media-33345
advertisement

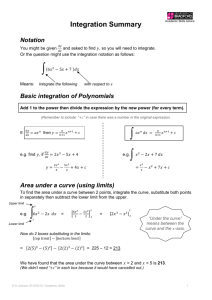
Academic Skills Advice Integration Summary Notation 𝑑𝑦 You might be given 𝑑𝑥 and asked to find 𝑦, so you will need to integrate. Or the question might use the integration notation as follows: ∫ Means: (6𝑥 2 − 5𝑥 + 7 )𝑑𝑥 with respect to 𝑥 Integrate the following Basic integration of Polynomials Add 1 to the power then divide the expression by the new power (for every term). (Remember to include “+𝑐” in case there was a number in the original expression. If: 𝑑𝑦 𝑑𝑥 𝑎 = 𝑎𝑥 𝑛 then 𝑦 = 𝑛+1 𝑥 𝑛+1 + 𝑐 𝑑𝑦 e.g. find 𝑦, if 𝑑𝑥 = 2𝑥 3 − 5𝑥 + 4 𝑦= 2𝑥 4 4 − 5𝑥 2 2 e.g. ∫ 𝑎𝑥 𝑛 𝑑𝑥 = ∫ 𝑥 2 − 2𝑥 + 7 𝑑𝑥 + 4𝑥 + 𝑐 = 𝑥3 3 𝑎 𝑥 𝑛+1 𝑛+1 +𝑐 − 𝑥 2 + 7𝑥 + 𝑐 Area under a curve (using limits) To find the area under a curve between 2 points, integrate the curve, substitute both points in separately then subtract the lower limit from the upper. Upper limit e.g. ∫ 5 6𝑥 2 − 2𝑥 𝑑𝑥 = [ 6𝑥 3 3 − 2𝑥 2 2 5 ] 5 = 2 [2𝑥 3 − 𝑥 2 ] 2 2 Lower limit “Under the curve” means between the curve and the 𝑥-axis. Now do 2 boxes substituting in the limits: [𝑡𝑜𝑝 𝑙𝑖𝑚𝑖𝑡] − [𝑏𝑜𝑡𝑡𝑜𝑚 𝑙𝑖𝑚𝑖𝑡] = [2(5)3 − (5)2 ] − [2(2)3 − (2)2 ] = 225 – 12 = 213 We have found that the area under the curve between 𝑥 = 2 and 𝑥 = 5 is 213. (We didn’t need “+𝑐” in each box because it would have cancelled out.) © H Jackson 2010/2013 / Academic Skills 1 Reverse chain rule For some integration problems (e.g. when you have a function of a function) you will need to use the reverse chain rule. This is because the original function was differentiated using the chain rule and so in order to integrate we need to “undo” the chain rule. Remember: Chain rule says: So reverse chain rule says: e.g. e.g. e.g. ∫ ∫ 𝑒 7𝑥 𝑑𝑥 ∫ = sin(5𝑥) 𝑑𝑥 differentiate the inside function and multiply differentiate the inside function and divide 𝑒 7𝑥 7 = − cos(5𝑥) (4𝑥 − 2)6 𝑑𝑥 = 5 (4𝑥−2)7 Outside (add one to power then divide by new power) 7 (4) Inside (we also have to divide by 4 because when we differentiate (4𝑥 − 2) we get 4) Reverse chain rule (some patterns) Sometimes you need to integrate functions of the form: 𝑓 ′ (𝑥)(𝑓(𝑥))𝑛 or 𝑓 ′ (𝑥) 𝑓(𝑥) . Functions in either of these forms are easy to integrate because they follow the chain rule in reverse. ∫ 𝑓 ′ (𝑥)(𝑓(𝑥))𝑛 𝑑𝑥 = Just ignore the 1st bit and integrate the ‘outside’ of the 2nd bit (i.e. add one to the 1 (𝑓(𝑥))𝑛+1 + 𝑐 𝑛+1 power then divide by the new power). ∫ 𝑓′ (𝑥) 𝑓(𝑥) 𝑑𝑥 Differentiates to ln of the denominator. = ln(𝑓(𝑥)) + 𝑐 Reverse chain rule (with adjustments) The function you need to integrate may be similar to either of the ones above but the 𝑓 ′ (𝑥) part may be a factor, or multiple, of 𝑓 ′ (𝑥). See the following examples: Question ∫ 𝟔𝒙(𝒙𝟐 + 𝟑)𝟕 𝒅𝒙 Ideal Function to integrate Compare with ideal ∫ © H Jackson 2010/2013 / Academic Skills (𝑥 2 +3)8 8 =[ (𝑥 2 +3)8 8 ] +𝑐 Ideal because differentiating (𝑥 2 + 3) gives 2𝑥. The question is 3x bigger than the ideal so the answer = 3 [ 2𝑥(𝑥 2 + 3)7 𝑑𝑥 ] +𝑐 2 Question ∫ 𝟑𝒙 Ideal Function to integrate Compare with ideal 𝒅𝒙 𝟔𝒙𝟐 +𝟖 ∫ 12𝑥 6𝑥 2 +8 = ln(6𝑥 2 + 8) + 𝑐 𝑑𝑥 Ideal because differentiating (6𝑥 2 + 8) gives 12𝑥. The question is 4x smaller than the ideal so the answer= 1 4 ln(6𝑥 2 + 8) + 𝑐 By parts This is used to integrate a function multiplied by a function. ∫ 𝑢 𝑑𝑣 𝑑𝑥 𝑑𝑥 ∫ 𝑢𝑣 − 𝑣 = 𝑑𝑢 𝑑𝑥 When choosing which term to call 𝑢 look for: 𝑑𝑥 1st – ln(𝑥) 2nd - 𝑥 𝑛 3rd - 𝑒 𝑥 Similar to the product and quotient rule (see differentiation) – write down the 4 bits of information you need then put them into the formula. You will then need to integrate the part in the integral sign again. 