Biomolecules - Dickinson ISD
advertisement
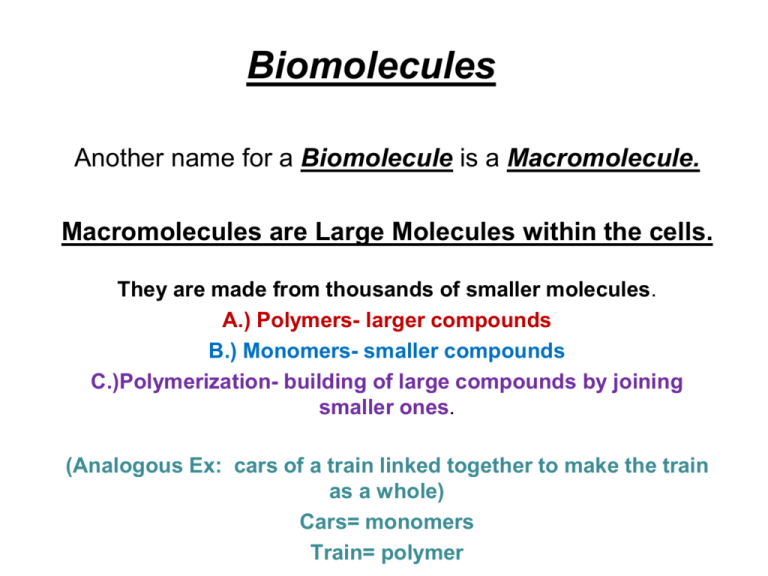
Biomolecules Another name for a Biomolecule is a Macromolecule. Macromolecules are Large Molecules within the cells. They are made from thousands of smaller molecules. A.) Polymers- larger compounds B.) Monomers- smaller compounds C.)Polymerization- building of large compounds by joining smaller ones. (Analogous Ex: cars of a train linked together to make the train as a whole) Cars= monomers Train= polymer Student Notes Using your knowledge of Root Words, explain how the terms Biomolecule and Macromolecule are related. Student notes Get with a partner next to you, without getting out of your seat. Come up with an example of monomers and polymers, other than the train!! 4 major biomolecules • 1.) Carbohydrates (sugars/starches) • 2.) Proteins ( amino acids) • 3.) Lipids (fats,oils,waxes,steroids) • 4.) Nucleic Acids (DNA,RNA) Student page Write down everything that you have eaten today, you can also include what you have had to drink. Student Notes p. 5 Without looking at your notes: 1. Give an example of a monomer and a polymer and label each one. 2. Name which macromolecule you would need the most for running a marathon. 3. What types of food would you eat before the marathon? # 1--Carbohydrates • • • • • • “Fast Fuel”- sugars & starches Sugar molecules made of C, H, & O Made in a 1:2:1 ratio C6H12O6 Two types of Sugars: Monosaccharides and Disaccharides Monosaccharides • simple sugars: • A.) glucose- “blood sugar” energy for cellular respiration • B.) galactose- sugar in milk & yogurt • C.) fructose- sugar found in honey • all 3 have same molecular structure (C6H12O6) but different structural formulas or shapes. Disaccharides • Are Monosaccharides covalently bonded together • 3 Common Disaccharides • A.) sucrose (table sugar)= glucose +fructose • B.) lactose (sugar in milk) =glucose + galactose • C.) maltose= (product of starch digestion)= glucose + glucose Starches • • • • Polysaccharides = starches Starches are polymers of glucose A.) amylose B.) amylopectin • Sugars are soluble in water • Starches are insoluble in water Student Notes Explain the difference between a monosaccharide, a disaccharide, and a polysaccharide. Draw and label the molecular structure of each type of carbohydrate Structural formula for Carbohydrates Student page 9 Make a chart of the 3 types of carbohydrates Monosaccharides (simple sugar) Disaccharides (simple sugar) Polysaccharides (starch) 1. 1. 1. 2. 2. 2. 3. 3. #2--Proteins Many structures/Many functions Proteins are made up of nitrogen, carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Formed from monomers called amino acids. Role of Proteins Each protein has a specific role ,such as: *A. regulating cell processes *B. controlling the rate of reactions (movement) *C. forming muscles or bones (structural support) *D. transporting substances into or out of cells *E. fighting disease (against foreign substances) Student Notes Choose one of the functions of the proteins. What would happen if the protein that controlled that function stopped working? Write your answer in a complete sentence!! Amino Acid Molecular Structure *compounds with an amino group (-NH2) on one end and a carboxyl group (-COOH) on the other end with a side chain called an “R-group” #3---Lipids *made mostly from carbon and hydrogen atoms. *Generally not soluble in water. (hydrophobic) *Consist of fats, oils and waxes, also steroids. Uses of Lipids **Used to store energy.* **Some are important parts of biological membranes and waterproof coverings. **Protection **Formed when glycerol joins a fatty acid group. st 1 Study the Ten Latin Root Words with your partner at your table for the next 5 minutes Student Notes Who do you think stores more fat in their bodies, Men or Women? Explain your answer in complete sentences!! Structure of a Lipid Types of Lipids Saturated fats- all carbons have the maximum number of hydrogens attached to them. Usually are solid at room temperature (lard, Crisco.) Unsaturated fats- contain at least one carbon-carbon double covalent bond. Usually are liquid at room temperature (cooking oils.) #4--Nucleic Acids *made up of hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, carbon and phosphorus *Formed from monomers called nucleotides. *Nucleotides- made up of a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. *Store and transmit hereditary or genetic information. Nucleotide Types of Nucleic Acids RNA-ribonucleic acid, contains the sugar ribose. DNA-deoxyribonucleic acid, contains the sugar deoxyribose.