5th grade science facts and standards
advertisement

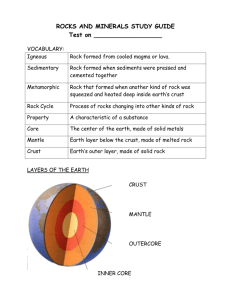
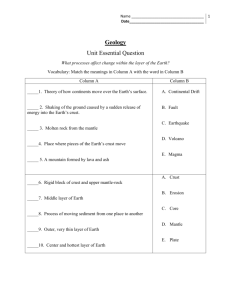
5th Grade Science Facts The Nature of Science and Engineering 1. Science is a way of knowing about the natural world, is done by individuals and groups, and is characterized by empirical criteria, logical argument and skeptical view. 2. Scientific inquiry requires identification of assumptions, use of critical and logical thinking, and consideration of alternative explanations. 3. Men and women throughout the history of all cultures, including MN American Indian tribes and communities, have been involved in engineering design and scientific inquiry. 4. Tools and mathematics help scientists and engineers see more, measure more accurately, and do things that they could not otherwise accomplish. (spring scale, metric measurement, tables, mean/median/range, spreadsheets, and appropriate graphs) Physical Science 1. An object’s motion is affected by forces and can be described by the object’s speed and the direction it is moving. 2. Friction slows down a moving skateboard. 3. A greater force on an object can produce a greater change in motion. 4. Simple machines demonstrate how they change the input and output of forces and motion. Earth and Space Science 1. The surface of the Earth changes. Some changes are due to slow processes and some changes are due to rapid processes. 2. Over time, rocks weather and combine with organic matter to form soil. 3. Slow processes, such as water erosion and rapid processes, such as landslides and volcanic eruptions, form features of the the Earth’s surface. 4. In order to maintain and improve their existence, humans interact with and influence Earth systems. 5. Water, iron ore, granite, sand and gravel, wind and forests are all renewable and nonrenewable energy and material resources found in MN. Life Science 1. Living things are diverse with many different characteristics that enable them to grow, reproduce and survive. 2. Plants and animals adapt to their environment. Without various adaptations, they would not be able to survive. 3. Natural systems have many parts that interact to maintain the living system. 4. Humans change environments in ways that can be either beneficial or harmful to themselves and other organisms. 5. Recreation, pollution, and wildlife management are examples of helpful and harmful human interaction with natural systems. Academic Vocabulary 1. Explain=to make plain or understandable 2. Describe=to tell or write about; to give a detailed account of 3. Variable=any factor that can change in a controlled experiment, observation, or model 4. Control=any factor that stays the same in an experiment 5. Contrast=to compare in order to show differences 6. Classify=to arrange or organize according to a category 7. Determine=to settle or decide upon 8. Inference=process of drawing a conclusion by reasoning from something known 9. Hypothesis=an educated guess or explanation 10. Observation=the act of noticing, perceiving, or seeing 11. Structure=the arrangement of all of the parts of a whole 12. Function=the normal or characteristic action of anything; role; job 13. Prediction=prophecy; a guess of the expected results 14. Identify=to find out or to establish the identity of 15. Conduct=to do; to perform 16. Conditions=an existing state; the factors involved in a situation 17. Process=a series of actions by which something develops or is brought about 18. Response=answer or reply 19. Compare=to examine (2 or more objects, ideas, people, etc.) in order to note similarities and differences 20. Analyze=to examine carefully and in detail so as to identify causes, key factors, possible results, etc. 21. Organism=living thing: group of systems working together to fulfill a common purpose 22. Advantage=something that is favorable to success, a benefit, gain, or profit; a plus or positive 23. Disadvantage=something that is unfavorable to success, not a benefit, gain, or profit; not a plus; a negative 24. Conclusion=the final result, decision or outcome 25. Data=a set of facts, information, statistics or observations Science Vocabulary 26. Adaptation=a characteristic that enables a living thing to survive in its environment 27. Amphibian=a vertebrate that lives part of its life in water and part of its life on land 28. Atmosphere=the blanket of gases that surrounds Earth 29. Bench mark=a plaque left by surveyors to tell the exact location and elevation of a place 30. Bird=a vertebrate that has both feathers and wings 31. Biome=one of Earth’s large ecosystems, with its own kind of climate, soil, plants, and animals 32. Camouflage=an adaptation in which an animal protects itself against predators by blending in with the environment 33. Carnivore=an animal that eats another animal 34. Chemical change=a change in matter that occurs when atoms link together in a new way, creating a new substance different from the original substances 35. Classification=the science of finding patterns among living things 36. Compression=a movement of plates that presses together or squeezes Earth’s crust 37. Consumer=any animal that eats plants or eats other plant-eating animals 38. Contour plowing=preventing erosion by plowing across rather than up and down a slope 39. Coquina=a sedimentary rock formed from seashell fragments 40. Crop rotation=growing different crops each year so that the soil does not use up the same kinds of minerals year after year 41. Crossbreeding=producing offspring by mating individuals from two distinct breeds or varieties of the same species 