Civilization, Past & Present
advertisement

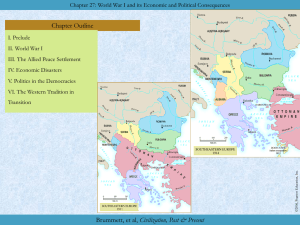
Chapter 10: Culture, Power and Trade in the Era of Asian Hegemony, 220-1350 Chapter Outline I. India in the Classical and Medieval Eras II. China: Cultural and Political Empires III. Korea: From Three Kingdoms to One IV. The Emergence of Japan Brummett, et al, Civilization, Past & Present Chapter 10: Culture, Power and Trade in the Era of Asian Hegemony, 220–1350 I. India in the Classical and Medieval Eras 184 B.C.E.–320 C.E., fragmentation A. Gupta Dynasty (320–500) Chandra Gupta I m. Kumaradevi, Licchavi clan Samudra Gupta (335–375) Chandra Gupta II (375–415) daughter Prabhavati Gupta m. Rudrasena II Vakataka dynasty Hinduism Bhagavad Gita (Song of the Blessed One) Bhakti (devotion) Kirshna Faxian, journals Brummett, et al, Civilization, Past & Present, Part One; Classical Origins Chapter 10: Culture, Power and Trade in the Era of Asian Hegemony, 220–1350 I. India in the Classical and Medieval Eras B. Gupta Achievements Ajanta monasteries Kalidasa Shakuntala Nalanda university Aryabhatta C. New Political and Religious Orders Huns, 515 Rajputs Harsha (606–647) T’ang delegation 647 > Regional Kingdoms Shankara (c. 788–820) Chola Kingdom Pallavar dynasty Brummett, et al, Civilization, Past & Present, Part One; Classical Origins Chapter 10: Culture, Power and Trade in the Era of Asian Hegemony, 220–1350 D. Muslims in India 1. 712 — Sind 2. Mahmud of Ghazni Gujarat Firdawsi (940–1020) Shahnamah al-Biruni (b. 973) 3. 1206 — Delhi Sultanate Qutb ud-Din Aibak, Sultan > new dynasty Iltutmish (1211–1236) consecrated by Abbasids Raziyya (1236–1240) Ala ud-Din (1296–1316) “Second Alexander” Tughluks Ibn Battuta Vijayangar Timur destruction of Delhi, 1398 Brummett, et al, Civilization, Past & Present, Part One; Classical Origins Chapter 10: Culture, Power and Trade in the Era of Asian Hegemony, 220–1350 II. China: Cultural and Political Empires A. Period of Division Xiongnu, Yuexhi (Turks) Jin Dynasty Sixteen Kingdoms (304–439) Northern Wei (439–534) sinified equal-field system Luoyang, capital 589 — unification Buddhism Mahayana bodhisattvas Pure Land Sui Dynasty (589–618) Emperor Wendi (581–604) son, Yangdi (604–618) Grand Canal, 605–609 Brummett, et al, Civilization, Past & Present, Part One; Classical Origins Chapter 10: Culture, Power and Trade in the Era of Asian Hegemony, 220–1350 II. China: Cultural and Political Empires B. Tang Culture Politics of the Early Tang Gaozu, Taizong, Gaozong (618–683) 653 — Law Code examination system Empress Wu (690–705) grandson, Xyanzong (712–756) Chan Buddhism (=Zen) Literature and the Arts 600 — Block printing The Understanding of History Li Bo (701–763) Du Fu (712–770) Wu Daozi emperor Xuanzong Tang Decline, Transformation Commanders e.g. An Lushan “Two Tax System” 881 — Chang’an taken Brummett, et al, Civilization, Past & Present, Part One; Classical Origins Chapter 10: Culture, Power and Trade in the Era of Asian Hegemony, 220–1350 II. China: Cultural and Political Empires C. Song Era (960–1279) 1. Politics Song Taizu (960–976) Shenzong (1067–85) Wang Anshi reforms Alliance with Jurchen Jin Dynasty 2. Economy Economic revolution paper money 3. Society Women footbinding — still rare female infanticide Brummett, et al, Civilization, Past & Present, Part One; Classical Origins Chapter 10: Culture, Power and Trade in the Era of Asian Hegemony, 220–1350 II. China: Cultural and Political Empires C. Song Era (960–1279) 4. Culture Su Shi (1037–1101) Sima Guang (1019–86) Fan Kuan (fl. 990–1020) Cheng Hao (1032–85) Cheng Yi (1033–1108) brothers li and qi = Neo-Confucians Zhu Xi (1130–1200) White Deer Grotto Academy Brummett, et al, Civilization, Past & Present, Part One; Classical Origins Chapter 10: Culture, Power and Trade in the Era of Asian Hegemony, 220–1350 II. China: Cultural and Political Empires D. Mongols 551 — Turkish Empire Uighur, Tangut Temujin (1162–1227) 1206 — Great Khan Ögödei (1229–1241) Möngke and Hülegü E. Yuan Rule Khubilai Khan (1260–94) > Yuan dynasty sinified Marco Polo, c. 1275 Christianity John of Plano Carpini, 1246 William of Rubruck, 1254 John of Monte Corvino 1289–1322 White Lotus Society Maitreya Zhu Yuanzhang = Taizu Brummett, et al, Civilization, Past & Present, Part One; Classical Origins Chapter 10: Culture, Power and Trade in the Era of Asian Hegemony, 220–1350 III. Korea: From Three Kingdoms to One Ko Choson from 1500 B.C.E. 109 B.C.E., Han A. Three Kingdoms Koguryo 37 B.C.E. King Sosurin (371–84) Paekche from 3rd B.C.E. Silla 57 B.C.E, foundation B. Koryo Dynasty King Taejo Mongols, 1238 King Kongmin (1351–74) 1374, assassination Ming, 1392 > Yi Dynasty (1392–1910) Brummett, et al, Civilization, Past & Present, Part One; Classical Origins Chapter 10: Culture, Power and Trade in the Era of Asian Hegemony, 220–1350 IV. The Emergence of Japan Neolithic — Jōmon 5000–3500 B.C.E. Japanese c. 300 B.C.E. Koreans to Kyūshū Yayoi period (300 B.C.E.–300 C.E.) A. Tomb Period (300–645) Records Kojiki, Nihongi Queen Himiko Shintō kami — clan deities uji — clan Yamato uji Amaterasu —Yamato kami Prince Shōtoku Hōryūji, 607 “Seventeen-Article Constitution,” 604 645 — Fujiwara family Taika Reforms, 645 B. Classical Period — Nara and Heian 710, Nara (710–784, Nara Period) 794, Heian (794–1181, Heian Period) = Kyoto Shōen tax-free estates 1181–1186 — Civil War Minamoto Yoritomo (1147–99) wife, Hōjō Masako (1157–1225) C. Classical Arts and Literature Lady Murasaki, Tale of Genji Man’yōshū (Collection of Ten Thousand Leaves) Kana script D. Japanese Buddhism Mahayana Buddhism, sixth century Tendai (805), Shingon (805) Buddhism widen participation Zen Buddhism E. Early Medieval Japan Minamoto Yoritomo 1185, shogun > Kamakura Period (1185–1333) Brummett, et al, Civilization, Past & Present, Part One; Classical Origins Chapter 10: Culture, Power and Trade in the Era of Asian Hegemony, 220–1350 The Ebersdorf Mappamundi Brummett, et al, Civilization, Past & Present, Part One; Classical Origins