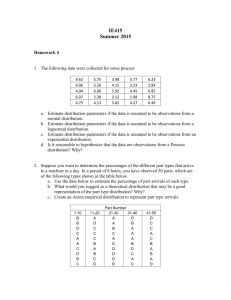
Newsvendor Problem
advertisement

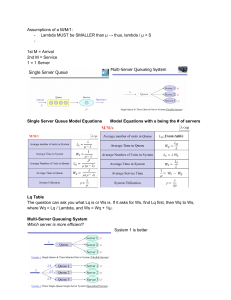
Previously • • • • Optimization Probability Review Inventory Models Markov Decision Processes Agenda • • • • • Hwk Projects Additional Topics Finish queues Start simulation Projects • 10% of grade • Comparing optimization algorithms • Diet problem • Vehicle routing – Safe-Ride – Limos • Airplane ticket pricing – Over time – Different fare classes / demands Additional Topics? • • • • Case studies Pricing options Utility theory (ch 9-10) Game theory (ch 16) Queues service rate µ departures arrivals rate queue c servers system • M/M/s (arrivals / service / # servers) M=exponential dist., G=general • W = E[T], Wq = E[Tq] waiting time in system (queue) • L = E[N], Lq = E[Nq] #customers in system (queue) • = /(cµ) utilization (fraction of time servers are busy) Networks of Queues (14.10) • Look at flow rates – Outflow = when < 1 • What is the distribution between arrivals? – Not independent, formulas fail. • Special case: all queues are M/M/s “Jackson Network” Lq just as if normal M/M/s queue Queueing Resources • M/M/s – Online http://www.usm.maine.edu/math/JPQ/ – Lpc(rho,c) function from textbook (fails on excel 2007,2008) • G/G/s – QTP (fails on mac excel) http://www.business.ualberta.ca/aingolfsson/QTP/ • G/G/s + Networks – Online http://staff.um.edu.mt/jskl1/simweb – ORMM book queue.xla at http://www.me.utexas.edu/~jensen/ORMM/frontpage/jensen.lib Distribution of Queue Length • Why care? – service guarantees emergency response, missed flights • M/M/1 case – N+1 ~ Geometric(1-) • Otherwise, – ORMM add-in “state probabilities” P(N=k) ER Example (p508) 12/hr 1/6 Surgery 5.3/hr c=3 µ=2/hr 2/hr 1/3 5/6 10/hr 3.3/hr Diagnosis c=4 µ=4/hr 2/3 Other units