42. Crust=the rocky surface that makes up the top of the lithosphere and includes the continents and the ocean floor 43. Deciduous=said of a plant that loses its leaves each fall 44. Deciduous forest=a forest biome with many kinds of trees that lose their leaves each autumn 45. Decomposer=any of the fungi or bacteria that break down dead plants and animals into useful things like minerals and rich soil 46. Delta=fan-shaped region formed by deposits of sediments found at the mouth of a river 47. Deposition=the dropping off of bits of eroded rock 48. Desert=a sandy or rocky biome, with little precipitation and little plant life 49. Diversity=a wide variety of traits in individuals from the same population 50. Ecosystem=all of the living and nonliving things in an environment, including their interactions with each other 51. Elevation=the height of a place above sea level 52. Erosion=the picking up and carrying away of pieces of rocks 53. Fault-a crack in the Earth’s crust whose sides show evidence of motion 54. Fault-block mountains=a mountain formed by blocks of Earth’s crust moving along a fault 55. Fish=a vertebrate that lives its whole life in water 56. Flood plain=land that is likely to be underwater during a flood 57. Fold mountain=a mountain made up mostly of rock layers folded by being squeezed together 58. Food chain=the path of energy in food from one organism to another 59. Food web=the overlapping food chains in an ecosystem 60. Force=a push or pull exerted by one object on another, causing a change in motion 61. Fossil=any remains or imprint of living things of the past 62. Fulcrum=the pivot point of a lever 63. Geologist=a scientist who studies rocks to tell how they formed and to predict when an earthquake may occur 64. Grassland=a biome where grasses, not trees, are the main plant life 65. Herbivore=an animal that eats plants, algae, and other producers 66. Heredity=the passing down of inherited traits from parents to offspring 67. Humus=decayed plant or animal material in soil 68. Hybrid=an organism produced by the crossing of parents that have different forms of the same trait 69. Hydrosphere=Earth’s water 70. Igneous rocks=a rock formed when melted rock material cools and hardens 71. Inherited trait=a characteristic that is passed from parents to offspring 72. Invertebrate= an animal that does not have a backbone 73. Lava=magma that reaches Earth’s surface 74. Lever=a simple machine made of a rigid bar and a fixed pivot point, called the fulcrum 75. Lithosphere=the hard outer layer of Earth 76. Magma=hot, molten rock deep below Earth’s surface 77. Mammal=a vertebrate that feeds its young milk 78. Meander=bends or s-shaped curves in a river 79. Metamorphic rock=a rock formed under heat and pressure from another kind of rock 80. Meteorite=a chunk of rock from space that strikes a surface of Earth or the Moon 81. Mimicry=an adaptation in which an animal is protected against predators by its resemblance to another, unpleasant animal 82. Omnivore=an animal that eats both plants and animals 83. Permafrost=a layer of permanently frozen soil found in arctic and Antarctic regions 84. Physical change=a change of matter in size, shape, or state without any change in identity 85. Plate=One of the moving pieces of Earth’s crust that has been broken by upward pressure in the mantle 86. Plate tectonics=a scientific theory that Earth’s crust is made of moving plates 87. Predator=an animal that hunts other animals for food 88. Prey=a living thing that is hunted for food 89. Producer=any of the plants and algae that produce oxygen and food that animals need 90. Protective coloration=a type of camouflage in which the color of an animal blends in with its background, protecting it against predators 91. Reptile=an egg-laying vertebrate with thick, dry skin 92. Rock=a naturally formed solid in the crust made up of one or more minerals 93. Rock cycle=rocks changing from one into another in a never-ending series of processes 94. Runoff-precipitation that flows across the land’s surface or falls into rivers and streams 95. Savanna=a tropical grassland with some trees and shrubs 96. Scavenger=a meat-eating animal that feeds on the remains of dead animals 97. Sediment=pieces of material carried and deposited by water or wind 98. Sedimentary rock=a rock made of bits of matter joined together 99. Shear=a movement of plates that twists, tears, or pushes one part of Earth’s crust past another 100. Simple machine=a machine with few moving parts, making it easier to do work 101. Strip farming=trapping runoff by alternating tightly growing grasses with more widely spaced plants 102. Surveyor=a specialist who makes accurate measurements of Earth’s crust 103. Taiga=a cool forest biome of conifers in the upper Northern Hemisphere 104. Temperate=free from extremes of temperature 105. Tension=a movement of plates that stretches or pulls apart Earth’s crust 106. Topsoil=the dark, top layer of soil, rich in humus and minerals, in which many tiny organisms live and most plants grow 107. Tropical rain forest=a hot biome near the equator, with much rainfall and a wide variety of life 108. Troposphere=the layer of the atmosphere closest to Earth’s surface 109. Tundra=Large, treeless plain in the arctic regions, where the ground is frozen all year 110. Variable=One of the changes in a situation that may affect the outcome of an experiment 111. Vertebrate=an animal that has a backbone 112. Watershed=area from which water is drained, region that contributes water to a river or river system 113. Weathering=breaking down rocks into smaller pieces