Naming Handout
advertisement

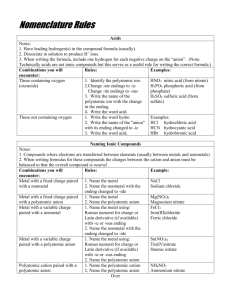
130 Nomenclature Handout: Covalent Compounds –two or more nonmetal atoms; can combine in multiple ratios; use prefixes to identify number of atoms in the compound 1st element – name the element 2nd element – ends in –ide (Exception: If there is only one of the first atom, we don’t use the prefix mono-) Examples: CO carbon monoxide CO2 carbon dioxide N2O4 dinitrogen tetroxide N2O5 dinitrogen pentoxide Ionic Compounds – metal + nonmetal; electron is transferred from the metal (it becomes a positively charged cation) to the nonmetal (it becomes a negatively charged anion) Binary (one metal, one nonmetal) 1st element – name the metal; if it’s a transition metal, use a roman numeral - except for Ag+, Zn2+, and Cd2+ 2nd element – ends in –ide Examples: NaF sodium fluoride CaCl2 calcium chloride CuCl2 copper (II) chloride Fe2N3 iron (III) nitride Contain polyatomic ions (two or more nonmetal atoms that are covalently bonded together that act as a single ion) Examples: NO3- (nitrate), SO42- (sulfate), NH4+ (ammonium – the only polyatomic cation) cation – name the metal; if it’s a transition metal, use a roman numeral - except for Ag+, Zn2+, and Cd2+ anion - name the polyatomic ion Examples: NaOH sodium hydroxide Mg(NO3)2 magnesium nitrate Zn(OH)2 zinc hydroxide Fe2(SO4)3 iron (III) sulfate Acids – usually start with H, are in the aqueous phase Know these 6: HCl(aq): hydrochloric acid; HF(aq): hydrofluoric acid; H2SO4(aq): sulfuric acid; H3PO4(aq): phosphoric acid; HNO3(aq): nitric acid; H2CO3(aq): carbonic acid Binary acids: H+ + single element nonmetal; name as hydro-______-ic acid Examples: HF(aq) hydrofluoric acid HCl(aq) hydrochloric acid HBr(aq) hydrobromic acid HI(aq) hydroiodic acid Oxoacids: acids made from polyatomic ions Ions that end it –ate become –ic as an acid Ions that end in –ite become –ous as an acid Examples: H2SO4(aq) H3PO4(aq) sulfuric acid phosphoric acid NO3- nitrate NO2- nitrite H2SO3(aq) H3PO3(aq) HNO3(aq) nitric acid HNO2(aq) nitrous acid sulfurous acid phosphorus acid Practice lead (II) sulfate PbSO4 copper (II) hydroxide Cu(OH)2 diphosphorus pentoxide P2O5 lithium cyanide LiCN calcium phosphide Ca3P2 krypton tetrafluoride KrF4 sodium oxide Na2O strontium chloride SrCl2 dihydrogen monoxide H2O zinc fluoride ZnF2 cobalt (III) acetate Co(C2H4O2)2 sulfur tetrafluoride SF4 FeCl3 iron (III) chloride KBr potassium bromide SF6 sulfur hexafluoride Ni3(PO4)2 nickel (II) phosphate Ag2S silver sulfide NO3 nitrogen trioxide NiCO3 nickel (II) carbonate PbO lead (II) oxide SO2 sulfur dioxide