𝑑𝑣 Remember: you are calling one bit 𝑢 and the other bit 𝑑𝑥. Reverse product You need to remember the product rule for differentiation – refer to the differentiation summary if necessary. Once you have spotted this pattern you can just write the answer. Differentiates to ∫ 𝑢 𝑑𝑣 𝑑𝑥 + 𝑣 𝑑𝑢 𝑑𝑥 𝑑𝑥 = 𝑢𝑣 Differentiates to Differentiates to e.g. ∫𝑒 𝑥 3 𝑑𝑦 𝑑𝑥 3 3 + 3𝑥 2 𝑒 𝑥 𝑦 = 𝑒 𝑥 𝑦 Differentiates to © H Jackson 2010/2013 / Academic Skills 3 Substitution A substitution can be used to simplify a complex integration. For this method you need to replace any 𝑥 or 𝑑𝑥 with a 𝑢 or 𝑑𝑢 and then integrate as normal. e.g. ∫ 𝑥(𝑥 − 7)5 𝑑𝑥 We can find all of these (and any others we need) by differentiating and/or rearranging the 𝑢 = 𝑥 − 7 Let 𝑢 = 𝑥 − 7 𝑑𝑢 ∴ 𝑑𝑥 =1 so 𝑑𝑢 = 𝑑𝑥 and 𝑥 = 𝑢 + 7 Substitute the above information into the original to produce an integration in terms of 𝑢. The question now becomes: ∫ ∫ (𝑢 + 7)𝑢5 𝑑𝑢 = 𝑢6 + 7𝑢5 𝑑𝑢 = 𝑢7 7 + 7𝑢6 6 +𝑐 = (𝑥−7)7 7 + 7(𝑥−7)6 6 +𝑐 Separation of Variables 𝑑𝑦 This is used to integrate a function which consists of 𝑥′𝑠, 𝑦′𝑠 and 𝑑𝑥 ’s mixed up (i.e. of the 𝑑𝑦 form 𝑑𝑥 = 𝑓 (𝑥, 𝑦). We cannot integrate directly because of the 𝑦 on the right hand side. To integrate: collect all the 𝑦 bits on one side and all the 𝑥 bits on the other. e.g. 𝑑𝑦 𝑑𝑥 = 𝑥2 𝑦−3 ∫ ∫ becomes (𝑦 − 3)𝑑𝑦 = 𝑥 2 𝑑𝑥 The integration symbols are introduced after rearranging. Integrating factor 𝑑𝑦 Used for functions of the form: 𝑑𝑥 + 𝑝(𝑥)𝑦 = 𝑄(𝑥) Integrating factor = 𝒆 ∫𝒑(𝒙)𝒅𝒙 = 𝑰 Multiply the whole function by the integrating factor and you will end up with the reverse product rule on the left hand side. So 𝑰𝒚 = ∫ 𝑰𝑸 𝒅𝒙 © H Jackson 2010/2013 / Academic Skills 4 Substitution (2 variables & homogenous) Used when the 𝑥’s and 𝑦’s can’t be separated and when the differential equation is homogenous. Homogenous means that the total degree in 𝑥 and 𝑦, for each term involved, is the same (e.g. 𝑥𝑦 is degree 2 and 𝑥 2 is degree 2). The method is as follows: 1. Substitute 𝒚 = 𝒗𝒙 (where 𝑣 is a function of 𝑥), 2. Differentiate 𝑦 with respect to 𝑥 using the product rule, 3. Substitute everything back into the original function, and cancel where possible so that you have a function with 𝑥 and 𝑣 which can then be integrated by separating the variables. e.g. 𝒅𝒚 𝒅𝒙 = 𝟒𝒚−𝒙 Using the product rule (and implicit differentiation). 𝑦 = 𝑣𝑥 1. Let 2. ∴ 𝟑𝒙 𝑑𝑦 𝑑𝑥 (This will be the same every time so you can just memorise it if you prefer.) 𝑑𝑣 = 𝑣 + 𝑥 𝑑𝑥 𝑑𝑦 3. Replace any 𝑦’s and 𝑑𝑥 in the original: 𝒅𝒚 Original question: 𝒅𝒙 𝑑𝑣 𝑣 + 𝑥 𝑑𝑥 = Becomes: 𝑑𝑣 𝑥 𝑑𝑥 = Simplify & rearrange: 𝑑𝑣 𝑥 𝑑𝑥 = = 𝟒𝒚−𝒙 𝟑𝒙 4𝑣𝑥−𝑥 The 𝑥’s will cancel 3𝑥 4𝑣−1 3 −𝑣 Combine the fractions: 4𝑣−1−3𝑣 3 𝑣−1 3 Now we can separate the variables and solve as normal: ∫ 3 𝑣−1 𝑑𝑣 = ∫ 1 𝑥 𝑑𝑥 Don’t forget the constant. (with logs, 𝑐 = 𝑙𝑛𝐴) 3 ln(𝑣 − 1) = 𝑙𝑛𝑥 + 𝑙𝑛𝐴 ln(𝑣 − 1)3 = ln(𝐴𝑥) (𝑣 − 1)3 = 𝐴𝑥 Remember that 𝑦 = 𝑣𝑥 ∴𝑣= 𝑦 𝑥 𝑦 3 (𝑥 − 1) = 𝐴𝑥 𝑦 𝑥 3 − 1 = √𝐴𝑥 3 𝑦 − 𝑥 = √𝐴𝑥 . 𝑥 (𝑦 − 𝑥)3 = 𝐴𝑥 4 © H Jackson 2010/2013 / Academic Skills 5