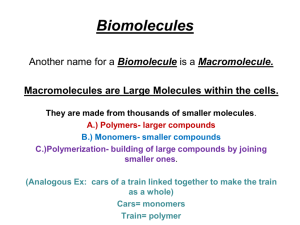
Find Guided Notes for This!! Chapter 6 The 4 main elements of life are: Oxygen (65%) Carbon (19%) Hydrogen (10%) Nitrogen (3%) Any molecule that contains carbon and hydrogen and is made by a living organism What does carbon need to become more stable? What kind of chemical bonds will it form? An organic compound made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio. Function: major source of energy for ALL cells on Earth. When “carbs” are broken down during digestion, a great deal of chemical energy is released. Good short-term energy source Examples: Pasta, bread, potatoes, rice 1. 2. 3. Monosaccharides – Single or simple sugars Disaccharides – Double sugars Polysaccharides – Long chains of glucose Smallest of the sugars – often called refined sugars, they are either simple or single sugars. Building blocks or monomers for larger carbs called polysaccharides. Chemical Formula = C6H12O6 (1:2:1 Ratio) 3 Common Monosaccharides: a. b. c. Glucose (made by green plants) Galactose (sugar in beets and dairy products) Fructose (fruit sugar) Glucose Fructose Galactose Transport sugars in plants (carpooling!) Made from bonding two monosaccharides dehydration synthesis (Double sugars) Chemical Formula = C12H22O11 Why? a. b. c. Sucrose = fructose + glucose (table sugar) Maltose = glucose + glucose (malt sugar) Lactose = galactose + glucose (milk sugar) Made from bonding three or more monosaccharides, usually glucose. Used for short-term energy storage and structural support in plants. a. b. c. Starches – energy storage in plants Cellulose – structure of wood and cell walls (indigestible fiber or roughage in human diet.) Glycogen - animal storage in liver and muscle cells 1. Dehydration Synthesis - (or Condensation) 1. Hydrolysis – Add water and split apart Combining two or more monomers (monosaccharides) to form polymers (disaccharides/polysaccharides) Dehydration = remove water Synthesis = making or putting together C6H12O6 + C6H12O6 = C12H22O11 + H2O The splitting apart of polymers to form monomers Hydrolysis = Add water and split apart (Opposite of Condensation) C12H22O11 + H2O = C6H12O6 + C6H12O6 Digestion is a good example of hydrolysis. Hydrophobic molecules that do not dissolve in water Main functions: Cell membranes – creates a barrier between cells and their environment. Long-term energy storage in plants – lipids can store twice as much energy as carbohydrates - Fat hummingbirds? Insulation and organ protection – Cold water animals Lipids are mainly composed of carbon, and hydrogen, with a little oxygen Most lipids are molecules called triglycerides which are made from one glycerol and three fatty acids. Fatty acids are long chains of hydrogen and carbon (hydrocarbon chains) and are not soluble in water (non-polar) Saturated Solids at room temperature = (fats) Mainly produced by animals Examples: butter and lard Cardiovascular Disease – heart attacks Unsaturated (Poly- and Mono-unsaturated) Liquids at room temperature = (oils) Usually produced by plants Examples: corn oil, olive oil, peanut oil Generally more healthy for you Large molecules that contain H, C, O, N, and sometimes S (but NOT Phosphorus) Building blocks or raw materials for making new organelles and cells (Growth and repair) Made up of subunits or monomers called amino acids, which bond to form long folded polypeptide chains Contractile proteins that make muscles contract – body movement Hemoglobin (in red blood cells) transports oxygen to body cells Keratin makes up your hair and fingernails Hormones like insulin – blood sugar Antibodies fight off infections Collagen keeps your skin young and healthy It is the order or arrangement of the amino acids that determines the type of protein STEAM… There are 20 amino acids used to make proteins (compare to English language) Enzymes: a special group of proteins that speed up the rate of chemical reactions in your body. They are catalysts that control all metabolic processes Used to either build or break down molecules. Ex. Digestive enzymes in your stomach. Energy or information storing molecules that are made from monomers called nucleotides. Nucleotides often bond together to make long chains (DNA and RNA) Nucleotides have 3 parts – a 5-carbon sugar, a nitrogenous base, and a phosphate group (PO4) 1. DNA (DeoxyriboNucleic Acid) 2. Two polynucleotide strands woven together in a double helix. Function: stores and uses genetic information for metabolism and heredity RNA (RiboNucleic Acid) Single stranded polynucleotide Function: helps ribosomes make proteins, acts as an enzyme for protein synthesis 1. 2. 3. ATP RNA ATP (Adenosine TriPhosphate) A single modified nucleotide It has 3 phosphates with special highenergy bonds Function: universal energy carrier molecule for all cells on Earth!