactivity Reactivity Series of Metals Recap: Chemical Properties of Metals Reaction with Water (Cold Water) Metal + Cold Water Metal Hydroxide + Hydrogen Gas Eg. 2Na(s) + 2H2O(l) 2NaOH(aq) + H2(g) Which are some metals that react with cold water? Recap: Chemical Properties of Metals Reaction with Water (Steam) Metal + Steam Metal Oxide + Hydrogen Gas Eg. Mg(s) + H2O(g) MgO(s) + H2(g) Which metals only react with steam? Recap: Chemical Properties of Metals Reaction with Hydrochloric Acid Metal + Hydrochloric Acid Salt + Hydrogen Gas Eg. 2K(s) + 2HCl(l) 2KCl(aq) + H2(g) The more vigorous the reaction The higher it is in the reactivity series The more reactive is the metal Reaction of Metals With the Aqueous Ions of Another Metal • Displacement of metals from solution • More reactive metals can displace less reactive metals from their salt solutions. • This can be used to find the position of metals in the reactivity series. Iron Nail in Copper(II) Sulphate Solution Observations: 1. 2. Reddish-brown solid forms on the surface of the iron nail Blue solution becomes pale green Fe (s) + Iron CuSO4 (aq) Copper(II) Sulphate Solution FeSO4 (aq) Iron(II) Sulphate Solution + Cu (s) Copper Iron Nail in Copper(II) Sulphate Solution Brown solid: Copper metal Solution turns pale green ◦ ◦ Copper has been removed from the solution. Iron(II) sulphate solution is pale green in colour. We say that… Iron has displaced copper from the copper(II) sulphate solution. What will happen when a piece of magnesium strip is immersed in a solution of copper(II) sulphate? Think! Some Possible Observations Deposit of the more reactive metal (from its aqueous solution) Colour of the solution may change Heat may be given off Displacement Reactions are Redox Reactions The more reactive metal is oxidized The less reactive metal is reduced REDOX reaction! For example, Chemical Equation: Fe (s) + CuSO4 (aq) FeSO4 (aq) + Cu (s) Ionic Equation: Fe (s) + Cu2+ (aq) Fe2+ (aq) + Cu (s) Displacement Reactions are Redox Reactions A more reactive metal: readily gives up electrons in reactions has greater tendency to form positive ions As a result… A more reactive metal can displace a less reactive metal, from its solution or metallic oxide. Reaction of Metals With the Oxide of Another Metal Displacement of metals from metallic oxides A more reactive metal can reduce the oxide of a less reactive metal. For example: Thermit reaction 2Al (s) + Fe2O3 (s) Al2O3 (s) + 2Fe (l) Reaction of Metals With the Oxide of Another Metal Thermit Reaction Iron(III) ions are reduced to become iron atoms 2Al (s) + Fe2O3 (s) Al2O3 (s) + 2Fe (l) Aluminium atoms are oxidized to become aluminium(III) ions The more reactive the metal is, the more readily it forms compounds. Unreactive metals tend to stay umcombined. Reaction of Metal Oxides With Carbon Carbon can remove oxygen from the oxides of metals that are not too high up in the Reactivity Series. The lower the position of a metal in the Reactivity Series, the easier it is for carbon to remove oxygen from the metal oxide. Reaction of Metal Oxides With Carbon metal oxide reaction potassium oxide sodium oxide calcium oxide magnesium oxide zinc oxide iron(II) oxide lead(II) oxide copper(II) oxide oxides are not reduced by carbon silver oxide oxide is reduced by heating oxides are reduced by carbon The Importance! Reaction of Metal Oxides With Carbon metals need to be extracted from their ores before we can use them metals below magnesium are often extracted from their ores by reduction with carbon (WHY?) metals above zinc cannot be extracted by reduction with carbon bc they are stable (THEN WHAT?) Reaction of Metal Oxides With Hydrogen Hydrogen can remove oxygen from metallic oxides, producing the metal and water(steam). metal oxide + hydrogen metal + steam The lower the position of a metal in the Reactivity Series, the easier it is for hydrogen to remove oxygen from the metal oxide. Reaction of Metal Oxides With Hydrogen metal oxide potassium oxide sodium oxide calcium oxide magnesium oxide zinc oxide iron(II) oxide lead(II) oxide copper(II) oxide silver oxide reaction with hydrogen heated metal oxides are not reduced by hydrogen heated metal oxides are reduced by hydrogen Effect of Heat on Metal Carbonates: Thermal Stability & Reactivity Most carbonates decompose when heated strongly to produce a metal oxide and carbon dioxide gas. The ease of decomposition depends on the position of the metal in the reactivity series. Recall the reactivity series. Thermal Stability of Metal Carbonates Metal Carbonate Potassium Carbonate Effect of Heat Sodium Carbonate Stable to heat No visible reaction Calcium Carbonate Decomposes into metal oxide and carbon dioxide Magnesium Carbonate Metal Metal Oxide + Carbon Dioxide Zinc Carbonate Iron (III) Carbonate Lead Carbonate Copper(II) Carbonate Silver Carbonate Decomposes into silver and carbon dioxide Reactions with water & dilute acids: More vigorous reaction Higher in the reactivity series The metal is more reactive Reaction with metal carbonates: The more stable the metal carbonate is to heat, the higher it is in the reactivity series. Check this out! http://www.chem.iastate.edu/group/Greenbowe/se ctions/projectfolder/flashfiles/redox/home.html Class Activity & Discussion So, what have you learnt today? Displacement Reaction ◦ They are redox reactions. ◦ A more reactive metal can displace a less reactive metal, from its solution or metallic oxide. Carbonates: Thermal stability & reactivity The more stable the metal carbonate is to heat, the higher it is in the reactivity series.