Atoms vs. Molecules
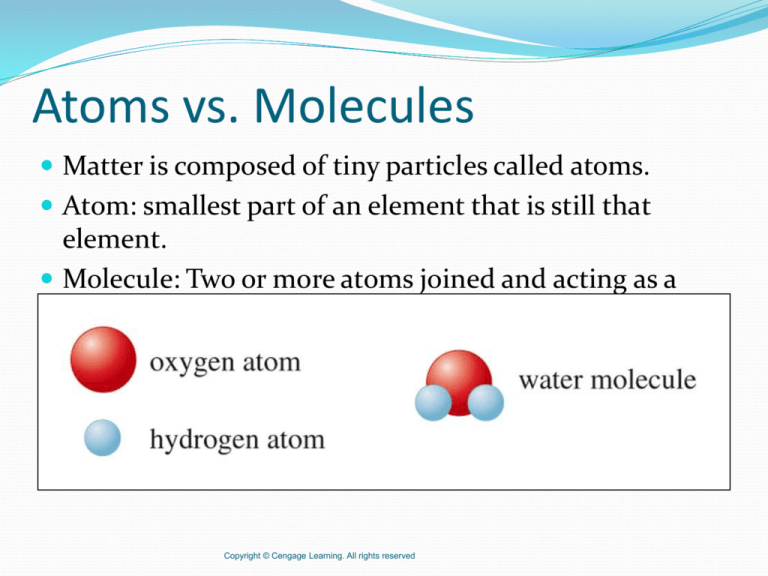
Matter is composed of tiny particles called atoms.
Atom: smallest part of an element that is still that
element.
Molecule: Two or more atoms joined and acting as a
unit.
Copyright © Cengage Learning. All rights reserved
Oxygen and Hydrogen
Molecules
• Use subscripts when more than one atom is in the
molecule.
Copyright © Cengage Learning. All rights reserved
A Chemical Reaction
One substance changes to another by reorganizing the
way the atoms are attached to each other.
Copyright © Cengage Learning. All rights reserved
Atomic Theory
Atoms are building blocks of elements
Similar atoms in each element
Different from atoms of other elements
Two or more different atoms bond in simple
ratios to form compounds
4
Subatomic Particles
Particle
Symbol
Charge
Relative
Mass
0
Electron
e-
1-
Proton
p+
+
1
Neutron
n
0
1
5
Location of Subatomic Particles
10-13 cm
electrons
protons
neutrons
nucleus
10-8 cm
6
Atomic Number This refers to how
many protons an
atom of that element
has.
No two elements,
have the same
number of protons.
Bohr Model of Hydrogen Atom
Wave Model
Atomic Number on the Periodic Table
Atomic Number
Symbol
11
Na
8
All atoms of an element have the
same number of protons
11 protons
11
Sodium
Na
9
Learning Check
State the number of protons for atoms of each
of the following:
A. Nitrogen
B. Sulfur
C. Barium
10
Solution
State the number of protons for atoms of each
of the following:
A. Nitrogen
7 protons
B. Sulfur
16 protons
C. Barium
56 protons
11
Mass Number
Counts the number
of
protons and neutrons
in an atom
12
Atomic Symbols
Show the mass number and atomic number
Give the symbol of the element
mass number
23 Na
atomic number
sodium-23
11
13
Number of Electrons
An atom is neutral
The net charge is zero
Number of protons = Number of electrons
Atomic number = Number of electrons
14
Subatomic Particles in Some Atoms
16
O
8
8 p+
8n
8 e-
31
P
65
Zn
15
30
15 p+
16 n
15 e-
30 p+
35 n
30 e15
Isotopes
Atoms with the same number of protons but
different numbers of neutrons.
Show almost identical chemical properties;
chemistry of atom is due to its electrons.
In nature most elements contain mixtures of
isotopes.
Copyright © Cengage Learning. All rights reserved
16
Atomic Mass and
Isotopes
While most atoms have the
same number of protons
and neutrons, some don’t.
Some atoms have more or
less neutrons than protons.
These are called isotopes.
An atomic mass number
with a decimal is the total
of the number of protons
plus the average number of
neutrons.
Two Isotopes of Sodium
Copyright © Cengage Learning. All rights reserved
18
Isotopes
Atoms with the same number of protons, but
different numbers of neutrons.
Atoms of the same element (same atomic
number) with different mass numbers
Isotopes of chlorine
35Cl
37Cl
17
17
chlorine - 35
chlorine - 37
19
Learning Check
Naturally occurring carbon consists of three
isotopes, 12C, 13C, and 14C. State the number of
protons, neutrons, and electrons in each of these
carbon atoms.
12C
13C
14C
6
6
6
#p _______
_______
_______
#n _______
_______
_______
#e _______
_______
_______
20
Solution
12C
13C
#p
6
6
6
#n
6
7
8
#e
6
6
6
6
14C
6
6
21
Learning Check
An atom of zinc has a mass number of 65.
A. What is the number of protons in the zinc
atom?
B. What is the number of neutrons in the zinc
atom
C. What is the mass number of a zinc isotope
with 37 neutrons?
22
Solution
An atom of zinc has a mass number of 65.
A. Number of protons in the zinc atom
30
B. Number of neutrons in the zinc atom
35
C. What is the mass number of a zinc isotope
with 37 neutrons?
67
23
Learning Check
Write the atomic symbols for atoms with
the following:
A. 8 p+, 8 n, 8 e-
___________
B. 17p+, 20n, 17e-
___________
C. 47p+, 60 n, 47 e- ___________
24
Solution
16O
8
A. 8 p+, 8 n, 8 e-
37Cl
B. 17p+, 20n, 17e-
17
C. 47p+, 60 n, 47 e-
107Ag
47
25






