Organic Molecules of Life
advertisement

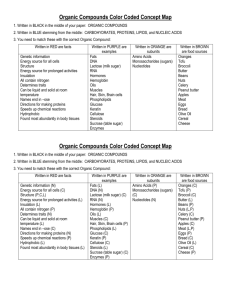
Organic Molecules of Life Chapter 2 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Understand the relationship between matter and elements. Know the general structure of atoms and the location and charge of each subatomic particle. Know what elements the symbols O, C, H, N, Ca, P, K and S represent. Understand the properties of water. Know the meaning of hydrophobic and hydrophilic. Know what types of substances water dissolves. (i.e. does water dissolve hydrophilic or hydrophobic substances?) 7. Know what acids and bases are and what the pH range is for acids and bases. 8. Know what buffers are. 9. Know the Organic Molecules of Life and understand why they are referred to as such. 10. Understand what ‘Organic’ really means and understand why organic compounds are important to living things. 11. Know the monomers (building blocks) for carbohydrates. 12. Know the monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides by name. 13. Be able to recognize foods that are high in carbohydrates. 14. Know some specific info about glucose, maltose, fructose, lactose, sucrose, cellulose, starch and glycogen (i.e. glucose is blood sugar, maltose is beer sugar, fructose is in fruits, lactose is milk sugar, etc.) 15. Know the monomers (building blocks) for lipids. 16. Be able to recognize foods that are high in lipids. 17. Know the difference between fats and oils. 18. Know where phospholipids are located in cells. 19. Understand the solubility (dissolving ability) of lipids in water. 20. Know the monomers (building blocks) for proteins. 21. Know what dipeptides and polypeptides are. 22. Be able to recognize foods that are high in proteins. 23. Know what kind of molecule Hemoglobin is and understand its importance. Understand the information about Sickle Cell Anemia. 24. Know the monomers (building blocks) for Nucleic Acids. 25. Know what nucleotides are made of. 26. Recognize that DNA, RNA and ATP are Nucleic Acids. 27. Know the names of the 4 nitrogenous bases in DNA. Cell Structure and Function Chapter 3 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Understand the ‘Cell Theory’. Understand the properties of cells. Understand the structure of cells. Understand the differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. Know which organisms are prokaryotic and which are eukaryotic. Understand the differences between plant cells and animal cells. Know what the cytoplasm is and know what organelles are. Understand the structure and function of the following organelles: nucleus, ribosomes, rough ER, smooth ER, golgi bodies, vesicles, lysosomes, peroxysomes, mitochondria, chloroplasts, cell wall, cytoskeleton, vacuoles, cilia, flagella. (see back of this page) 9. Understand what ‘protein synthesis’ means. Organic Molecules of Life / Organelle Functions ORGANIC MOLECULES OF LIFE Carbohydrates (sugars) Proteins Lipids (fats and oils) Nucleic Acids (DNA, RNA, ATP) Monosaccharides Disaccharides Polysaccharides ORGANELLE Nucleus Ribosomes Rough ER Smooth ER Golgi Bodies Vesicles Lysosomes Mitochondria Plasma Membrane Peroxysomes Cytoskeleton Flagella Chloroplasts (plants only) Vacuole (plants only) Cell Wall (plants; some bacteria) BUILDING BLOCKS (MONOMERS) Monosaccharides Amino Acids Fatty Acid Nucleotides CARBOHYDRATES Glucose – blood sugar Fructose – fruit sugar Maltose – beer sugar Sucrose – table sugar Lactose – milk sugar Glycogen – carb storage (in animals) Starch – carb storage (in plants) Cellulose – dietary fiber, roughage FUNCTION DNA and RNA storage Protein Synthesis Modification of synthesized proteins Lipid Synthesis Modification and Packaging of synthesized proteins Transport of synthesized proteins to their final destination Intracellular digestion Powerhouse of the cell; ATP formation Regulates which substance can enter and exit the cell detoxification Provides cell shape, internal transport of materials cell motility (movement) Photosynthesis -converts light energy to chemical energy (glucose) Storage of water and other substances Support and protection